Biosecurity is a set of measures used to reduce the chance of the introduction and spread of disease causing organisms and pests.
Animals can remain infectious long after they have died. Any activity that involves the handling of dead animals and their bodily fluids is a biosecurity risk. Therefore, it is important to implement biosecurity measures to contain and transport deadstock.
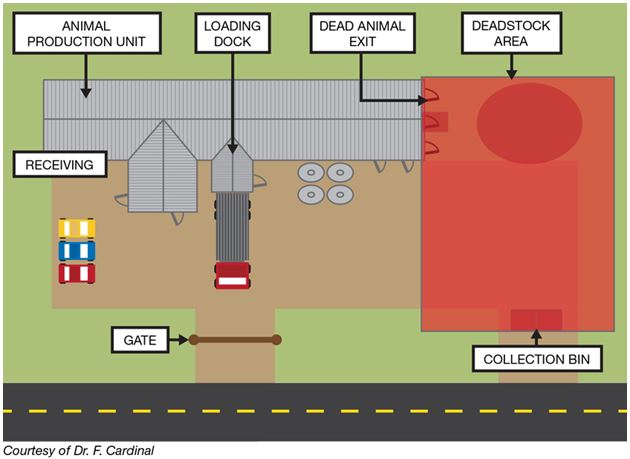
Recommendations to mitigate the biosecurity risks associated with deadstock collection
- Locate the deadstock collection site away from animal production units and feed, bedding and equipment storage sites.
- Keep deadstock collection vehicles as far away as possible from other livestock on the premises.
- Have a designated pathway for deadstock collection that is clean and free of manure and that is separate from paths used by producers and farm workers.
- Store deadstock in a sealed and leak-proof container or, for large livestock, store on a concrete pad with fencing around it to prevent scavenging.
- Check with your municipality and province or territory regarding requirements for deadstock removal.
- Have deadstock removed as soon as possible.
- Inform the deadstock transporter if you suspect your animals may have died from an infectious disease. This will allow the deadstock transporter to modify the route or collection procedure to protect other animal production sites in your area.
Location of deadstock collection bins
To minimize the risk of contamination, deadstock collection bins are best located away from production units, at the edge of the high-risk work area. This will allow deadstock transporters access without entering the farm.