The following chart provides recommended pH and moisture content combinations for non-refrigerated products to prevent the growth of spore-forming bacteria after heat treatment. Moisture content and pH have an inverse relationship within a narrow range. For higher moisture contents lower pH's are recommended and vice-versa.
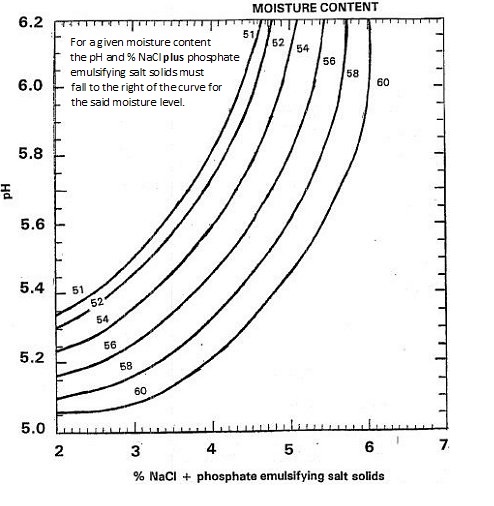
Description of image - Cheese spread microbiological stability chart for non-refrigerated products
This image shows a cheese spread microbiological stability chart for non-refrigerated products. The chart shows, for a given moisture content, the recommended maximum pH and the minimum percentage of sodium chloride (salt) plus phosphate emulsifying salt solids needed to prevent the growth of spore-forming bacteria after heat treatment.
- The Y-axis of the chart shows pH levels ranging from 5.0 to 6.2.
- The X-axis of the chart shows the percentage of sodium chloride and phosphate emulsifying salt solids, ranging from 2 to 7.
- Moisture content ranges from 51 to 60.
Note
If the product does not fall within the ranges given, validate the safety of the product.
Reference
- Tanaka N, Traisman E, Plantinga P, Finn L, Flom W, Meske L, Guggisberg J. 1986. Evaluation of factors involved in antibotulinal properties of pasteurized process cheese spreads. J Food Prot 49:526–31.