AAC Prairie
| Denomination: | 'AAC Prairie' |
|---|---|
| Previously Proposed Denomination: | 'TR17255' |
| Botanical Name: | Hordeum vulgare |
| Applicant/Holder: |
Agriculture & Agri-Food Canada, Brandon Brandon Research Centre, 18th St. & Grand Valley R P.O. Box 1000A, R.R. #3 Brandon, Manitoba R7A 5Y3 Canada |
| Breeder: |
Ana Badea, Agriculture & Agri-Food Canada, Brandon, Manitoba |
| Agent in Canada: |
Agriculture & Agri-Food Canada Office of Intellectual Property and Commercialization 107 Science Place Saskatoon, Saskatchewan S7N 0X2 Canada Tel: (306) 203-1383 |
| Application Date: | 2020-12-11 |
| Provisional Protection:: | 2020-12-11 |
| Application Number: | 20-10399 |
| Grant of Rights Date: | 2022-11-21 |
| Certificate Number: | 6677 |
| Grant of Rights Termination Date: | 2042-11-21 |
Variety Description
Varieties used for comparison: 'AC Metcalfe', 'CDC Kindersley', 'AAC Synergy' and 'AAC Connect'
Summary: At tillering, 'AAC Prairie' has sparse to medium density of pubescence on the lower leaf sheaths while 'AC Metcalfe' has absent or very sparse pubescence on the lower leaf sheaths. At booting, the frequency of plants with recurved flag leaves is low for 'AAC Prairie' while it is absent or very low for 'AC Metcalfe' ,'CDC Kindersley', and 'AAC Connect'. The flag leaf of 'AAC Prairie' is narrower than that of 'AAC Connect'. The lemma awn tips of 'AAC Prairie' have a medium to strong intensity of anthocyanin colouration, while anthocyanin colouration is absent on the lemma awn tips of 'AC Metcalfe' and 'AAC Synergy'. At maturity, the plants, including the awns, of 'AAC Prairie' are shorter than the plants of 'AC Metcalfe'. The spike, excluding the awns, of 'AAC Prairie' is shorter than those of 'AAC Synergy' and 'AAC Connect'. The first segment of the rachis for 'AAC Prairie' is long while it is short for 'AC Metcalfe' and of medium length for 'CDC Kindersley'. The inner lateral nerves of the dorsal side of the lemma on the kernel of 'AAC Prairie' have a medium degree of spiculation while those of 'CDC Kindersley' have absent or very weak spiculation and those of 'AAC Connect' have strong spiculation.
Description:
YOUNG PLANT: semi-erect to intermediate growth habit at tillering, sparse to medium density pubescence on lower leaf sheaths
PLANT: two row, spring malting barley, low frequency of plants with recurved flag leaves, spike emergence occurs mid-season
FLAG LEAF (AT BOOTING): absent or very sparse to sparse pubescence on blade
FLAG LEAF SHEATH: very strong glaucosity, absent or very sparse pubescence
AURICLES: weak to medium intensity of anthocyanin colouration, absent or very sparse to sparse pubescence on margins
SPIKE: medium to strong glaucosity, erect to semi-erect attitude, v-shaped to cup shaped collar, parallel shape, medium to dense, weakly divergent to divergent sterile spikelet attitude, glume and awn of the median spikelet are equal in length relative to the grain
LEMMA AWNS: medium to strong intensity of anthocyanin colouration of tips, longer than spike, rough spiculations on margins
FIRST SEGMENT OF RACHIS: long, medium to strong curvature
KERNEL: whitish aleurone layer, long rachilla hairs, husk present, absent or very weak anthocyanin colouration of nerves of lemma, medium spiculation of inner lateral nerves of dorsal side of lemma, hairless ventral furrow, clasping disposition of lodicules, horseshoe shaped basal markings, medium in length and width
AGRONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS: fair to good resistance to lodging, good malting quality
DISEASE REACTIONS: moderately resistant to Stem rust (Puccinia graminis), Net blotch-net form (Pyrenophora teres forma teres), Covered smut (Ustilago hordei), False loose smut (Ustilago nigra); moderately resistant to moderately susceptible to Spot blotch (Cochliobolus sativus), Net blotch-spot form (Pyrenophora teres forma maculate), Fusarium head blight (Fusarium graminearum); susceptible to True loose smut (Ustilago nuda)
Origin & Breeding History: 'AAC Prairie' (experimental designations TR17255, BM0850-029, and SB140071) originated from the cross conducted between the varieties 'CDC Kindersley' and TR08204 conducted in 2008 at the Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada Brandon Research Centre in Brandon, Manitoba. The F1 generation was bulked in the greenhouse and the F2 grown in a bulk plot in the field in Brandon, Manitoba. In 2009-2010, the F3 generation was bulk increased at a winter nursery in Leeston, New Zealand and in 2010, the F4 generation was grown as two bulk plots in Brandon, Manitoba. Three hundred spikes were harvested and threshed individually and planted as single F5 hill plots in the irrigated field leaf disease nursery in Brandon, Manitoba. The 162 lines selected were grown as F6 progeny rows. One of the selected 49 lines, designated as BM0850-029, was grown as a single plot for preliminary yield tests in 2013 and was advanced to replicated preliminary yield trials in 2014, in Brandon but these were lost due to flooding. The line was entered into a new intermediate yield test, grown in Brandon, Manitoba and Lacombe, Alberta. BM0850-029 was grown in an advanced yield test at 5 locations in Western Canada in 2016 and advanced as a malting line in the 2017 Western Cooperative Two-row Barley Registration test as TR17255. TR17255 was also evaluated in the 2018 and 2019 Collaborative Malting Barley Trials. Breeder seed was established from a bulk of 191 F13 derived lines in 2019. Selection criteria included agronomic appearance, plant height, plant maturity, lodging resistance, yield, heading date, kernel plumpness, test weight, kernel weight, kernel brightness, hull peeling, malting quality and disease resistances.
Tests & Trials: The comparative trials for 'TR17255' were conducted during the 2018 and 2021 growing seasons at the Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Brandon Research and Development Centre in Brandon, Manitoba. There were 4 replicates per variety arranged in an RCB design. Plots consisted of 6 rows with a row length of 4 metres and 0.18 metre inter row spacing. The seeding density was 1200 seeds per plot resulting in approximately 4800 plants per variety. Measured characteristics were based on a minimum of 20 measurements per variety per year. Mean differences were significant at the 5% probability level based on a paired Student's t-test. Disease reaction ratings were provided through the Disease Evaluation team of the Prairie Recommending Committee for Oat and Barley conducted in 2018 and 2019.
Comparison tables for 'AAC Prairie' with reference varieties 'AC Metcalfe', 'CDC Kindersley', 'AAC Synergy' and 'AAC Connect'
Flag leaf width (mm)
| 'AAC Prairie' | 'AC Metcalfe' | 'CDC Kindersley' | 'AAC Synergy' | 'AAC Connect' | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean 2018 | 6.0 | 6.35 | 6.15 | 6.30 | 7.55 |
| std. deviation 2018 | 1.30 | 2.03 | 1.09 | 1.26 | 2.19 |
| mean 2021 | 5.45 | 6.35 | 5.65 | 7.30 | 6.75 |
| std. deviation 2021 | 0.69 | 1.53 | 1.04 | 1.03 | 1.48 |
Plant height (stem plus spike,including awns) (cm)
| 'AAC Prairie' | 'AC Metcalfe' | 'CDC Kindersley' | 'AAC Synergy' | 'AAC Connect' | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean 2018 | 64.7 | 65.85 | 64.30 | 65.10 | 65.45 |
| std. deviation 2018 | 0.60 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.54 |
| mean 2021 | 63.8 | 67.1 | 63.75 | 63.95 | 66.45 |
| std. deviation 2021 | 0.77 | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.60 | 1.00 |
Spike length (excluding the awns) (cm)
| 'AAC Prairie' | 'AC Metcalfe' | 'CDC Kindersley' | 'AAC Synergy' | 'AAC Connect' | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean 2018 | 6.42 | 6.56 | 6.84 | 7.04 | 7.74 |
| std. deviation 2018 | 0.60 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.54 |
| mean 2021 | 7.71 | 8.01 | 8.07 | 9.20 | 9.31 |
| std. deviation 2021 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.43 | 0.65 | 0.78 |
Click on image for larger view

Barley: 'AAC Prairie' (right) with reference variety 'AC Metcalfe' (left)
Click on image for larger view
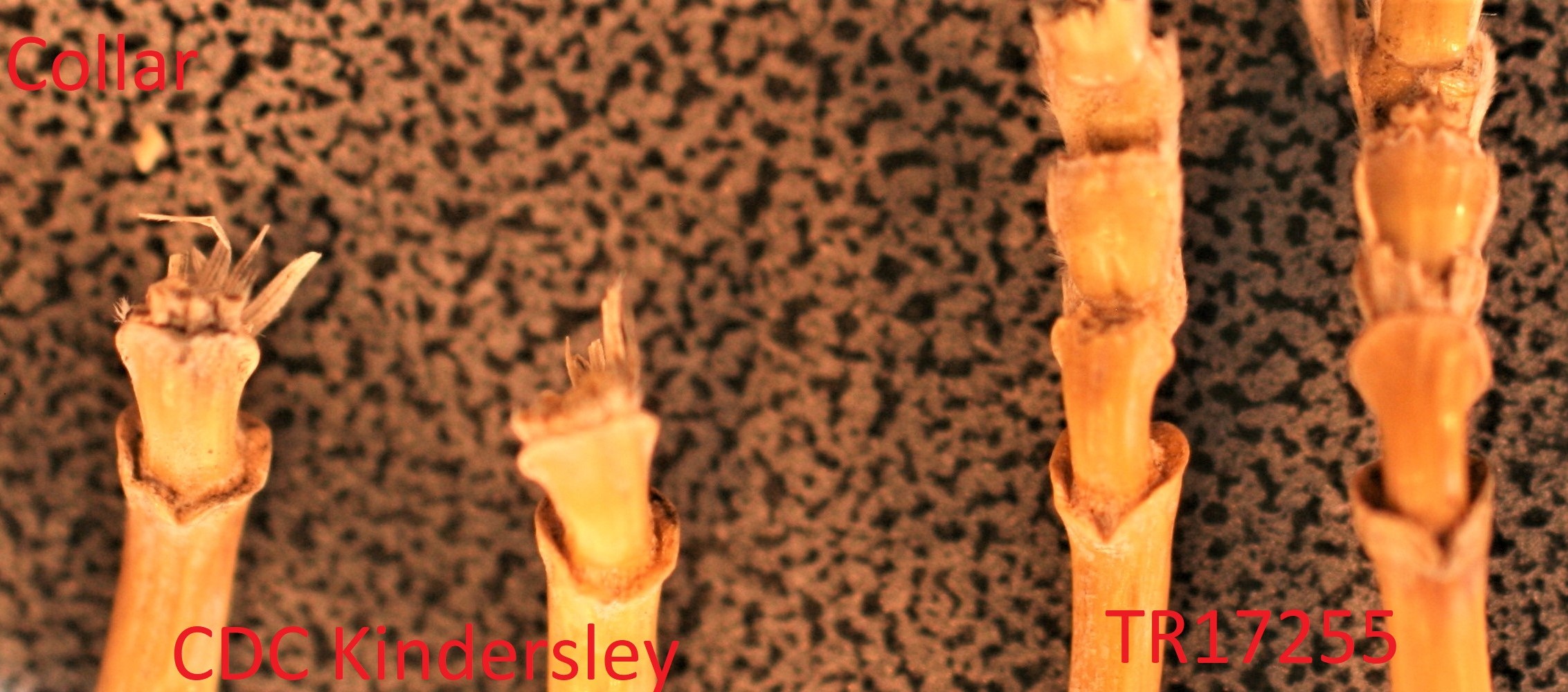
Barley: 'AAC Prairie' (right) with reference variety 'CDC Kindersley' (left)
- Date modified: