On this page
- 1. Cattle
- 2. Swine (hogs, sows, boars, wild boar)
- 3. Sheep, Lambs, Goats
- 4. Bison
- 5. Horses
- 6. Cervids (Includes elk, fallow deer, white tail)
- 7. Rabbits
1. Cattle
1.1 Mechanical
Important factors:
- Handling and restraint facilities should be appropriate to avoid movement of cattle during stunning.
- Cattle, especially mature males with horns, have very thick frontal bones overlaying the brain.
- Plan the trajectory so that the bolt or projectile travels through the brain (cerebral hemispheres, midbrain, brainstem). The most significant of these are the midbrain and brainstem, which are at the level of the bottom of the attachment of the ears.
Note: Together the midbrain and brainstem are responsible for eye movement and body movement, the level of consciousness and maintaining vital body functions, such as breathing and heart rate. (The cerebral hemispheres are associated with higher brain functions.)
The trajectory is especially important when a firearm is used and the shooter may need to be on steps or an elevation to achieve the proper angle. Be aware that the trajectory of the projectile must pass through the midbrain and brainstem (angle is very important). (See [b] below.)
1.1.1 Landmarks and approaches
1.1.1.1 Perpendicular to the front of the head approach
Penetrative Captive Bolt
The intersection of diagonal lines from the middle of the attachment of each horn, or the nuchal crest (the ridge at the back of skull where the neck muscles attach to the head) to the eyes, depending on cattle breed and head shape. The muzzle of the gun should be perpendicular to the front of the skull surface to direct the bolt through the upper brain towards the brainstem. (See [a] and [b] below.)
This is the approach used with captive bolt stunning devices (pneumatic and cartridge fired). This approach is sometimes used with firearms. (See pictures [a] and [b] below.)
Perpendicular to the Front of the Head Approach


foramen magnum
brainstem
and midbrain
[in the centre
of the skull]

| Image | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Landmark and angle relative to the front of the skull when cattle are stunned with either a penetrating captive bolt stunning device or firearm. They are discharged perpendicular to the front of the head. |
 |
Location of the foramen magnum, brainstem and midbrain in centre of the skull. |
 |
Intersection of the diagonal lines indicates the entry point for the bolt or projectile of a mechanical stunning device held perpendicular to the front of the skull. |
Non-penetrative Captive bolt
This method requires an extremely accurate aim. As the amount of damage to the skull is reduced, placement of the shot must become precise to achieve instantaneous insensibility. Observations indicate that non-penetrating stunners may be less effective on cattle with woolly heads such as Herefords compared to short haired cattle.
The position of the non-penetrative captive bolt pistol is approximately 20 mm above the position used for the penetrative captive bolt. The animal must be bleed within 30 seconds. The muzzle of the gun must be perpendicular to the front of the skull surface to direct the impact of the blow through the upper brain towards the brainstem.

1.1.1.2 Firearm discharged with the operator standing at ground level in front of the animal
When an animal is stunned with the operator standing at ground level in front of the animal, the entry point of the projectile into the front of the head (skull) must be much lower than what is used with the perpendicular approach, if it is to penetrate the midbrain and brainstem. (See pictures [a] and [b] below.)
In general, it is recommended that the employee to be on steps or an elevation so the firearm shooting can be done perpendicularly to the skull to achieve a better angle more readily. When done this way, the targeted areas will be the same as for captive bolt except for the poll shot which should be used for firearms only (the firearm is the most reliable method to destroy the brainstem from this angle). This angle is for animals with thick skull mass, horns or the frontal shot is difficult to make.
The midbrain and brainstem are the central and lower portions of the brain. They are located in the central and lower portion of the cranial vault [space containing the brain]. (See [a] and [b] below.)
Ground Level Approach

[firearm and projectile aimed at the midbrain and brainstem]

| Image | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Level of the brainstem - in the middle of the skull |
 |
Location of the brainstem and midbrain - middle of the skull |
 |
Entry point of the projectile (bullet) if the operator is standing at ground level |
 |
Trajectory of the projectile as it travels to the midbrain and brainstem |
1.1.2 Mechanical Stunning Devices
1.1.2.1 Captive bolt
- Use the appropriate landmarks. (See 1.1.1.1.)
- Do not stun from the top of the head or behind the ears, due to the risk of pithing the animal.
- Discharge the stunning device perpendicular to the front of the head.
- For class of animals other than veal calves, the bolt length must be at least 12 cm (4 ¾ in.). The bolt length for bulls must be 15 cm (6 in.).
- Calibres (diameter) available for the cartridge bolts include .22, .25, and .33.
- The .25 calibre and larger captive bolt stunning devices with heavier charges are far more effective on bulls than the .22 calibre. (Temple Grandin recommends .25 calibre or larger.)
- Trigger and contact firing options are available.
- Use the manufacturer's recommended charge, cleaning, maintenance and stunning protocols.
- Assess bolt velocity by using the manufacturer's bolt velocity testing device, or similar means. (daily)
| Animal | Calibre | Bolt Lengths | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calves | .22 | Depends on size | Depends on size |
| Steers, heifers, cows | .22, .25, .33 | 12 cm (4 ¾ in.) or 15 cm (6 in.) |
≥ 55 m/s (183 ft/s) |
| Young bulls | .22, .25, .33 | 15 cm (6 in.) | ≥ 72 m/s (236 ft/s) |
| Mature bulls | .25, .33 | 15 cm (6 in.) | ≥ 72 m/s (236 ft/s) (> 100 m/s preferred) |
1.1.2.2 Firearms
- Muzzle (kinetic) energy is frequently used as an indicator of a bullet's destructive potential
- The heavier the bullet and the greater its velocity, the higher its muzzle energy and capacity for destruction of objects in its path
- Selection of an appropriate bullet and firearm is critical to good performance when conducting stunning or humane killing
- Lighter weight, higher velocity bullets can have a high muzzle energy but decreased penetration which can be an issue when penetrating thick bones
- Use the slowest velocity and minimum energy (muzzle) required to effectively stun the animal.
- Maximum velocity < 2000 ft/s to help prevent ricochet from the surface of the skull.
- Maximum energy (muzzle) < 1000 ft/lbs to help prevent skull perforation (exiting the opposite side of the skull).
- Plan the trajectory so the projectile travels through the midbrain and brainstem, which are located at the level of the bottom of the attachment of the ears. See 1.1 "Important factors" above.
| Animal | Calibre | Grain | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
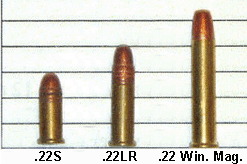
| Calves | .22 S (short)Table Note 1 | 29 | 1095 | 77 |
| Calves | .22 LR (long rifle)Table Note 1 | 40 | 1255 | 140 |
| Steers, heifers, cows | .22 LR (long rifle)Table Note 1 | 40 | 1255 | 140 |
| Steers, heifers, cows | .22 Winchester Magnum | 40 | 1910 | 324 |
| Bulls | .22 Winchester Magnum | 40 | 1910 | 324 |
Table Notes
- Table Note 1
-
Do not use hollow point; use solid point bullets. If possible, .22 Magnum recommended for general use to kill livestock over long rifles.
| Animal | Calibre | Grain | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Bulls | .30 Remington Carbine | 110 | 1990 | 967Table Note 2 |
Table Notes
- Table Note 2
-
Upper limit of energy as the projectile may perforate the skull and enter the neck muscle.
| Animal | Gauge | Length | Slug | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Bulls | .410 | 2 ½ in. | 1/5 oz (87 gr) | 1830 | 651 |
| Large Bulls | .410 | 3 in. | 1/4 oz (108 gr) | 1800 | 788 |

1.2 Electrical
Important Factors:
- Handling and restraint facilities must meet current industry standards.
- Individual animal restraint is required.
- The electrodes are firmly pressed against the animal until stunning is complete. This is to ensure they remain in contact and to facilitate current flow.
- A water spray is to be used to improve contact.
- Immediate post stun sticking is required (before or after hanging on line).
- OSH provisions required due to high amperage and voltage.
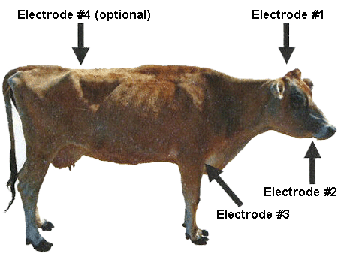
1.2.1 Landmarks and approaches
- Electrodes are firmly pressed against the top of the head (nuchal crest), the chin and the brisket.
- A two-stage stunning technique must be used; a third stage may be used if required.
1.2.1.1 Phase I - Head-to-head
- In this stage a current is sent through one electrode that is firmly pressed against the top of the head (usually behind the nuchal crest) and a second electrode is firmly pressed pressed against the chin. (See [a] below.)
1.2.1.2 Phase II - Head-to-brisket (body)
- Follows phase I
- In this stage a current is sent through an electrode firmly pressed against the top of the head and a third electrode that has been firmly pressed against the brisket [heart area]. (See [a] below.)
1.2.1.3 Phase III (Optional)
- Follows phase II
- This is an optional phase of electrical stunning in bovine.
- Current is sent from the electrode pressed against the top of the head to a fourth electrode pressed against the spine.
- This phase is used to minimize post stun kicking. (See [a] below.)
Recommended Electrical Stunning Parameters - Cattle
Phase I - Head to Head
- Check the electrical settings as per the following table.
Electrical settings Amperage Frequency Volts Time 2.0 - 2.5 50 - 60 Hz 400 4 seconds - Apply current; when insensible (unconscious), start Phase II.

Phase II - Head to Brisket
- Check the electrical settings as per the following table.
Electrical settings Amperage Frequency Volts Time 3 - 4 50 - 60 Hz 450 4 - 15 seconds - There is less kicking with a longer stun, and/or use Phase III spinal depolarization.

Phase III (Optional) - Head to Spine
- Check the electrical settings as per the following table.
Electrical settings Amperage Frequency Volts Time 3 - 4 50 - 60 Hz 450 as required - Apply current as required.
Landmarks for electrical stunning
2. Swine (hogs, sows, boars, wild boar)
2.1 Mechanical
Important factors:
- Handling and restraint facilities must promote good animal welfare standards.
- Pigs have small brains relative to the size of their head; therefore the target area is very small and may make stunning effectively more difficult.
- Sows and boars have very thick frontal bones in their skull which may make penetration of the bolt more difficult, so the power of the device must be adapted
- Note: There can be breed variation in head shape in mature animals. "Yorkshire" type animals (not necessarily a Yorkshire hog) have a prominent curvature in the front of their head; this "dish face" can also make it difficult to find the target area. (See [e] below.)
- Immature animals and mature animals with a straight front to their head can be stunned by holding the stunning device perpendicular to the front of their head. (See [d] below.)
- This approach may need to be modified in "Yorkshire" type animals with a pronounced curvature to the front of their head, or if an animal is stunned with a firearm. (See [e] below.)
- Plan the trajectory so the bolt or projectile travels through the brain (cerebral hemispheres, midbrain and brainstem) The most significant of these are the midbrain and brainstem which are located in the centre of the skull at the level of the bottom of the attachment of the ears (See [b], [c], [d] and [e] below.)
- Use precise landmarks. (See all below.)
2.1.1 Landmarks and approaches
2.1.1.1 Market Hog
Intersection of diagonal lines from the midpoint of the attachment of each ear to the medial canthus (middle corner) of the opposite eye. This is approximately 2 ½ cm or 1 in. above the eyes. (See [a] and [b] below.)
2.1.1.2 Sow or boar
Intersection of diagonal lines from the top of the attachment of each ear to the medial canthus (middle corner) of the opposite eye. (See [c] below.)
Note: Regardless of the entry point, the angle of the stunning device with the front of the head must result in a path of the bullet or bolt that will intersect with an internal line from the base of one ear to the other, running through the brain stem. (See [a], [b], [c], [d] and [e] below.)
Frontal View


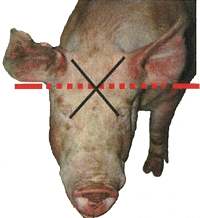

Note: Breed and age effect on curvature of the front of the head in the side view. (See [d] and [e] above.)
| Image | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Level of the brainstem - in the middle of the skull. |
 |
Location of the brainstem and midbrain - in the middle of the skull. |
 |
Intersection of the diagonal lines indicates the entry point for the bolt or projectile of a mechanical stunning device held perpendicular to the front of the skull. |
 |
Trajectory of the projectile as it travels to the midbrain and brainstem. |
2.1.2 Mechanical Stunning Devices
2.1.2.1 Captive bolt
- Bolt length must be at least 12 cm (4 ¾ in.). Bolt length must be 15 cm (6 in.) for sows and boars.
- Calibres (diameter) available for the cartridge bolts include .22, .25 and .33.
- Larger bolt diameters (.25 and .33) are far more effective for larger animals.
- Use manufacturer's recommended charge, operation, cleaning and maintenance program.
- Assess bolt velocity by using the manufacturer's bolt velocity testing device, or similar means (daily).
- See 2.1.1, Landmarks and approaches, above.
| Animal | Calibre (options) | Bolt Lengths | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hogs | .22, .25, .33 | 12 cm (4 ¾ in.) | ≥ 55 m/s (183 ft/s) |
| Sows and Boars | .25, .33 | 15 cm (6 in.) | ≥ 72 m/s (236 ft/s) |
2.1.2.2 Firearms
- Use the slowest velocity and minimum energy (muzzle) required to effectively stun the animal.
- Planning the trajectory is particularly important if the stunner operator is shooting from a standing position on the ground.
- See 2.1.1, Landmarks and approaches, above.
| Animal | Calibre | Grain | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hogs | .22 LR (long rifle)Table Note 1 | 40 | 1255 | 140 |
| Sows and Boars | .22 LR (long rifle)Table Note 1 | 40 | 1255 | 140 |
| Sows and Boars | .22 Winchester Magnum | 40 | 1910 | 324 |
Table Notes
- Table Note 1
-
Do not use hollow point.
| Animal | Calibre | Grain | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very Large Boars | .30 Remington Carbine | 110 | 1990 | 967 |
| Animal | Gauge | Length | Slug | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Sows and Boars |
.410 | 2 1/2 in. | 1/5 oz (87 g) | 1830 | 651 |
| Large Sows and Boars |
.410 | 3 in. | ¼ oz (108 g) | 1800 | 788 |

2.2 Electrical
Important factors:
- Handling and restraint facilities must promote good animal welfare.
- Constant amperage and variable voltage is to be used. (See minimum values below.)
- Electrodes must be firmly applied and not moved during the stunning process.
- The application of automated electrodes must not injure the animals.
- Dampen the hog (mist or spray) to improve electrical conduction (do not use an excessive amounts).
2.2.1 Landmarks and approaches
2.2.1.1 Head-to-head
- Span the brain by placing the electrodes behind the eyes on each side of the head, or
- Span the brain by placing the electrodes just under the base of each ear, or
- Place the electrodes on the bony process of the skull behind each ear.
- Do not place the electrodes on the neck.
- Bleeding must start in less than 30 seconds.
- With high frequency (> 350 Hz), low amperage, head-only stunning bleeding must start within 15 seconds.
2.2.1.2 Head-to-body
Option #1: Place two electrodes on the head (see 2.2.1.1) and a third electrode behind the heart on the 4th rib. Current is first directed to the two head electrodes, which is followed by applying current to the head and chest electrodes.
Option #2: Place one electrode on the front of the skull, or on the bony process behind the ear (see 2.2.1.1) and place the second electrode behind the heart on the 4th rib. Current is applied head to chest.
| Animal | Amperage | Volts | Frequency | Time (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hogs (head only) | ≥ 1.25 | > 250-300 | 50-60 | 1-3 |
| Hogs (head to body) | Head: ≥ 1.25 | > 250-300 | 50-60 | 1-2 |
| Hogs (head to body) | Body: ≥ 1.30 | > 300 | 50-60 | 3 |
| Sows or Boars | ≥ 2.0 | > 300 | 50-60 | 3 |
Note: Other voltages, frequencies and times may be used if:
- the plant operator presents documentation by a recognized animal welfare specialist outlining the protocol and demonstrable evidence that the method(s) used are consistently effective and humane; or
- a trial period of stunning is undertaken; or
- the procedure consistently meets animal welfare stunning requirements; or
- amperage (current) stuns; therefore, use constant amperage and variable volts.
2.3 Controlled Atmospheric Stunning (CAS) (CO2 and Gas Mixtures)
Important Factors:
- Pre-stun handling stress has a significant impact on animal response during induction of anaesthesia.
- Induction with CAS can be highly stressful, especially for some genetic strains of hogs.
- Pre-existing pneumonia can prolong the induction of anaesthesia.
- Handling, restraint and stunning facilities must meet current World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH; founded as Office International des Épizooties (OIE)) and industry standards.
- Design and function of the lairage and pre-stun handling area are important to minimize prestun stress in animals, which minimizes stress during the induction of anaesthesia.
- Gas stunner design and operation play an important role in minimizing stress during the induction of anaesthesia.
- Exposure time to the gas and the time between stunning and bleeding are important to ensure there is no return to sensibility before death. (See the stun-to-stick interval chart below.)
- The bleeding rail length is critical. There must be sufficient room to accommodate and stick stunned animals exiting the gas chamber during a kill line stoppage.
- Prior to installation of the CAS, planning must include provisions for possible increased line speeds.
- Stocking density of the chamber must be optimal: pigs must be able to stand without being on top of one another.
- Monitoring during pre-stun handling, induction of anaesthesia, sticking and bleeding is critical.
- Induction must be monitored by means of a camera or observation portal. Monitoring must occur at start up, after breaks in production and for a group of hogs differing in size or age from previous groups, for example, from different producers. More frequent monitoring may be required if there are problems with induction.
- Gas concentrations, startup gas mixing procedures and stunning procedures must conform to the manufacturer's recommendations. For alternate procedures see below.
- A maximum stun to stick interval must be validated.
- If hogs regain sensibility the gas concentration, and /or exposure time (to the highest concentration of gas), must be increased until all animals are properly stunned. (Backup mechanical stunners must be available and used when needed.)
- Example guidelines. Note: these times will vary with the system, genetic of hogs, etc. Monitoring return to sensibility is required. Time of exposure to the gas and stun to stick time must be adjusted if animals are returning to sensibility.
| First Stop 70-80% CO2 Total Time of Exposure [dwell time] (sec) |
Second Stop > 90% CO2 Stick within (sec) |
|---|---|
| 120 | 30 |
| 130 | 45 |
| 140 | 60 |
| 150 | 75 |
| 160 | 90 |
Note: Time is counted from last stop just before exiting the gondola.
2.3.1 Carbon dioxide (CO2) and Gas Mixtures
Concentration
- It is an WOAH requirement that no less than 80% concentration of CO2 be used (90% is preferable).
- Exposure time to the gases must be sufficient to ensure no pigs regain sensibility before death occurs due to cardiac arrest or bleeding.
- Stun to stick interval must be as per the stun-to-stick interval chart. (Shorter time frames may be required if there are return to sensibility problems.)
- Stunning
- The gas mixture and induction of anaesthesia must be non-aversive and must not be distressing.
- The chamber and methods of conveyance through it must avoid stress to the animals.
- The density of animals in the gondola must be such that animals do not fall or lay on each other during the stunning operation.
- The chamber must be lit.
- The chamber must be designed so that the animals in the chamber can be monitored at all times by direct observation ports, cameras, or similar means.
- The chamber must be equipped to continuously measure and display the CO2 concentration (or other gas used in the stunning process) at the point of induction and the maximum concentration.
- The system must provide visible and audible warnings if the gas concentration falls below the required levels.
- Stunning must be as per the manufacturer's stunning protocol. See below for alternate stunning procedures. Pigs usually require 3 minute exposure time to the concentrations indicated below.
| Type | Method of Stunning | Gas(es) | Concentration | Other Gases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | High blood levels of CO2 (Hypercapnia) | CO2 | ≥ 80% 90% (preferred) |
oxygen, nitrogen, etc. |
| Gas Mixtures |
Low blood levels of O2 (Hypoxia) | O2 | ≤ 2% (O2) | carbon dioxide, argon, nitrogen |
| Gas Mixtures |
Low blood levels of O2 and High blood levels of CO2 |
O2, and CO2 | ≤ 2% (O2) ≤ 30% (CO2) |
argon, nitrogen, etc. |
Note: Other gas mixtures and concentrations may be used if:
- The plant operator presents documentation by a recognized animal welfare specialist outlining the protocol and demonstrable evidence that the method(s) used are consistently effective and humane.
- A trial period of CAS stunning is not undertaken.
- The procedure consistently meets CAS animal welfare stunning requirements.
3. Sheep, Lambs, Goats
3.1 Mechanical
Important factors:
- Handling and restraint facilities must meet current World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH; founded as Office International des Épizooties (OIE)) and industry standards.
- There is a marked variation between the thickness of the skulls of horned and hornless animals.
- Horned animals, especially mature males, have very thick frontal bones.
- Know the approximate location of the brain in the skull.
- Use the appropriate landmarks. (See below.)
- Plan the trajectory so the bolt or projectile travels through the following parts of the brain (cerebral hemispheres, midbrain, brainstem). Of these the midbrain and brainstem are the most important. They are located in the centre of the cranium at the level of the attachment of both ears. (See [e] below.)
3.1.1 Landmarks and approaches
3.1.1.1 Hornless sheep
Hold and discharge the mechanical stunning device so that the bolt/bullet enters the top of the skull at the midpoint of an imaginary line drawn between the animal's ears (See [a], [b] and [c] below.)



| Image | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Line connecting the base of the two ears. The midpoint of this line indicates the location of the brainstem in the middle of the skull. |
 |
Trajectory of the projectile as it travels to the midbrain and brainstem. |
3.1.1.2 Horned sheep and all goats
- Horned sheep and goats must be stunned from the top of the head (see 3.1.1.1 Hornless for landmarks), unless the presence of horns prevents the use of this approach (see [c], [d], [e] and [f] for the top of the head approach).
- If the configuration of the horns make it necessary to stun from poll position, discharge the mechanical stunning device so that the bolt/bullet enters the skull just behind the midpoint of the nuchal crest or ridge between the horns and is directed towards the base of the tongue. (See [g].)
- Stunning in the poll position (just behind the horns or on the nuchal crest) can result in a rapid recovery of consciousness. Therefore, bleeding must be commenced within 15 seconds by cutting both carotid arteries, or the vessels from which they originate. (See [g].)




| Image | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Location of the brainstem and midbrain - in the middle of the skull. |
 |
Trajectory of the projectile as it travels to the midbrain and brainstem. |
 |
Trajectory of the projectile as it travels to the midbrain and brainstem. |
3.1.2 Mechanical Stunning Devices
3.1.2.1 Captive Bolt
- Use the manufacturer's recommended charge, cleaning, maintenance and stunning protocols.
- Use 4 ¾ in. bolt. A shorter bolt may be used on small lambs.
- Bolt velocity and charge must be appropriate to the species, animal size and the presence or absence of horns.
- Assess bolt velocity daily by using the manufacturer's bolt velocity testing device, or similar means.
3.1.2.2 Firearms
Use the slowest velocity and minimum energy (muzzle) required to effectively stun the animal. (See below).
| Stunning Device | Hornless | Horned |
|---|---|---|
| Captive Bolt | Small charge | Appropriate charge |
| Firearm | .22STable Note 1 is sufficient | .22 LRTable Note 2 |
Table Notes
- Table Note 1
-
.22 short
- Table Note 2
-
22 long rifle Do not use hollow point cartridges.

3.2 Electrical
Important factors:
- Handling and restraint facilities must meet current WOAH and industry standards.
- Sheep can be the most difficult animals to stun electrically - due to the resistance of wool.
- Mature large animals have greater resistance to the flow of electrical current through their body; therefore, greater amperage and voltage must be used to effectively stun them. (See below).
3.2.1 Landmarks and approaches
3.2.1.1 Head-Only
- Electrodes must be placed over each temple (between the eye and ear) to span the brain.
- Placing the electrodes over the occipital condyles (behind the ears) is not effective with head-only stunning.
- Electrodes must be designed to facilitate penetrating the wool and making good contact with the animal's head.
- Electrodes and contact location must be wet (or water flow) to facilitate conduction of the electrical current.
- Current must flow for 3 seconds.
- The animal must be stuck within 15 seconds as recovery from head-only stunning is rapid.
3.2.1.2 Head-to-Body
- Head-to-body stunning is far more effective than head-only stunning (head to body is preferred).
- Electrodes must be designed to facilitate penetrating the wool and making good contact with the animal's head.
- Electrodes and contact location must be wet (or water flow) to facilitate conduction of the electrical current
- Current must flow for 3 seconds
- The head and back (body) electrodes are placed 25 to 40 cm (10 in.-16 in.) apart.
- Options include:
- Place two contacts on top of the head (between the ears) with a third contact placed over the spine.
- Place one contact on each side of the head (spanning the temples) with a third "saddle" contact placed over the spine. (Note: using the condyles is far less effective than the temple area)
- Place one contact on top of the head with a second contact made over the left chest (arm pit).
| Animal | Amperage | Volts | Frequency | Time (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lambs (shorn) and kids | 0.6 | 250-350 | 50-60 | 3 |
| Sheep and goats | 1.0 | 300-400 | 50-60 | 3 |
3.3 Gas, Gas Mixture
These are not commonly used to stun sheep as the wool absorbs a lot of gas, making the system very inefficient.
4. Bison
4.1 Mechanical
Important Factors:
4.1.1 Handling and restraint
- Handling and restraint facilities must be sturdy and meet current industry standards for bison, including safety measures and sight lines.
- Suitable facilities are essential.
- Restraint must facilitate stunning the animal from the front of the head.
4.1.2 Landmarks and approaches
- Mature bulls have very thick frontal bones overlaying the brain. The hide over the frontal bone and the frontal bone itself can each be up to 1.5 in (3.8 cm) thick.
- Mature bulls frequently have long thick hair on their heads, which makes it difficult to see landmarks other than the horns.
- Bison typically hold their heads lower than cattle.
- Know the approximate location of the brain in the skull.
- Plan the trajectory so that the bolt/projectile travels through all parts of the brain (cerebral hemispheres, midbrain, brainstem). Of these the midbrain and brainstem are the most important parts of the brain. They are located in the centre of the brain at the level of the attachment of the ears. (See [d].)
- Landmarks are very important and they are not the same as for cattle. (See [a] to [i] below.)
- Intersection of the midpoint of the front of the head and a line running between the lower part of the attachment of each horn. (See [b], [e], [f] and [h] below.)
- Discharge the stunning device perpendicular to the front of the head. (See [a], [c], [d], [g] below.)
- Do not stun from the top of the head or behind the head, or behind the ears, due to the risk of pithing the animal instead of properly stunning it.
- Discharging the mechanical stunning device at the locations on the skull other than the front of the head is not permitted due to the risk of missing the appropriate sections of the brain.
- Stunning problems are usually due to using improper landmarks and/or holding the mechanical stunning device at an angle other than perpendicular to the skull. (See [a] to [i] below.)
Proper Landmarks for Stunning
Mature males



Immature Males


Mature Female

Projectile Entry Point

[f]

Projectile Entry Point

[h]

| Image | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Line running from the base of one horn to the other. |
 |
Location of the brainstem and midbrain - in the middle of the skull. |
 |
Entry point of the projectile (bullet). |
 |
Trajectory of the projectile as it travels to the midbrain and brainstem. |
 |
Arrow indicating projectile entry point to the skull and brain cavity. |
Improper Landmarks for Stunning
Bison Skull
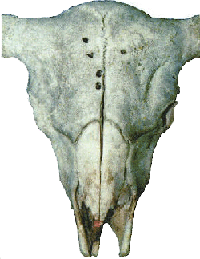
Note: This is an example of the impact of using improper landmarks. This bison skull contained 10 bullet holes. They were in the front, side and back of the skull. Most of the bullet holes in the front are too low (bovine landmarks), or too much off the midline of the skull (thereby missing the midbrain and brainstem) to be effective.
4.1.3 Mechanical Stunning Devices
4.1.3.1 Captive Bolt
- The bolt length for immature animals must be at least 12 cm (4 ¾ in); the bolt length for animals over one year of age must be at least 15 cm (6 in).
- The .25 calibre and larger captive bolt stunning devices with heavier charges are far more effective.
- Use the manufacturer's recommended charge, cleaning, maintenance and stunning protocols.
- Assess bolt velocity daily by using the manufacturer's bolt velocity testing device, or similar means.
- Can be used on immature animals.
- See 4.1.2 Landmarks and approaches for stunning problems.
Note: Standard bolts are not long enough for large bulls.
| Animal | Calibre | Bolt Length | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immature | > .25 | > 12 cm (4 ¾ in) or 15 cm (6 in) |
> 72 m/s (236 ft/s) | Heavy Charge |
| Over one year of age |
>.25 | 15 cm (6 in) | > 72 m/s (236 ft/s) | Heavy Charge |
4.1.3.2 Firearms
- Perforation and ricochet are a safety concern with high velocity calibre firearms.
- Use the slowest velocity and minimum energy (muzzle) required to effectively stun the animal.
- Maximum velocity < 2000 ft/s to help prevent ricochet from the surface of the skull.
- Maximum energy < 1000 ft/lb to help prevent skull perforation (exiting the opposite side of the skull).
- Plan the trajectory so that the bullet travels through the midbrain and brainstem, which are located below the horn and between the ears.
- See 4.1.2 above for stunning problems.
| Animal | Calibre | Grain | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immature + Cows | .22 Winchester Magnum | 40 | 1910 | 324 |
| Animal | Calibre | Grain | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mature Bulls | .30 Remington Carbine | 110 | 1990 | 967Table Note 1 |
Table Notes
- Table Note 1
-
Upper limit of energy as the projectile may perforate the skull and enter the neck muscle.
| Animal | Gauge | Length | Slug | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mature Bulls | .410 | 2 ½ in | 1/5 oz (87 g) | 1830 | 651 |
| Mature Bulls | .410 | 3 in | ¼ oz (108 g) | 1800 | 788 |

5. Horses
5.1 Mechanical
Important factors:
5.1.1 Handling and Restraint
- Horses vary a great deal in size.
- Handling and restraint facilities must promote good animal welfare standards at all times.
- Restraint facilities must be adaptable and appropriate to the size variation of the animals slaughtered.
- The restraint facilities must be suitable for the operator to stun the animal in an effective manner.
5.1.2 Landmark and approaches
- Just above the intersection (1 in) of imaginary diagonal lines from the attachment of each ear to the medial canthus (middle corner) of the opposite eye. (See [b] and [c] below.)
- Plan the trajectory so that the bolt travels through the brain (cerebral hemispheres, midbrain, brainstem). The most significant of these are the midbrain and brainstem which are at the level of the bottom of the attachment of the ears. (See [a] below.)
- Hold and discharge the stunning device perpendicular to the front of the skull.
- The frontal bone over the brain is quite thin.



| Image | Description |
|---|---|
 |
diagonal lines running from the inner corner of each eye to the upper edge of the attachment of the opposite ear |
 |
diagonal lines running from the inner corner of each eye to the upper edge of the attachment of the opposite ear |
 |
entry point of the projectile which is approximately one inch above the intersection of the diagonal lines |
 |
entry point of the projectile which is approximately one inch above the intersection of the diagonal lines |
 |
arrow indicating entry point into the skull and brain cavity |
 |
location of the brainstem and midbrain - in the middle of the skull |
5.1.3 Mechanical Stunning Devices
5.1.3.1 Captive bolt
- Horses are very effectively stunned with captive bolt devices (e.g. Australia).
- Bolt length 12 cm (4 ¾ in) can be used to stun all horses effectively.
- Various types and triggering devices are available.
- Use the manufacturer's recommended charge, cleaning, maintenance and stunning protocols.
- Assess bolt velocity by using manufacturer's bolt velocity testing device, or similar means daily.
| Animal | Calibre | Bolt Lengths | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All horses | .22, .25, .33 | 12 cm (4 ¾ in) | 55 m/s (183 ft/s) | Appropriate charge |
5.1.3.2 Firearms
- When a proper restraint system is used firearms are not necessary to effectively stun horses.
- Firearm use is discouraged.
- Perforation and ricochet are a safety concern; therefore use the slowest velocity and minimum energy (muzzle) required to effectively stun the animal. (See below.)
| Animal | Calibre | Grain | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All horses | .22 S Table Note * | 29 | 1095 | 77 |
| All horses | .22 LR Table Note * | 40 | 1255 | 140 |
Table Notes
- Table Note *
-
Do not use hollow point.
6. Cervids (Includes elk, fallow deer, white tail)
6.1 Mechanical (Elk)
Important factors:
6.1.1 Handling and restraint
- Cervids are flighty and can become stressed easily.
- Appropriate handling, facilities and restraint are imperative. Facilities must promote good animal welfare standards at all times.
6.1.2 Landmarks and approaches
- Elk hold their head very high, especially when they are alert - so plan your trajectory.
- Plan the trajectory so that the bolt or projectile travels through the brain (cerebral hemispheres, midbrain, brainstem). The most significant of these are the midbrain and brainstem, which are located in the centre of the cranium at the level of the bottom of the attachment of the ears.
- When animals are alert, the surface of the frontal bone is almost horizontal to the ground (see below); therefore, mechanical stunning with the stunner operator standing in front of the animal is difficult.
- Cervids have large brains with thin frontal bones.
- The male frontal bone (1.25 cm) is somewhat thicker than the female frontal bone (0.78-0.97 cm).
| Female Elk | Male Elk |
|---|---|
| [a]
|
[b]
|
| Female Elk | Male Elk |
|---|---|
| [c]
|
[d]
|
| [e]
|
[f]
|
| Image | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Intersection of diagonal lines running from the inner corner of each eye to the upper edge of the attachment of the opposite ear. |
 |
Indicates the entry point for the projectile on the "side" of the animal's head (temple). |
 |
Indicates the direction that the stunning device should be pointed and the entry point when the bolt or projectile is directed towards the "top" (front) of the animal's head. |
| Sex | Side of the head | Front or "top" of the head |
|---|---|---|
| Males |
|
|
| Females |
OSH Concerns (therefore only use .22 short)
|
|
Best practices include:
- the stunner operator approaches the front of the animal's head from above; or
- the stunner operator stuns the animal from the side of the head (firearms only).
6.1.3 Mechanical Stunning Devices
6.1.3.1 Captive Bolt (only from above head, frontal bone approach)
- The bolt length is standard (4 ¾ in) or short (3 3/8 in).
- All calibres can be used.
- This is effective for all sizes of cervids.
- Use the manufacturer's recommended charge, cleaning, maintenance and stunning protocols (daily).
- Assess the bolt velocity daily by using the manufacturer's bolt velocity testing device, or similar means.
- See 6.1.2 "Landmarks and approaches" for stunning problems.
| Animal | Calibre | Bolt Length | Muzzle Velocity(ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female + male | .22 | Either | 55 m/s (183 ft/s) | Appropriate charge |
6.1.3.2 Firearms
- Ricochet is a potential hazard to any persons in the vicinity when elk hold their heads high and the frontal approach is used.
- Perforation is a potential hazard to any persons in the vicinity when animals are stunned from the side of the head.
- Note: Perforation occurs when the projectile exits the side of the head opposite to the entry point.
- Use the slowest velocity and minimum energy (muzzle) required to effectively stun the animal. (See below.)
- See 6.1.2 "Landmarks and approaches" for stunning problems.
| Animal | Calibre | Grain | Muzzle Velocity(ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | .22 STable Note 1 | 29 | 1095 | 77 |
| Female | .22 LRSTable Note 2 | 40 | 1255 | 140 |
| Male | .22 LRTable Note 2 | 40 | 1255 | 140 |
| Male | .22 Winchester magnum Note: mature males and frontal "top" approach only |
40 | 1910 | 324 |
Table Notes
- Table Note 1
-
.22 short (lead round nose)
- Table Note 2
-
.22 long rifle (lead round nose)
Do not use hollow point.
6.2 Mechanical (Other Cervids - fallow deer, white tail)
Important Factors:
6.2.1 Handling and restraint - similar to elk
6.2.2 Landmarks and approaches - similar to elk
Frontal bone to the skull is very thin e.g. fallow deer 0.33 - 0.48 cm (0.13 - 0.19 in.)
6.2.3 Mechanical stunning devices
6.2.3.1 Captive Bolt
See elk.
Appropriate light charge (similar to that used for calves and lambs).
| Animal | Calibre | Bolt Length | Muzzle Velocity (ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female + male | .22, .25, .33 | Either | 55 m/s (183 ft/s) | Appropriate charge |
6.2.3.2 Firearms
See elk.
| Animal | Calibre | Grain | Muzzle Velocity(ft/s) | Energy (ft/lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female + male | .22 STable Note 1 Table Note ** | 29 | 1095 | 77 |
Table Notes
- Table Note 1
-
.22 short (lead round nose) Do not use hollow point.
- Table Note **
-
Side of the head not recommended in fallow deer due to the risk of perforation.
7. Rabbits
Acceptable methods for stunning rabbits in federal slaughter facilities include captive bolt pistol stunning (penetrative and non-penetrative) and electrical stunning.
7.1 Mechanical (penetrative and non-penetrative)
A non-penetrative captive bolt gun uses a compressed air driven, non-penetrating captive bolt to humanely and effectively stun rabbits of all weights and sizes.

A penetrative captive bolt is a spring-fired captive bolt gun which is effective when operated correctly. In some food markets, rabbit meat is sold with the head attached therefore the penetrating captive bolt may not be the most appropriate tool to use due to the force of the stun.
Care needs to be taken when placing the gun against the rabbit's head as the skin over the head of a rabbit is loose and if it slips, it can make the aim inaccurate.


7.2 Electrical (electronarcosis)
Electronarcosis, using the head-only method, is the more commonly used stunning method in rabbit slaughter facilities when larger numbers of animals are processed.
Rabbit fur is resistant to an electrical current therefore the required stun amperage for an effective stun is 0.14 amps and 100 volts for a period of three seconds or 0.2 amps for at least 2 seconds.
Wetting the rabbit slightly can increase electrical conductivity. However it must not be so wet as to cause part of the stunning current to flow over the surface of the body instead of through the head and the brain.
Rabbits return to sensibility from head only electric stun rapidly; therefore rapid bleeding within 5 seconds is essential to avoid a return to consciousness. When using a transverse incision of the neck, both carotid arteries should be severed for rapid bleed-out.
Example of electrodes for stunning rabbits:








