A food recall is the removal of a food from further sale or use, or the correction of its label, at any point in the supply chain as a risk mitigation action. It is the responsibility of industry to effectively remove the recalled food from the marketplace.
The Canadian Food Inspection Agency's (CFIA) role is to inform the public, oversee implementation of the recall and verify that industry has effectively removed recalled food from the marketplace.
The CFIA oversees approximately 154 recall incidents a year.
Most recalls in Canada are voluntary meaning that they are conducted by the recalling food business, with oversight from the CFIA. If a food business is unable or refuses to conduct a voluntary food recall, the Minister of Health has the power to order a mandatory recall for any food that poses a health risk.
To read more about food recalls, please consult our fact sheet.
Informing the public
Informing the public about high-risk recalls is critical as consumers may have recalled food in their homes that they should not consume.
- The CFIA issues recall warnings through the media to inform the public about high-risk recalls
- The CFIA also posts all food recalls on the Recalls and safety alerts website
- Subscribe to receive the latest recall information.
- You can also view public health notices issued by the Public Health Agency of Canada
Food recall incidents and total recalls
A recall incident represents a breakdown in the food safety system leading to the request for a recall. A recall incident may lead to additional recalls (secondary) and have a common factor(s) such as product, cause, process deviation, etc. (For example, an out of country manufacturer recalls food that was shipped to 5 importers. This is captured as 1 recall incident and 5 recalls in total.)
The total number of food recalls is the measure of all recalls conducted and includes recall incidents and secondary recalls. The number of secondary recalls varies by recall incident.
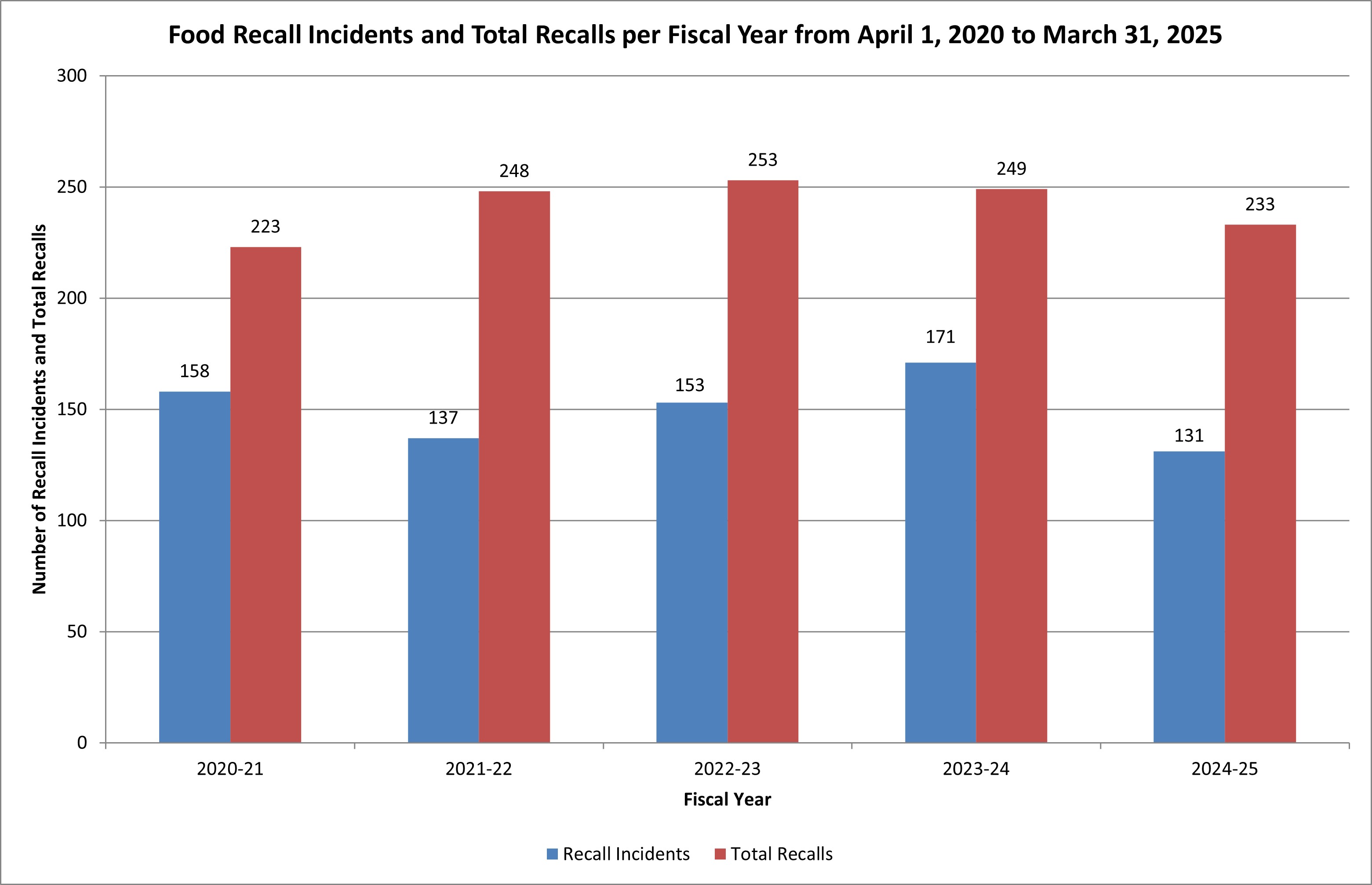
Description for bar graph – April 2020 to March 2025
| - | April 2020 to March 2021 | April 2021 to March 2022 | April 2022 to March 2023 | April 2023 to March 2024 | April 2024 to March 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of recall incidents | 158 | 137 | 153 | 172 | 131 |
| Number of total food recalls | 223 | 248 | 253 | 248 | 233 |
Food recall incidents and total recalls by hazard
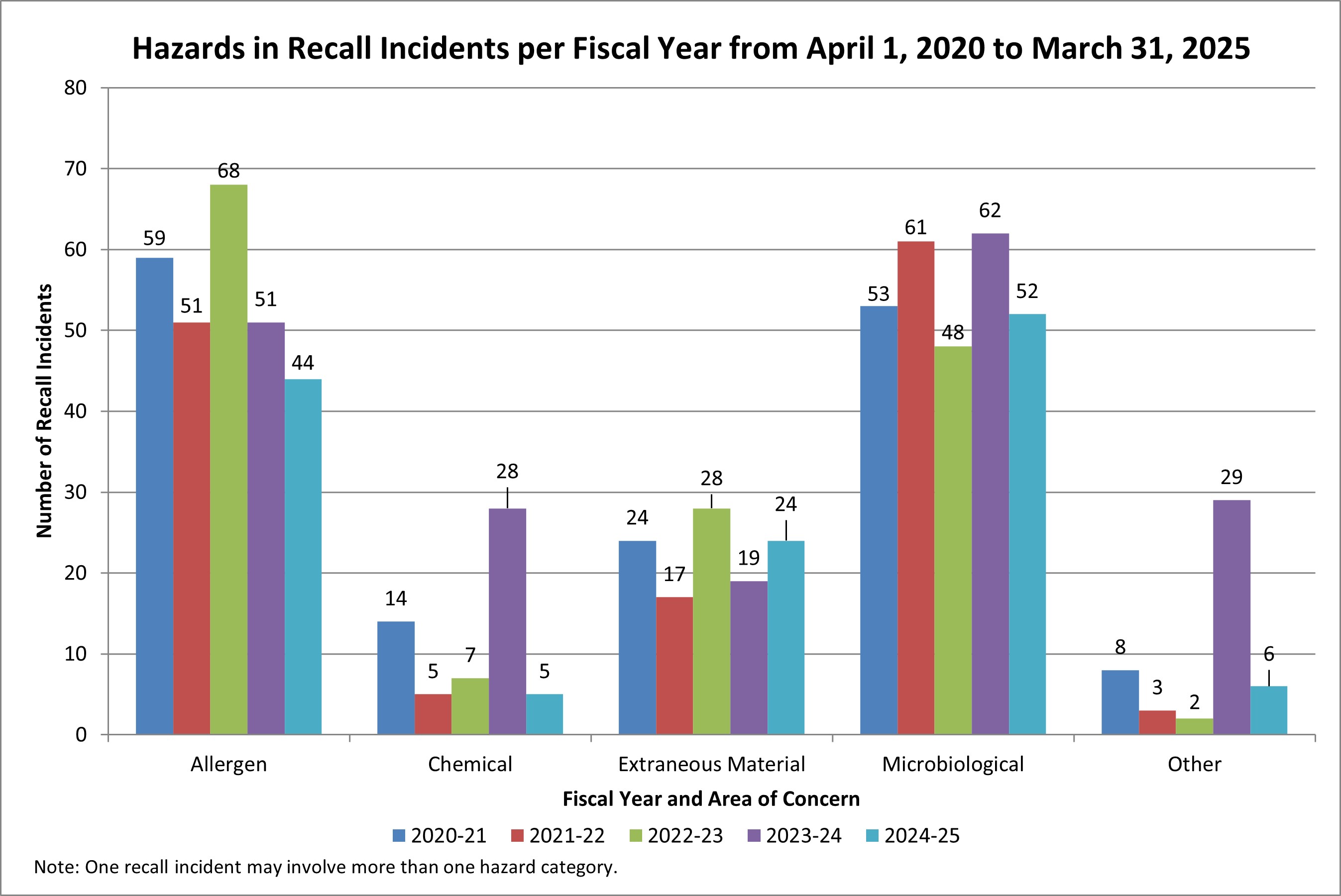
Description for bar graph – April 2020 to March 2025
| - | April 2020 to March 2021 | April 2021 to March 2022 | April 2022 to March 2023 | April 2023 to March 2024 | April 2024 to March 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allergen | 59 | 51 | 68 | 51 | 44 |
| Chemical | 14 | 5 | 7 | 28 | 5 |
| Extraneous material | 24 | 17 | 28 | 19 | 24 |
| Microbiological | 53 | 61 | 48 | 62 | 52 |
| Other | 8 | 3 | 2 | 29 | 6 |

Description for bar graph – April 2020 to March 2025
| - | April 2020 to March 2021 | April 2021 to March 2022 | April 2022 to March 2023 | April 2023 to March 2024 | April 2024 to March 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allergen | 72 | 84 | 96 | 70 | 66 |
| Chemical | 18 | 11 | 8 | 46 | 5 |
| Extraneous material | 29 | 21 | 36 | 19 | 47 |
| Microbiological | 94 | 129 | 111 | 99 | 109 |
| Other | 10 | 3 | 2 | 51 | 6 |
Food recall incidents and total recalls by class
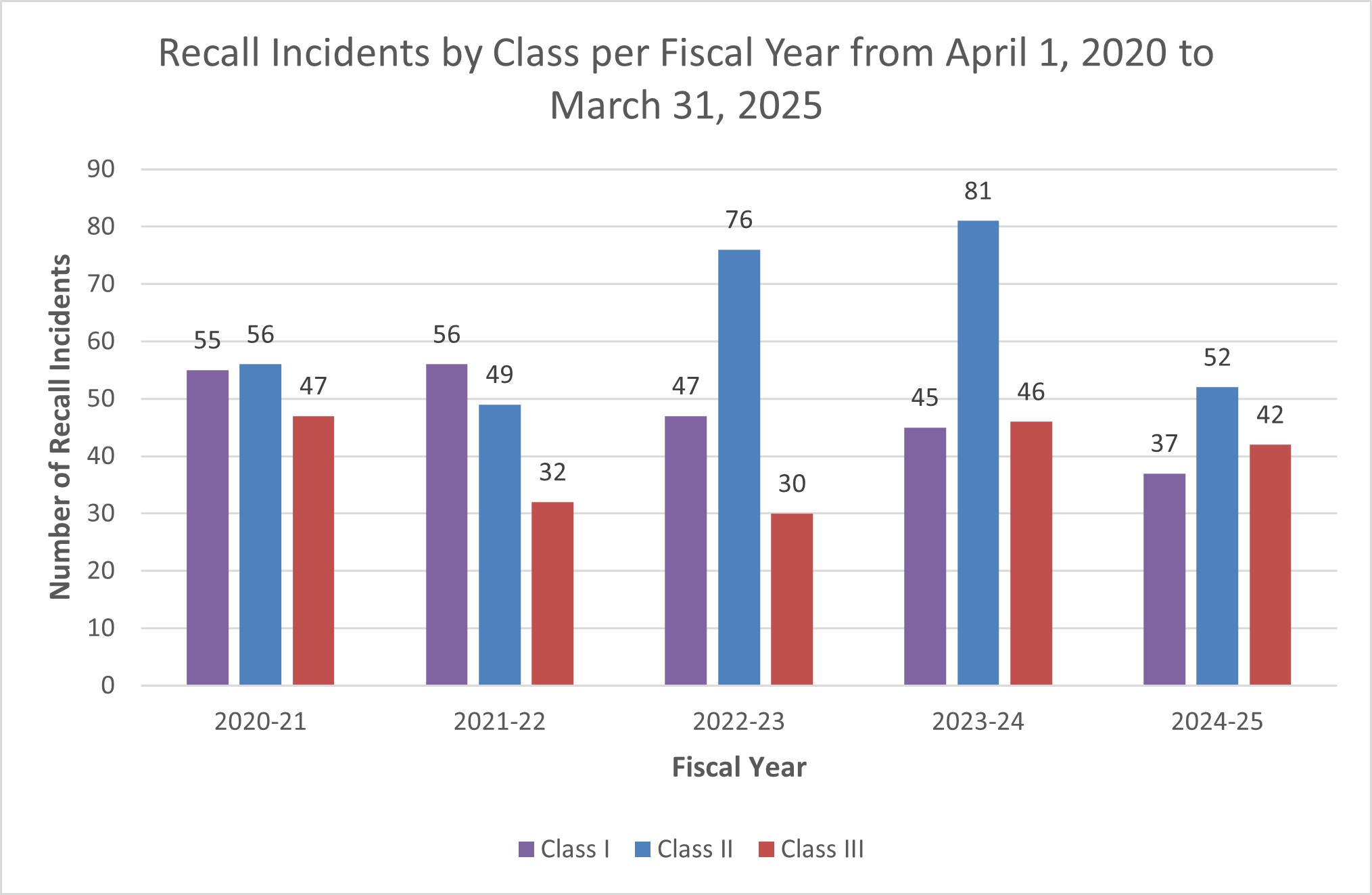
Description for bar graph – April 2020 to March 2025
| - | April 2020 to March 2021 | April 2021 to March 2022 | April 2022 to March 2023 | April 2023 to March 2024 | April 2024 to March 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | 55 | 56 | 47 | 45 | 37 |
| Class II | 56 | 49 | 76 | 81 | 52 |
| Class III | 47 | 32 | 30 | 46 | 42 |

Description for bar graph – April 2020 to March 2025
| - | April 2020 to March 2021 | April 2021 to March 2022 | April 2022 to March 2023 | April 2023 to March 2024 | April 2020 to March 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | 106 | 114 | 83 | 57 | 96 |
| Class II | 62 | 95 | 131 | 137 | 89 |
| Class III | 55 | 39 | 39 | 54 | 48 |
Glossary
- Allergen
- A food product may contain ingredients such as peanuts, milk or eggs that are not identified or are incorrectly identified on the label and that can cause adverse reactions in people who are allergic to the item.
- Chemical
- A food product contains chemical residues such as lead, mercury or pesticides that, at certain levels, can affect human health.
- Extraneous material
- A food product contains material from an outside source, such as metal, glass or hair. These are not necessarily a risk to human health.
- Microbiological
- A food product is contaminated by micro-organisms, such as bacteria, viruses or parasites, which have the potential to cause illness.
- Other
- A food product is of concern due to the presence of a hazard that does not fall within one of the above categories. Examples include non-permitted ingredients, nutrition concerns and potential tampering.