Acknowledgement
The national livestock, poultry and deadstock biosecurity guidance document is primarily founded on existing sources of biosecurity guidance, manuals and scientific articles. Only direct quotes or data are specifically referenced throughout the document. It is recognized that many sources that have contributed to the general content and biosecurity best practices have not been acknowledged. The committee would like to recognize all contributions from academia, industry, provincial and federal sources.
Table of Contents
1.0 Introduction
The Biosecurity Standard for Livestock, Poultry and Deadstock Transportation was developed to encourage both commercial companies and independent drivers to incorporate biosecurity measures in their transportation practices. It is a resource to create awareness, to educate, to provide a common understanding of biosecurity and to serve as a reference guide for continuous industry improvement. This document is not intended to be adopted by federal, provincial, or territorial governments to be used for law or regulation. Commodity specific farm level biosecurity guidance is available on the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) website.
This document focuses on biosecurity for ground transportation but can also be used for air and sea transport events. The information is presented in two sections: The Transportation of Livestock and Poultry and The Transportation of Deadstock and Rendering Material.
It is recognized that not all of the biosecurity guidance provided in this document will be applicable to every transportation event. Similarly, protocols have been provided in the annexes as examples only and may not be directly transferrable between the transportation of different classes of animals or within operations that transport multiple species of livestock and poultry. It is recommended that transporters consider the guidance provided in this document and work with the various industry sectors and consult specialistsFootnote 1 to develop biosecurity protocols that are specific to the transportation event, the species of animal that is transported and animal disease risks.
Some biosecurity best practices may not be achievable due to gaps in infrastructure and the logistics involved in implementing the best practices. Efforts should be made to identify gaps that impede biosecurity implementation, seek alternative approaches to facilitate biosecurity and work on solutions to improve biosecurity for the transportation sector in Canada.
There is a complex interaction between welfare, biosecurity and stress in the transportation of livestock and poultry. All drivers should be aware of and comply with the Codes of Practice for the Care and Handling of Farm Animals, Codes of Practice for the Care and Handling of Farm Animals: Transportation, as well as humane transportation federal regulationsFootnote 2.
1.1 What is biosecurity?
Biosecurity is the implementation of actions that reduce the chance of introducing and spreading infectious agents that cause animal disease and/or the spread of plant pests. Among the many biosecurity measures that can reduce disease transmission are some simple measures that have little or no cost associated with them. You likely are already implementing many good biosecurity practices without realizing it, for example: wearing clean clothes and clean boots, washing your hands with soap and water or using hand sanitizer before and after handling livestock and/or poultry. The cost of a disease outbreak (e.g. depopulation, cleaning and disinfection, reopening export markets, etc.) can far exceed the cost of implementing biosecurity to minimize the risk of introduction and spread of disease.
"An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure"
Benjamin Franklin
1.2 Why is biosecurity important to your customer and the agricultural community?
Biosecurity implementation can reduce the chance of introduction and spread of disease, thereby minimizing the impact of disease. Implementation of biosecurity best practices in agricultural activities contributes to maintaining a healthy plant and animal resource base, consumer confidence, public trust, as well as maintaining and accessing new markets and opportunities. Flourishing animal and plant agriculture commodities contribute to supporting or providing the foundation for a healthy transport sector.
Disease and pests can:
- reduce productivity
- reduce the value of animals and products
- reduce domestic consumption
- increase animal health and welfare issues
- increase veterinary and labour costs
- reduce the producers' and transporters' incomes
- close export markets
- negatively impact the environment and human health
1.2.1 Examples of economic impact of commodity specific disease
Disease examples have been provided to emphasize the impact and cost of disease.
1.2.1.1 Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) is a viral disease that infects swine and results in poor reproduction, pneumonia in post-weaned pigs, reduced rate of growth and increased mortality in all age groups. In Canada, it is estimated that PRRS costs the Canadian pork industry in the range of $130 million per yearFootnote 3. Transportation is considered an important risk factor for transferring PRRS infection from farm to farm.
1.2.1.2 Porcine epidemic diarrhea
When introduced into naïve populations, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDv) outbreaks in young pigs can result in mortality rates between 70 and 100%, thereby having a profound effect on the swine sector. In Canada, PEDv was first diagnosed in Ontario in January 2014 and had spread to over 62 farms in the province within six months of the initial detection (Pasma et al., 2016). Cases were also detected in Prince Edward Island, Quebec and Manitoba.
It is estimated that PEDv outbreaks in Canada will cost producers in the range of $243 to $432 per sow, with varying costs depending on management practices (Engele and Whittington, 2014). The recent outbreak of PEDv in the U.S. in its first year (2013–2014) has resulted in loss of more than 10% of total pig population, amounting to approximately seven million piglets. The economic analysis of PEDv outbreak in U.S. has estimated annual losses of $900 million and $1.8 billion for 3% and 6% annual pig loss scenarios, respectively (Paarlberg, 2014).
Various factors, including transportation, have been shown to contribute to the introduction and spread of PEDv. For instance, the surveying of transport units at PEDv contaminated site (e.g. slaughter facilities, assembly yards and auction marts) demonstrated that transport units are at risk of becoming contaminated and spreading PEDv (Yeske et al, 2014; Lowe & Gauger, 2014). To control the spread of PEDv, various governments, industry associations and transporters continue to work together to increase awareness and promote biosecurity.
1.2.1.3 Equine influenza in Australia
In 2007, an equine influenza (EI) outbreak in Australia cost $263 million in government assistance packages and $97.1 million in disease eradication costs (Smyth et al., 2011).
To prevent the disease from spreading throughout Australia, restrictions on horse movements were implemented soon after the disease was confirmed. These movement restrictions lasted eight months and resulted in the cancellation of 261 Standardbred race meetings. This resulted in economic impacts to those who organized and participated in these event, as well as businesses that generate income because of these events (mainly service providers such as catering, hospitality and the transportation industry). The estimated economic impacts for various groups were:
- $23.8 million for the Australian Harness Racing Industry's (includes drivers, trainers, owners, breeders, race clubs and state racing authorities);
- $381 million for households, businesses and horse associations.
1.2.1.4 Avian influenza disease outbreak in 2004
During the avian influenza (AI) outbreak in British Columbia in 2004, 42 commercial poultry farms were infected with the AI virus. In order to stop the spread of the virus, 17 million birds from 125 poultry operations were depopulated (Bowes, 2007). The Government of Canada paid $63.7 million in compensation for birds ordered destroyed (Bowes, 2007).
In addition, the agricultural community sustained a total economic loss of $380.9 million dollars, which included;
- $216.9 million of direct costs to the poultry industry;
- $156 million in economic losses for the poultry service industry (such as truck drivers, live-haulers, catching crews); and
- $7.5 million in one-time losses.
1.2.1.5 Foot-and-mouth disease outbreak in 1952
Canada's last outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) was in 1951–1952 in Saskatchewan. Forty-two premises were involved, of which 29 were infected and 13 were considered in contact. The number of livestock destroyed included: 1,313 cattle, 294 swine, 97 sheep, 1 goat, 2,372 fowl and 15,828 eggs.
The eradication costs totalled $1 million, but owing to the ban on exports, the value of livestock fell by $651 million and $70 million was spent in support prices by the Canadian government. The total loss was $722 million plus one year's loss of trade in livestock and livestock products (Sellers & Daggupaty, 1990).
1.3 Significance of transport
With the availability of efficient transportation and advancements in logistical capacity, animals are transported long distances in relatively short timeframes. During the lifetime of some animals, there may be a high frequency of transport events that occurs. For example:
- Horses are highly mobile; some travel on a weekly basis to areas where they commingle with other horses, cattle and wildlife.
- On average, food producing animals have three to four transport events in their lifetime (Serecon Management Consulting Inc., 2015).
- An approximation of 67 million annual transport events for swine and cattle can be made through extrapolation of the data from the PigTrace Canada and Serecon movement study.
- In 2015, 576,053 swine transportation events resulted in the movement of 43.8 million swine throughout Canada (Canadian Pork Council, 2016, see Table 1)
- In 2014, it was estimated that there were over 20 million beef cattle movements (see Figure 1), approximately 4 million dairy and veal cattle movements, and 1.6 million sheep movements (Serecon Management Consulting Inc., 2015).
This data only represents a fraction of the transport events since it does not include data on the poultry, goat, equine or cervid movements. Considering the number of transport events, and that each event provides an opportunity to spread disease, this highlights the need for the transportation industry to implement biosecurity best practices.
The frequency and complexity in the transportation of animals (as illustrated in Figure 1) and deadstock in Canada emphasizes the importance of maintaining animal identification and administrative reports (trip logs) to enable the monitoring of animal movements over large distances and relatively short periods of time. Maintaining the continuity of animal identification during transport events provides the foundation for tracing disease outbreaks back to the source, as well as identifying animals that may have come in contact with infected animals.
| Origin | Destination | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm | Assembly Yard or Auction | Export | Fair | Lab | Slaughterhouse | Render / Disposal | ||
| Farm | 114,013 | 30,636 | 7,983 | 18 | 302 | 391,597 | 21,993 | 566,542 |
| Assembly Yard or Auction | 571 | 2,107 | 2,814 | 2,191 | 292 | 7,975 | ||
| Import | 38 | 6 | 44 | |||||
| Fair | 5 | 1 | 6 | |||||
| Lab | 108 | 161 | 4 | 82 | 355 | |||
| Slaughterhouse | 162 | 967 | 1,129 | |||||
| Render / Disposal | 2 | 2 | ||||||
| Total | 114,735 | 32,910 | 10,797 | 19 | 302 | 393,954 | 23,336 | 576,053 |

Description of Figure 1
Figure 1: This illustrates the transportation of beef cattle as a percentage of the national herd (10.3 million beef cattle representing 76,515 farms, 2013) to various locations throughout the lifecycle of the animal (Serecon Management Consulting Inc., 2015). The individual ID indicates that the person receiving the animals reported individual identification number on the tags applied to an animal. The group ID indicates that the person receiving the animals reported that they received a group of animals, site of origin and species, without providing individual ID numbers. "Unknown" indicates that the person receiving the animals is not required to report animal movements.
Total number of beef cattle = 10.3 million and total number of beef farms = 76,515 (2013).
- Farm 1 (Individual ID) to Export (Individual ID) = 104 (0.51%)
- Farm 1 (Individual ID) to Slaughter (Individual ID) = 75 (0.37%)
- Farm 1 (Individual ID) to Feedlot (Individual ID) = 585 (2.9%)
- Feedlot (Individual ID) to Slaughter (Individual ID) = 1705 (8.5%)
- Feedlot (Individual ID) to Export (Individual ID) = 701 (3.5%)
- Farm 1 (Individual ID) to Auction (Group ID) = 2565 (13%)
- Auction (Group ID) to Feedlot (Individual ID) = 1683 (8.3%)
- Auction (Group ID) to Auction (Group ID) = 24 (0.12%)
- Auction (Group ID) to Slaughter (Individual ID) = 435 (2.2%)
- Auction (Group ID) to Export (Individual ID) = 103 (0.5%)
- Auction (Group ID) to Dealer (Unknown) = 540 (2.7%)
- Auction (Group ID) to Farm 2 (Unknown) = 1210 (6%)
- Farm 1 (Individual ID) to Pastures (Group ID) = 33030 (15%)
- Pastures (Group ID) to Farm 1 (Individual ID) = 3030 (15%)
- Farm 1 (Individual ID) to Fairs (Individual ID) and back to Farm 1 (Individual ID) = 16 (0.08%)
- Farm 1 (Individual ID) to Dealer (Unknown) = 44 (0.22%)
- Dealer (Unknown) to Auction (Group ID) = 59 (0.3%)
- Farm 1 (Individual ID) direct to Farm 2 - Backgrounder (Unknown) = 756 (3.75%)
- Farm 2 (Unknown) to Export (Individual ID) = 120 (0.6%)
- Farm 2 (Unknown) to Slaughter (Individual ID) = 531 (2.6%)
- Farm 2 (Unknown) to Feedlot (Individual ID) = 140 (0.7%)
- Farm 2 (Unknown) to Auction (Group ID) = 1349 (6.7%)
A percentage of movement between Farm 1 to Feedlot, Feedlot to Slaughter, and Farm 1 to Farm 2 occur through Satellite Auctions.
1.4 How are livestock and poultry diseases introduced and spread during transportation?
There is a tendency for people to place an emphasis on biosecurity when disease has been identified. To minimize the chance of disease introduction, biosecurity should be implemented at all times, including when handling animals that appear healthy. Infected animals do not always show signs of disease; they can appear healthy yet still infect other animals and contaminate equipment, vehicles, hands, clothing, footwear and gloves.
There are two common pathways of disease spread (see Figure 2):
- Direct: Direct transmission to susceptible animals occurs via physical contact with infected animal or carcass (for example; through rubbing, licking, breeding, biting, etc.) or through contact with body fluids (for example; blood, saliva, feces, urine, milk), lesions, aerosols (through coughing, sneezing), and other discharges of infected animal or carcass. This includes livestock or poultry that do not look sick but have the disease and can transfer it to another animal, bird or person (zoonotic diseases);
- Indirect: Indirect transmission involves an intermediate carrier that becomes contaminated and is a source of infection for susceptible animal. The body fluids (for example; blood, saliva, feces, urine, milk,), lesions, aerosols (through coughing, sneezing), etc. from from infected animals or carcasses can contaminate equipment, vehicles, people (including their clothing and footwear), etc. which may subsequently transmit pathogens to susceptible animal who come in their contact.
The pathogens can also be indirectly transmitted through living vectors such as birds, rodents or insects that come in contact with the infected animals or their excretion. Shared feed and water which is contaminated by discharges from infected animals can also indirectly transmit pathogens to healthy animals.
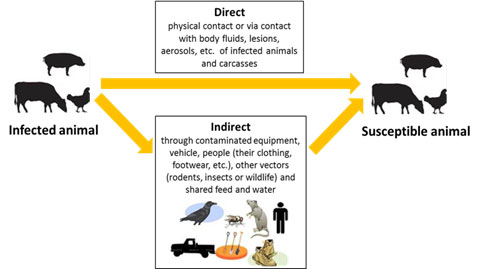
Description of Figure 2
Figure 2: The two common pathways of spread of disease from infected to susceptible animals are: 1) direct transmission from infected to susceptible animals, 2) Indirect transmission through an intermediate carrier.
Spread of disease from infected animal to susceptible animal occur by 1) direct transmission via physical contact or through contact with body fluids, lesions, aerosols of infected animals or carcasses; 2) Indirect transmission occurs through intermediate carriers; for example, vehicles, equipment, people (their clothing, footwear, etc.), other vectors (rodents, insects, or wildlife) and shared feed and water.
The five most common scenarios where disease transmission may occur during a transport event are:
- Loading livestock or poultry into a contaminated transport unit. For example:
- an unwashed or improperly washed transport unit; or
- a transport unit that was contaminated during or following washing.
- Contamination of the transport unit at the premises (either during loading or unloading). For example:
- service personnel vehicles and facility personnel come into contact with the transport unit and/or power unit;
- using or allowing facility equipment to be used inside the transport unit (for example; using a hand barrow, skid steer or tractor from the slaughter facility or farm to remove an injured animal);
- docking the transport unit against a facility; and
- allowing animals that have come into contact with the destination environment (shoots, pens, paddocks) to return to the transport unit during the unloading process.
- Contamination of the premises due to contact with an unclean transport unit/equipment or driver by:
- contact with the premises and with animals that are not to be transported;
- not respecting separation zones or following farm biosecurity protocols; and
- drivers traveling with pets and then entering premises.
- Contamination of the animals in the transport unit at a commingling site. Commingling sites are not just limited to animals—people from farms and other drivers that have been on farms commingle as well, such as at restaurants and truck stops. Additional examples include commingling at:
- a slaughter facility;
- rest stations or areas;
- auctions;
- assembly yards;
- feedlots and transfer docks; and
- events such as competitions and exhibition facilities.
- Animals are exposed to a pathogen due to contact with contaminated personnel or equipment (either during loading or unloading).
- The driver enters the farm or commingling facilities (e.g. offices, restaurants, border customs, slaughter, auction marts, assembly yards) and then enters the power unit and/or animal transport compartment without following biosecurity protocols;
- Other people: Facility personnel (e.g. slaughter, assembly yards, auction marts, catching crews) enter the transport unit and handle animals;
- Contaminated equipment (e.g. handling boards, rattle paddles and shovels, prods, buckets, poultry gates and nets, etc.) are used.
2.0 Transportation of livestock and poultry
This section will focus on biosecurity best practices when transporting live animals. Everyone involved in the transportation of animals or arranging for their transport shares in the responsibility of ensuring the well-being and safety of animals throughout the entire transportation cycle.
2.1 Routine biosecurity measures
The biosecurity measures that are appropriate for a given transportation event should reflect the:
- disease risks associated with transporting animals from or to particular areas or establishments;
- transporters' roles during the transportation phases; and
- logistics, including the availability of biosecurity infrastructure.
The baseline level of biosecurity that's implemented for every transportation event, even in the absence of a client specifying the need for biosecurity, is referred to as the routine biosecurity measures. Routine biosecurity measures are based on basic biosecurity principles. A few examples of basic biosecurity practices are:
- loading animals in clean trailers using clean equipment
- minimizing cross-contamination between trailers and unloading sites or vice versa
- minimizing cross-contamination from clothes and footwear.
Due to variations within the country and between the various commodity groups, it is impractical to define the routine biosecurity measures that would apply to all commodity groups in Canada. It is recommended that transporters refer to the biosecurity best practices in this document and work with industry associations, provincial representatives and veterinarians to establish routine biosecurity measures that are adapted to their specific risks and challenges.
Once routine biosecurity measures are established, transporters are encouraged to share them with their clients and to work with them to ensure that their biosecurity requirements are met. For more information on identifying the client's biosecurity requirements, see section 2.4.1.
2.2 Enhanced biosecurity measures
In situations where disease is suspected or has been identified and there is an increase in risk, then enhanced biosecurity measures are required to prevent disease spread and possibly eradicate the disease from an area. Again, transporters are encouraged to refer to the biosecurity best practices in this document and work with industry associations, provincial governments and veterinarians to establish enhanced biosecurity measures that will address the disease transmission risks.
Examples of enhanced biosecurity measures include:
- designated transport units, equipment and wash facilities for the transportation of diseased animals;
- designated routes that avoid agriculturally dense areas and/or susceptible animal populations;
- specific cleaning and disinfection protocols; and,
- manure and bedding management:
- designated scrape-out locations for conveyances that have transported diseased animals; may be restricted to specific locations that have manure management systems; and
- restrictions for use of the contaminated bedding for other agricultural purposes, such as spreading on fields for fertilizer.
In the event of a reportable, notifiable or disease of economic significance, industry, provincial and/or federal governments will provide specific biosecurity measures for drivers. Biosecurity measures may include movement restrictions and permits.
2.3 Cycle of transportation phases and related activities
The transportation of livestock and poultry is a continuum of activities starting with the completion of one transportation event to the planning and preparing for the next transportation event. For the purposes of this document, this continuum of activities has been described in four separate phases (see Figure 3):
- between loads phase,
- loading phase,
- on the road phase, and
- unloading phase

Description of Figure 3
Figure 3: The relationship between the four phases of transportation: Between Loads, Loading, On the Road, and Unloading. A transportation event can include multiple Loading, On the Road and Unloading phases.
A box in the centre of the diagram with the text, "Multiple loading and unloading sites," has four arrows pointing out to four boxes (above, to the right, below, and to the left). Each box represents a phase of transportation. There are arrows pointing in a clockwise direction between each of the four boxes.
Starting at top of the diagram and moving clockwise, each box contains the following text:
- The between loads phase includes activities following unloading and prior to loading of subsequent load, such as:
- Scraping out
- Cleaning and disinfection of the transport unit and equipment
- Planning for the next transport event (what, where and when)
- The loading phase includes activities to load animals into the transport vehicle, generally on-farm or at an intermediary location, such as:
- Accessing the site
- Entering & exiting the power unit
- Entering the trailer
- Applying bedding & assisting with loading
- Exiting the trailer and re-entering the power unit after handling animals
- The on the road phase includes activities between the point of loading and unloading, such as:
- Selecting a route
- Stops
- Rest stations
- The unloading phase includes activities related to removing animals from the transport unit at destination, such as:
- Accessing the site
- Entering and exiting the power unit
- Entering the trailer
- Exiting the trailer and re-entering the power unit after unloading animals
- Scraping out (at destination)
2.4 Between loads phase
The Between Loads Phase of transportation encompasses the following activities:
- identifying the customer's biosecurity requirements;
- cleaning and disinfection, which includes:
- removal of organic matter; and
- the inactivation of pathogens
- planning and preparing for the transportation event.
2.4.1 Customer's biosecurity requirements
Customers may have biosecurity requirements specific to their risk tolerance, animal production type and business model. These requirements are often in addition to the transporter's routine biosecurity measures. The customer's biosecurity requirements may include but are not limited to:
- use of a transport unit that is designated to transport a specific type of animal with a specified health status;
- a timeframe of non-use (commonly referred to as downtime) after cleaning and disinfecting the trailer;
- the identification of specific truck wash stations to be used;
- the use of specific cleaning and disinfection protocols, including:
- third party validation of cleaning and disinfection;
- provision of a transport unit wash report (see Annex 1: Transport unit wash report);
- specifying the driver's involvement in loading and unloading;
- specifying where to park on the premises and the route, including the driver's stops, and rest stations; and,
- scrape-out location.
A trip information sheet is a tool commonly used by transport companies to communicate customer biosecurity requirements to the driver. A template and an example of a customer's additional biosecurity requirements has been provided in Annex 2a: Trip information sheet and Annex 2b: Trip information sheet example, respectively.
The early identification of the customer's biosecurity requirements allows drivers to ensure that they have the required biosecurity supplies, documentation and equipment for the transportation event.
Biosecurity best practice
- Implement routine biosecurity measures at all times.
- Identify the customer's biosecurity expectations early in the planning phase.
Encourage the uptake and implementation of biosecurity within industry by practicing routine biosecurity measures at all times, even in situations where the customer has not identified any biosecurity requirements. For assistance, refer to the following sections in this document: Why is biosecurity important to your customer (section 1.2) and the Significance of transport (section 1.3).
2.4.2 Cleaning and disinfection
This section describes:
- biosecurity principles for cleaning and disinfection
- biosecurity considerations when choosing a wash station
- storage of transportation units following cleaning and disinfection
- record-keeping for cleaning and disinfection
Biosecurity best practice
- Perform the cleaning and disinfection steps necessary to optimize the reduction or inactivation of pathogens to reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
Protocols and best practices may not apply to all transportation events and are not directly transferrable between the transportation of different classes of animals or within operations that transport multiple species of livestock and poultry. It is recommended that drivers and transport companies consult specialistsFootnote 5 to develop cleaning and disinfection protocols that are specific to the transport unit and the species of animal that is transported.
This section will focus on the general biosecurity principles for cleaning and disinfection. Biosecurity best practices for cleaning and disinfection, as well as cleaning and disinfection example protocols have been provided in the annexes, see:
- Annex 3: Biosecurity best practices for cleaning and disinfection
- Annex 4a: Example of a wash bay protocol for livestock transport units
- Annex 4b: Example of a truck and crate cleaning and disinfection standard operating procedure in a slaughterhouse
- Annex 4c: Example of a cleaning and disinfection protocol for equine trailers at a wash station
2.4.2.1 Biosecurity principles for cleaning and disinfection
Biosecurity protocols may not include all of the cleaning and disinfection steps identified below – ultimately the combination of steps and frequency will be based on the level of risk. The level of risk varies considerably based on a number of factors, such as type and nature of the pathogen(s), species, herd or flock health status. To illustrate the progressive effectiveness of combining process steps, a percentage of pathogen load reduction for each step has been provided. The percentage is based on extrapolated data from existing reference materialFootnote 6.
Removal of organic matter
- Cleaning – involves a dry phase to remove the organic matter (primarily bedding and manure) commonly referred to as "scrape-out", and a wet phase involving a high volume of clean water to flush out organic matter that remains after scraping out. Pressure washing is not recommended to remove the organic matter during the cleaning phase as it tends to scatter the organic matter within the transport unit rather than flush it out. Proper attention to dry cleaning will make the washing step much easier. The combined effort of dry and wet cleaning could result in a seventy-five percent (75%) reduction in pathogen load.
- Washing – involves the application of a solution of clean water and detergent or degreaser at low pressure to disrupt biofilms and loosen organic material on surfaces. After the organic material is thoroughly saturated, continue washing using a low to medium pressure spray of water to dislodge or loosen the biofilm and organic matter; mechanically scrubbing or scraping surfaces with brushes, brooms or scrapers may be required. The effluent (detergent and biofilm) is then removed from the unit using clean water.
Washing is not complete until organic matter has been completely removed from all surfaces. It may be necessary to wash the transport unit several times to remove organic matter. Removal of organic material and detergent residues is important to ensure chemical disinfectants are not inactivated during the disinfection step. Removing all organic matter and using detergent to wash a transport unit has been shown to result in an 80% reduction in pathogen load.
- Visual inspection of all surfaces is completed to ensure that all organic matter has been removed. This is best done when rinsed water is drained away. See Annex 5a: General visual inspection checklist and 5b: Example of a visual inspection form used for swine transport units.
Inactivation of pathogens
Disinfection, drying (natural or thermal assisted) and baking are steps that help to inactivate pathogens.
- Disinfection – most commonly this involves the application of a chemical at a specific concentration for an identified time period. The type of disinfectant will depend on the pathogens of concern. The concentration will depend on the objective of this step. Some of the disinfectants at lower concentrations can be used for cleaning, while a higher concentration is needed to achieve disinfection. Surfaces must be visibly clean, without pooled water and dry (if possible) prior to applying a disinfectant and the disinfectant must stay wet and fully cover the surface for a specific amount of time to achieve the desired pathogen inactivation or reduction. As temperatures drop below 10°C many chemical disinfectants require an increased contact time and concentration to achieve effective disinfection. As temperatures approach 0°C, cleaning and disinfection should be performed in a heated building or using antifreeze agent. Review disinfectant labels, follow the manufacturer's directions and contact the manufacturer if guidance is required. Disinfectants may be applied by different applications (e.g. spraying or foaming). When used properly, applying a disinfectant has been shown to reduce the pathogen load by over 99%.
- Drying involves natural drying or using thermal assisted processes to ensure that all moisture has evaporated from the transport unit. This additional step ensures that pathogens that may have escaped contact with the disinfectant and that are susceptible to desiccation are inactivated.
- Baking, a thermal process used to inactivate pathogens, may be recommended for some pathogens that escape contact with the disinfectant and require high temperatures to be inactivated. It is acknowledged that there are few facilities with this capability in Canada.
Cleaning and disinfection protocols may involve a combination of the disinfection, drying or baking steps for the inactivation of pathogens. The nature of the pathogen, condition of the transport unit, customer's biosecurity requirements and lack of scientific evidence are just some of the reasons that other inactivation steps, in addition to disinfection, may be required. For example, other inactivation methods, such as thermal assisted drying or baking are recommended when:
- damaged equipment (e.g. damaged or frayed rubber matting or docking bumpers) or the design of the trailer or compartment (e.g. open tubing or gaps) prevents surfaces from coming into contact with the disinfectant;.
- conditions do not allow the disinfectant to be applied in accordance with the manufacturer's directions.
2.4.2.2 Biosecurity considerations when choosing a wash station
It is recognized that biosecurity infrastructure, wash station capacity and cleaning and disinfection protocols vary between wash stations. When feasible, incorporate biosecurity criteria when selecting a wash station to ensure that the wash station:
- can achieve the required level of cleaning and disinfection of the transport unit and associated equipment;
- has identified routes for the site that respect segregation of clean transport units from contaminated units in dirty areas; and,
- has protocols in place that minimize the risk of cross-contamination between transport units.
For detailed guidance refer to Annex 6: Biosecurity guidance for choosing a wash station.
Biosecurity best practice
- Incorporate biosecurity criteria when selecting a wash station.
- Choose a wash station that has the infrastructure and capacity to achieve the required level of cleaning and disinfection.
- Choose a wash station that is designed, organized and maintained in a way that ensures that there is no cross-contamination.
The implementation of biosecurity best practices at wash facilities contributes to:
- increasing drivers' capacity to meet their customer's biosecurity requirements;
- minimizing the risk of the wash station being the source of, or contributing to, contamination of the transport unit; and
- the capacity of industry and provincial and federal governments to mitigate the risk of introduction and spread of disease, which assists in the control and eradication of diseases.
2.4.2.3 Storage of transportation units following cleaning and disinfection
Once a transport unit has been cleaned and disinfected it is important to keep it clean prior to loading. Ideally, transport units should be stored in an area that is:
- physically and functionally separate from transport units that have not been cleaned or disinfected.
- away from pets, farm animals, rodents and wildlife.
- away from people, contaminated equipment, feed and bedding.
- away from exhaust fans and dusty areas.
Biosecurity best practice
- Keep transport units clean prior to loading.
2.4.2.4 Record-keeping for cleaning and disinfection
Drivers, transporter companies and wash facilities should maintain up-to-date records for cleaning and disinfection of the transport unit. Good record-keeping and written protocols provide the ability to evaluate, verify and modify biosecurity programs for transportation events over time. See Annex 1 for an example of a transport unit wash report.
2.4.3 Planning and preparing for the transportation event
Factors that will influence the preparation required for the transportation event include:
- number of loading and unloading sites;
- driver's involvement in loading and unloading animals;
- location for scrape-out;
- route;
- driver stops, which may include:
- weigh stations;
- gas stations;
- restaurants; and
- border crossings.
2.4.3.1 Multiple loading sites
From a biosecurity perspective, the ideal transport event includes a single loading and unloading site since the risk of disease contamination and spread increases significantly with each loading and unloading event. It is recognized that this is not always practical or economical. Regardless, drivers and customers should both be aware of the risks and the biosecurity best practices that mitigate the risks associated with multiple loading and unloading sites.
Physically separating animals within the transport unit does not adequately mitigate the risk of infectious disease spread between animals within a trailer. For this reason, the contamination status of the transport unit is reflected by the lowest health status of the animals loaded into the trailer. For multi-loading and unloading sites, the biosecurity best practice is to only load animals that have an equivalent health status.
Biosecurity best practice
- Only load animals that have an equivalent health status.
- Always travel from sites with a higher health status to those with a lower health status
In addition, the risk that the driver and transport unit may become contaminated increases with each loading and unloading event. This in turn increases the risk that the transporter might spread disease at loading and unloading sites. Always travel from sites with a higher health status to those with a lower status. Note that this biosecurity best practice alone offers limited protection. Diseased animals don't always show signs of disease, and customers may not always know or share the disease status of their animals with the driver.
The driver's vigilance in employing the biosecurity best practices throughout the transportation event is crucial in helping prevent disease spread. With the increasing complexity of logistics, likewise there is an increase in the complexity of the biosecurity measures required.
2.4.3.2 Obtain biosecurity equipment and supplies
The amount and type of biosecurity equipment required for a particular transportation event is dependent on the following:
- The number of loading and unloading sites.
- The amount of interaction that the driver will have with the animals, equipment and staff at the loading and unloading sites.
In all cases, it is recommended that the biosecurity equipment contain the supplies required to either clean and disinfect footwear between sites or include at least one pair of footwear (or disposable boot covers – as personal safety considerations allow) and gloves for each loading and unloading site. In situations where the driver will be involved in the loading and handling of animals, the recommendation is that the biosecurity kit include (see Figure 4):
- clean footwear designated to the power unit;
- rubber boots that can be cleaned and disinfected;
- new, freshly laundered cloth or disposable coveralls;
- gloves;
- hat;
- large disposable garbage bags to store used dirty clothing and other reusable items that need to be laundered and cleaned;
- disinfectant and hand sanitizer;
- paper towel; and
- water and wash bucket.
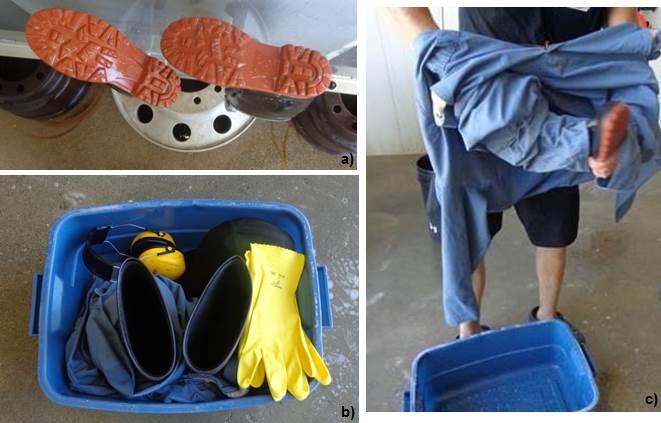

Ensure that the equipment required for the transportation event is either new or has been cleaned and disinfected. Additional equipment may include:
- animal handling equipment such as poultry gates and nets, rattle paddles, shakers and chase boards;
- a shovel for scraping out the trailer following the transportation event; and
- equipment required to secure the load.
Prevent contamination of your equipment by storing clean equipment in a clean location on your transport unit (for example, a tote or plastic bag that can be closed and kept separate from dirty equipment).
2.4.3.3 Documentation related to biosecurity for a transport event
The documentation requirements for any given transportation event will vary depending on the type of movement and the customer's requirements. From a biosecurity perspective, electronic document exchange is preferred over providing customers with hard copies. When hard copies of documents are required they should always be stored in a clean location.
Exports, imports and interprovincial transportation events may require specific documentation and in some situations, the documentation must accompany the load. Examples of the type of documentation required for these types of movements include; import permits, permits to transport or move, animals transfer documents, animal health records and/or export certificates. Ensure that the required documentation has been obtained prior to leaving.
The driver/transporter should have all the relevant documents readily available during transportation. It may include following:
- transport unit wash report (see the example provided in Annex 1: Transport unit wash report)
- trip information sheet (see Annex 2a: Trip information sheet template and Annex 2b: Trip information sheet example)
- verification and validation of wash protocol
- visual inspection after washing (see Annex 5a: General visual inspection checklist and Annex 5b: Example of a visual inspection form used for swine transport units)
Additional documentation that the driver might have to provide includes:
- veterinary certification;
- animal identification (e.g. a tag, tattoo or chip) to allow animal traceability to the premises of departure and, where possible, to the premises of origin;
- details of any animal's condition that may be a risk (e.g. history of disease, stage of pregnancy);
- documentation of the period of location, period of rest, access to water and feed while on the road; and, disclosure of transport history. The following documentation templates are available in:
- Annex 7a: Disclosure of transport history
- Annex 7b: Transport unit travel history
2.4.3.4 Obtain bedding and feed
Bedding can be obtained prior to leaving for the transportation event or at the loading site. Bedding and feed can transport pests such as the cereal leaf beetle. Prior to loading bedding or feed into the transportation unit, ensure that it is clean, free of contaminants and that it is not a risk of introducing plant pests to another area or region. It is recommended that bedding and feed be obtained from a reputable commercial supplier.
Obtain confirmation from the supplier that validates the bedding or feed is dry, free of wildlife droppings and feathers, and was stored in an appropriate pest monitored location.

Cereal leaf beetle
The risk of spreading cereal leaf beetle to western Canada during efforts to provide feed from eastern Canada to animals during the drought in 2004 was significant. The potential introduction of cereal leaf beetle to western Canada threatened trade with the USA of an estimated $500 million in cereal crops annually.
In addition, once obtained from a supplier, it is recommended that bedding be stored in a clean secure area where it does not come into contact with animals (wild animals, rodents, birds or farm animals) and contaminated equipment or personnel.
2.4.3.5 Driver preparation
Drivers can be a source of contamination, especially if they've come into contact with pets, farm animals, wildlife or contaminated equipment. Before leaving for a transportation event, it is recommended that drivers:
- wash and wear freshly laundered clothing;
- wear clean footwear; and
- avoid contact with any animals (including pets) or wildlife.
Do not travel with your personal pets in the power unit. Personal pets are not trained to respect biosecurity requirements; contaminated paws and fur present the same risk as contaminated footwear, hands and clothing.
2.5 Loading phase
The various types of animal containment systems (trailer vs. crates or compartments), as well as the variance in driver involvement in loading, creates challenges in providing biosecurity guidance that will apply to all transport events. It is important to assess the guidance provided and use your judgment to determine whether it applies to a specific transportation event.
The loading phase includes the following activities:
- Accessing the site
- Entering and exiting the power unit
- Preparing the trailer for loading
- Applying the bedding and loading animals
2.5.1 Accessing the site
When accessing the site, always follow the premises biosecurity protocols. Pay attention to instructions (see Figure 6) provided by the customer on how to access the site, where to pick up bedding (if applicable), parking and signing visitors' logs (if applicable).

Description of Figure 6
Figure 6: Two examples of signage indicating that biosecurity is in effect and must be respected.
Two photographs side-by-side. The photo on the left is an octagon shaped sign with the text, "No unauthorized pedestrian or vehicle traffic. Stop. Controlled access zone Biosecurity in effect." The photo on the right is a sign that reads, "Visitors, Please respect farm biosecurity. Please contact the manager before entering. Phone:  . Do not enter property without prior approval. Keep to roadways and laneways."
. Do not enter property without prior approval. Keep to roadways and laneways."
The customer may request additional biosecurity measures prior to accessing the loading site. Examples may include:
- cleaning and disinfecting the back of the transport unit prior to making contact with the loading site; and
- cleaning and disinfecting wheels and wheel wells.
Encourage customers to maintain access routes that are free of manure and/or mud or snow. Organic matter, potentially infected with pathogens can accumulate on wheels, wheel wells and the undercarriage, if access routes are contaminated and not poorly maintained. In circumstances where there are no biosecurity protocols on site, at a minimum you should:
- avoid roadways or laneways contaminated by manure or organic matter.
- drive slowly to minimize dust, manure and/or mud from contaminating the transport unit.
- park in the area designated for loading.
- Avoid parking by exhaust fans and air inlets (if possible).
Caution
Always follow the premises biosecurity protocols when on site.
2.5.2 Entering and exiting the power unit
When entering and exiting the power unit, avoid contaminating the interior via the implementation of biosecurity practices. Pay particular attention to contamination via hands, clothing and footwear. One way to avoid contaminating the interior of the power unit is by wearing clean clothing, having dedicated footwear for the power unit (driving shoes) and by having separate footwear for exiting the power unit. Always wash your hands prior to entering the power unit or use hand sanitizer prior to touching anything in the interior of the power unit. An example of protocol for entering and exiting the power unit and trailer is available in Annex 8.
2.5.3 Preparing the trailer for loading
When preparing the trailer for loading, it is important to minimize the risk of contamination to the interior of the trailer or crates. Consider people, equipment and things required for loading and put in place biosecurity measures to prevent the contamination of the trailer or crates. For example;
- Place crates in a clean area.
- Do not allow potentially contaminated premises or facility staff or equipment to enter the trailer.
- Do not come into contact with animals that are not involved in the transport event.
2.5.4 Entering the trailer
Follow biosecurity best practices when leaving the power unit and entering the trailer to prevent contaminating the inside of the trailer. It is recommended to wear a clean outer layer of clothing, hat, boots and gloves that are dedicated to tasks performed in the trailer. Store clothing, hats, boots and gloves in a clean location (such as a clean tote or bag) to ensure that they do not become contaminated prior to being used.
Clean and sanitize hands prior to entering the trailer and handling animals for loading, as well as prior to re-entering the power unit. Refer to Annex 8 for an example of protocol for entering and exiting the power unit and trailer.
Biosecurity best practice
- When performing tasks in the trailer, wear clean clothing, hat, footwear, gloves and use loading equipment that is dedicated to the trailer.
2.5.5 Applying the bedding and loading animals
Once in the trailer, apply clean bedding to areas where animals will be loaded. If bedding is provided at the loading site, then ensure that the bedding is dry and clean (e.g. free of contaminants or pests, feces and dirt).
During loading:
- follow onsite biosecurity protocols, including complying with restricted access on entry, such as demarcation at loading zones.
- prevent backward movement of livestock or bedding/manure from transport unit when loading.
- avoid contact with the animals that are not associated with the transportation event.
2.5.5.1 Compromised animals
Transporters have the right to refuse to load any animal they deem is compromised or unfit for transport. For a list of conditions, please refer to Transporting unfit or compromised animals.
Compromised animals can only be transported directly to the nearest suitable place where they can receive care or be humanely killed (does not include an assembly center), and special transport conditions must be applied.
Unfit animals can only be transported to a place to receive veterinary care, following a veterinarian recommendation and special transport conditions must be applied.
If there are concerns with loading a compromised or unfit animal, refer to the humane transportation federal regulations (Part XII of the Health of Animals Regulations), the Interpretive Guidance for Regulated Parties and the species specific codes of practice (see Codes of Practice for the Care and Handling of Farm Animals).
2.5.6 Exiting the trailer and re-entering the power unit after handling animals
The exterior layer of clothing, hands (either exposed hands or gloved), hat and footwear (designated boots or boot covers) will be contaminated after having handled animals during loading. Without biosecurity measures, the power unit becomes a commingling site for any bacteria, virus or fungi that you have been exposed to either by handling an animal or by contact with the environment.
Biosecurity best practice
- After having handled animals during loading, remove the outer layer of clothing, hat, footwear and gloves and sanitize hands prior to re-entering the power unit.
The ideal biosecurity practice prior to re-entering the power unit at the conclusion of loading after having handled animals is to remove the outer layer of clothing, footwear, and gloves. If the articles are disposable, check with the customer and, dispose of them onsite if possible. Otherwise, contain the articles in a sealable container such as a garbage bag or tote, prior to loading them into a compartment of the transport unit. Sanitize hands prior to entering the power unit and sanitize all contact points within the power unit once you've entered. Refer to Annex 8 for example of protocols on exiting and entering the power unit and trailer.
2.6 On the road phase
While on the road, there is a risk of introduction and spread of disease if you park in close proximity to other animals that are carrying disease or if disease has been identified on premises in close proximity to the route you are travelling. It is important to keep records to document the route travelled, stops made and animal rest stations. Biosecurity can play an important role in mitigating the risk of disease when:
- selecting a route;
- stopping; and,
- at commingling sites.
2.6.1 Selecting a route
The sequence of pick up or delivery should take into consideration the risk of disease transmission (for example; animals of high health status should be loaded first as not to arrive at such premises with a contaminated transport unit). Loading animals of lower health status when transporting with a higher health status will reduce the health status of the high health animals and may also put them at risk of disease. Loading young animals with older animals may also create a risk of spreading disease to the young animals since they could be less immunocompetent (i.e. they're more likely to become sick if exposed to pathogens).
Biosecurity best practice
- Avoid agriculturally dense areas and areas where disease has been identified.
Where possible, avoid agriculturally dense areas and avoid areas where a disease has been identified, particularly if the disease has been identified in the same type of animals being transported. Various tools are being developed by industry associations and provincial governments to make the agricultural community aware of high risk areas in the event of a disease outbreak.
2.6.2 Stops
Stops can include border crossings, restaurants, gas stations and weigh stations. Stops can be a source of contamination for the driver, transport unit and, if stopped in close proximity to other animals, it could result in the direct transfer of pathogens to the animals being transported. Some commodity sectors have developed specific protocols for various types of stops, for example border crossings (refer to Annex 9: Example of transport boot protocol to follow when entering and exiting the power unit at high-risk stops). The following biosecurity best practices are recommended at all places a driver may stop:
- park as far away as possible from other animal transport units.
- follow biosecurity best practices when entering and exiting the power unit (see section 2.5.2 – Entering and exiting the power unit).
- discourage people from touching or handling the animals being transported.
2.6.3 Rest stations
In some situations, livestock will be unloaded to rest at some point during the transport event. Rest stations can pose a biosecurity risk since these locations may be frequented by animals of unknown health status. In addition, some rest stations have limited capacity and infrastructure to support the implementation of basic biosecurity measures (e.g. no running water, limited effectiveness in cleaning and disinfecting of animal holding areas such as stalls and paddocks).

Plan in advance and consider the site's capacity for mitigating biosecurity risks when choosing rest stations. If possible, identify rest stations that have health status requirements and request information on potential risks such as previous tenants, disease concerns and biosecurity protocols implemented between tenants, including the cleaning and disinfection protocol used in areas where animals will be kept. Ensure that the rest station has a scrape-out site available.
At commingling sites, give biosecurity consideration to other vehicles, access pathways, the ground type and conditions, equipment, other animals and people. At rest stations, follow additional biosecurity practices to those recommended for stops (see section 2.6.2):
- avoid sharing or using communal equipment (such as shovels, buckets for feed or water, pitch forks, ropes) available for use on site, or clean and disinfect equipment prior to use.
- keep animals segregated from animals of unknown or lower disease status.
- unload and keep your animals in an area that has been cleaned and disinfected.
2.7 Unloading phase
The driver is responsible for the animals until they are unloaded at the destination. The following biosecurity best practices, previously identified in the section on loading (see section 2.5), also apply to unloading:
- Accessing the site
- Entering and exiting the power unit
- Entering the trailer
- Exiting the trailer and re-entering the power unit after unloading animals.
During unloading:
- follow onsite biosecurity protocols (refer to unloading biosecurity requirements recorded in Annex 2a: Trip information sheet), including complying with restricted access on entry, such as demarcation at unloading zones.
- prevent backward movement of livestock, bedding and manure back into transport unit when unloading.
For livestock, the driver may need to unload animals that are injured, sick or dead at destination. If specialized equipment is required to remove these animals, attempt to clean and disinfect them as much as possible prior to use in your conveyance.
The perception that biosecurity requirements are not needed for animals being transported to a final life cycle destination, such as a slaughter facility, is short-sighted. The risk of transmitting pathogens associated with the transport event is equivalent to other commingling locations or even higher. The slaughter establishment and equipment has the potential to be a source of contamination for transport units, drivers and equipment that will be used to move healthy animals.
2.7.1 Scraping out at destination
From a biosecurity perspective, the biosecurity best practice includes scraping out at the unloading site because it:
- allows bedding and manure to be removed following unloading;
- eliminates the need for the driver to go to an additional location just to scrape-out.
Cleaning and disinfection following scrape-out is highly recommended since scrape-out locations can serve as important contamination points.
For biosecurity best practices during scrape-out, refer to Annex 3.1 – Scrape-out.
3.0 Transport of deadstock and rendered material
This section will provide biosecurity guidance that specifically applies to the transportation of deadstock throughout the four phases of transportation (between loads, loading, on the road, and unloading). Many of the biosecurity best practices that are highlighted in section 2 will also apply to this section. In the interest of avoiding redundancies, the reader will be referred to specific sub-sections of section 2 Transport of livestock and poultry when appropriate.
Biosecurity is important when transporting deadstock because deadstock can remain infectious long after an animal has died, and contact with deadstock, their bodily fluids and secretions may transmit pathogens to live animals. Once decomposition begins, liquefied tissues and bodily fluids escape from the body, these fluids, which may be infectious, can be difficult to contain and can easily contaminate the environment, drivers, equipment and the transport unit.
Consider all deadstock pick-up sites as potential source of infection.
These sites are considered high risk whether it is a pile next to a production unit, slaughter facility, salvaging facility or approved provincial or municipal collection site. Deadstock transport units, associated equipment and drivers pose a biosecurity risk to live animal production. For this reason, to mitigate biosecurity risks associated with deadstock collection, it is recommended that deadstock pick-up sites be located away from production sites and have physical barriers and biosecurity protocols.
Ideally, but practically or economically unviable, deadstock transportation events would include a single loading and unloading event. Typically, it is more economically feasible for deadstock transportation events to include several loading locations in one transport event (e.g. multiple farms, slaughter establishments, salvaging facility or other approved provincial or municipal collection sites).
Some provinces and municipalities have legislative requirements associated with the handling and transportation of deadstock to address environmental considerations and social and biosecurity concerns. Deadstock trasnporters are responsible for making sure that they are aware of and are in compliance with these legislative requirements. Since the objective of this document is to provide biosecurity guidance, environmental considerations, public trust and legislative requirements associated with the transportation of deadstock will not be addressed in this section.
Note: There are federal rules governing the transport of cattle (or other bovine animal) from which Specified Risk Material (SRM) has not been removed. SRM refers to certain cattle tissues capable of transmitting bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE). For information regarding SRM permits, refer to the Canadian Food Inspection Agency website.
3.1 Risks associated with deadstock transportation
The three biosecurity risks associated with deadstock transportation include:
- contamination of the driver or transport unit during the loading and unloading phase;
- contamination of the production site or premises by the driver or transport unit during the loading and unloading phase; and,
- contamination of the environment when on the road and between loads phases.
In situations where disease is suspected or has been identified and there is an increase in risk, then enhanced biosecurity measures are required to be adopted by the deadstock transporters. The deadstock transporters are encouraged to refer to the biosecurity best practices in this document and work with industry associations, provincial governments and veterinarians to establish enhanced biosecurity measures that will address the disease transmission risks. Examples of enhanced biosecurity measures include:
- designated transport units, equipment and wash facilities for the transportation of deadstock from infected premises;
- designated routes that avoid agriculturally dense areas and/or susceptible animal populations; and
- specific cleaning and disinfection protocols.
3.2 Transport unit design
The transport unit design and construction can help mitigate the biosecurity risks associated with the transportation of deadstock. It is recommended that deadstock transport units (includes the power unit, trailers, containers and loading equipment) be:
- designed in a manner that allows for cleaning and disinfection (including the wheel wells, undercarriage etc.); and
- constructed from materials that can withstand repeated cleaning and disinfection.
It is also recommended that trailers and containers used to transport deadstock be:
- contained – leak- and spill-proof; and
- covered or closed to prevent access by scavengers.
Biosecurity best practice
- The deadstock transport unit is designed and maintained to contain carcasses and fluid.
- The transport unit and associated equipment can be cleaned and disinfected.
3.3 Between Loads Phase
The between loads phase of a transportation event includes the following:
- Cleaning and disinfecting the transport unit following the previous transportation event;
- Planning for the next transportation event:
- identifying pick-up and drop-off locations;
- considering the biosecurity protocols of customers;
- identifying and assessing biosecurity risks;
- planning your route;
- ensuring that you have required supplies for the next transportation event.
3.3.1 Cleaning and disinfecting the transport unit following the previous transportation event
After unloading at destination (licensed disposal facility or authorized site), it is recommended that the transport unit and associated equipment be cleaned and disinfected. Ensure that the disinfectant that is used will be effective in inactivating potential pathogen(s). The cleaning and disinfection process includes:
- removing or taking apart equipment (e.g. hoses and chains) so that they can be cleaned and disinfected;
- disposing of any equipment that may have been exposed to contaminants and can't be cleaned and disinfected;
- cleaning the transport unit to remove all loose organic matter and then washing it using a detergent;
- inspecting the transport unit and associated equipment to ensure organic matter has been completely removed following the cleaning step; and,
- applying a disinfectant at the right concentration and contact time. Follow manufacturer's instructions when storing, mixing and applying disinfectants.
For more information, refer to the subsection 2.4.2 Cleaning and disinfection.
Biosecurity best practice
- The transport unit and equipment must be completely cleaned and disinfected following each transportation event (i.e. at the completion of the route and unloading of the deadstock).
3.3.2 Planning for the next transportation event
When planning for the next transportation event, consider the customer's biosecurity protocol. For new customers, discuss biosecurity and obtain their deadstock protocols. Consider the following:
- cause of death (if known) and any medical treatment.
- the location of deadstock, specifically whether the deadstock are located:
- within an animal holding facility;
- next to an animal holding facility; or
- away from animal holding facilities.
- the customer's biosecurity protocols; such as
- the use of dedicated access routes.
- whether access pathways are clean and kept free of mud, manure and other organic matter.
- whether the driver is required to handle the deadstock and/or remove them from the production area.
- the level of decomposition of the animals (fresh dead vs. in decomposition)
- whether the deadstock are stored in a leak-proof container.
Recognizing that a lot of the logistics are dependent on the economics of deadstock collection, consider biosecurity risks when planning your route. Typically it is preferable to either dedicate a trip to collect high risk deadstock or to collect them last. High-risk deadstock includes those:
- that may have succumbed to an infectious disease; and
- from a premises identified as infected by industry and/or provincial or federal authorities.
In addition, when there's a greater likelihood that the transport unit or driver will become contaminated during loading then the recommendation is to collect deadstock from that site last so that you don't risk contaminating the next collection sites. These situations include those where;
- access pathways are contaminated with manure and other organic matter; and
- the deadstock are fresh dead vs. in decomposition and cannot easily be loaded into the transport unit (i.e. the deadstock are not stored in a contained bin).
In situations where the driver or transport unit could pose a risk of contaminating the production site, the recommendation is to dedicate a trip to the collection of deadstock from that site or go to that site last. An example would be when the driver must enter the production site to remove deadstock. Although it is recommended that the driver not enter animal holding sites to limit their exposure to contaminated material and prevent contamination of production sites; it is recognized that it may be required in situations where not all customers will have the equipment required to remove deadstock from their facility.
If the driver is required to handle deadstock, then it is recommended that they bring the following for each site:
- a disposable outer layer of clothing or one that can be cleaned and disinfected;
- disposable gloves;
- hats; and,
- boot covers and/or boots that can be cleaned and disinfected prior to re-entering the transport unit.
If handling of deadstock by the driver is not required, then it is recommended that they bring:
- disposable gloves; and,
- boot covers and/or boots that can be cleaned and disinfected prior to re-entering the transport unit.
Store clothing, hats, boots and gloves in a clean location (such as a clean tote or bag) to ensure that they do not become contaminated prior to being used.
3.4 Loading Phase
The customer has a role in deadstock management prior to collection, which can significantly impact the biosecurity consideration for the driver, including:
- timely deadstock removal before the carcasses reach an advanced state of decomposition;
- type and condition of deadstock storage:
- secure from scavengers;
- leak-proof;
- ease of loading from contained unit.
- ensure location of deadstock storage:
- is situated away from production sites;
- has dedicated clean access and egress pathways for the deadstock transport unit; and
- has dedicated pathways for equipment and staff associated with the production site.
3.4.1 Accessing the deadstock collection site
When accessing the deadstock collection site, always follow the premises biosecurity protocols. Refer to biosecurity best practices outlined in the subsection 2.5.1 – Accessing the site.
3.4.2 Entering and exiting the power unit
When entering and exiting the power unit, the driver should follow biosecurity best practices to avoid contaminating the interior of the power unit. Refer to the biosecurity guidance outlined in the subsection 2.5.2 – Entering and exiting the power unit.
3.4.3 Loading deadstock into the transport unit
The biosecurity best practices that apply to a particular deadstock loading event depend on the level of handling required by the driver and whether they need to enter the animal holding sites to remove deadstock.
Biosecurity best practice
- Deadstock collection sites are situated away from animal holding sites.
- Minimize the driver's contact with the production site by collecting animals at a location that is away from the production unit.
The biosecurity best practice is to load deadstock from an area situated away from live animal holding facilities to prevent their contamination. It is recommended that staff from the animal holding facility remove deadstock from the production site and place at a designated location for pick up. This limits the driver's contact with the production site.
In situations where the driver must enter an animal production unit to remove a carcass then the biosecurity best practice is to wear a clean outer layer of clothing, hat, boots and gloves that are dedicated to tasks performed at the loading site.
Biosecurity best practice
- Contamination of the exterior of the transport unit and loading site is minimized and managed during loading.
If there is contamination to the exterior of the transport unit, then it is recommended that the deadstock transporter:
- moves the transport unit to an area away from the production facility and any pathways leading to or from the production facility;
- sprays the exterior of the transport unit and any exposed equipment with a disinfectant;
- uses a brush to remove any visible organic matter and respray those areas with the disinfectant; and,
- inspects the exterior of the transport unit and equipment to ensure it has been cleaned.
In a situation where the contamination is extensive, abort the route and go directly to your destination.
3.5 On the Road Phase
While on the road, be observant of any spillage or leaks. If you observe leaks, then stop and take appropriate corrective action to stop the leak. It is recommended that transporters carry a spill kit to contain and manage any accidental spills. From a biosecurity prospective, include the following in your spill kit:
- personal protective equipment (e.g. disposable coverall, eye protection, footwear, gloves, etc.);
- absorbent material (absorbent clay, fine sand, sawdust), liquid containment tubes, disinfectant and disinfectant sprayer;
- shovel and broom;
- disposal bags;
- duct tape; and
- a list of emergency contact information in the event of a large spill.
It is recommended that the spill kit be stored in a container with a lid and that its contents be checked regularly to ensure adequate supplies and expiration dates for the kit components.
3.5.1 Stops
Stops should be minimized and avoided when possible due to the high risk associated with transporting deadstock and rendering materials. Good planning can avoid the need to stop at restaurants and gas stations. If stops cannot be avoided:
- park as far away as possible from live animal transport units;
- avoid parking on gravel or loose surfaces;
- park on hard surface that can be decontaminated if leakage of fluids occurs; and,
- follow the entering and exiting the power unit biosecurity guidance outlined in section 2.5.2.
3.6 Unloading Phase
When accessing the unloading site follow any biosecurity requirements in place at the site. In addition:
- drive slowly upon arrival to limit the amount of debris that can contaminate the undercarriage and wheel wells;
- it is recommended that the driver work with someone on site to avoid having to handle the deadstock during unloading. If this is not possible, then personal protective clothing needs to be worn during unloading and disposed of prior to re-entering the power unit; and,
- unload the deadstock in such a way that prevents contamination of the exterior of the transport unit as much as possible.
If the driver needs to get out of the transport unit, then it is recommended that they wear:
- footwear that can easily be cleaned and disinfected (for example, rubber boots); and,
- an outer layer that can be taken off before re-entering the transport unit.
Biosecurity best practice
- Any disposable personal protective equipment such as boot covers, coveralls and gloves are disposed of on site.
Prior to leaving the site and/or commencing another deadstock pick-up route, it is recommended that the deadstock transport unit be cleaned and disinfected on site. If this is not possible, then it should be cleaned and disinfected at the earliest opportunity in a suitable facility.
Prior to leaving the site:
- place all potentially contaminated disposable boot covers and outer layers in a sealed bag and dispose of them on site; and,
- place cleaning brushes in a contained tote or bag that can be sealed prior to disposal.
4.0 Glossary
- Animal holding facility:
-
Any premises where live animals are kept for production (e.g. farms, feedlots).
- Best practices:
-
For this document, a best practice is a program, process, strategy, or activity that has been shown to be most effective in preventing and controlling disease. Best practices may have to be modified before implementation to accommodate a specific farm or facility and enhance practicality.
- Between Loads Phase:
-
Commences after the animals are unloaded and is completed when animals are loaded for the next transportation event. If the removal of organic matter (scrape-out) was not conducted at the destination, it may become a requirement during this phase.
- Biofilm:
-
A thin layer of microorganisms adhering to the surface of a structure, which may be organic or inorganic.
- Biosecurity:
-
Procedures and physical measures designed to reduce the risk of introduction, establishment and spread of animal or plant diseases, infections or infestations to, from and within a population.
- Cleaning:
-
A practice of removing visible organic matter. Cleaning is often considered a two-step process; dry cleaning by scraping out the transport unit followed by a wet cleaning with water.
- Disease:
-
A change from the normal state. A deviation or disruption in the structure or function of a tissue, organ or part of a living animal's body.
- Disinfection:
-
The process that is used to inactivate, decrease or eliminate pathogens from a surface or object.
- Downtime:
-
The period of time that a piece of equipment has not been used, usually after having been cleaned and disinfected.
- Health status:
-
Current state of health of the animal or herd, including both its condition and the presence of pathogens in the animal or herd. Information used to establish the health status includes the disease history and the results of any diagnostic testing, herd health management practices, vaccination and deworming protocols in sufficient detail to determine compatibility with the resident herd, and housing and movement detail sufficient to identify any potential recent disease exposure.
- Infection:
-
The invasion and multiplication or reproduction of pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites in the tissues of a living animal.
- Infectious disease:
-
Disease caused by pathogens (e.g. parasites, bacteria, viruses, fungi or prions).
- Livestock:
-
Includes animals of the bovine, caprine, equine, ovine and porcine species.
- Pathogens:
-
Biological agents, such as bacteria, virus, fungi, parasites or other microorganisms, which have the potential to cause diseases.
- Personnel:
-
Staff, owners, and operators and their family members.
- Pests:
-
Includes insects, birds and vermin (including mice, rats).
- Poultry:
-
All birds reared or kept in captivity for breeding, the production of eggs or meat for consumption, for production of other commercial products, for restocking supplies of game birds, or for breeding these categories of birds.
- Power unit:
-
Refers to the motorized component of the transport unit.
- Protocol:
-
A defined and documented procedure to be followed, detailing the steps to follow to meet an objective.
- Risk:
-
The likelihood of an unfavorable event occurring and affecting health.
- Susceptible animal:
-
An animal that lacks the immunity or ability to resist the invasion of pathogens which then multiply or reproduce resulting in infection.
- Transport unit:
-
Includes the power unit (or tractor) and trailer.
- Washing:
-
A practice of removing remaining organic matter after cleaning. Washing may involve application of low or medium pressure water, degreaser or detergent and if needed, scrubbing to disrupt biofilms and loosen organic material.
- Wash station:
-
Refers to any facility where transport units are cleaned and disinfected.
- Zoonotic diseases:
-
Diseases and infections that are naturally transmitted between vertebrate animals and humans (e.g. rabies, anthrax).
Annex 1: Transport unit wash report
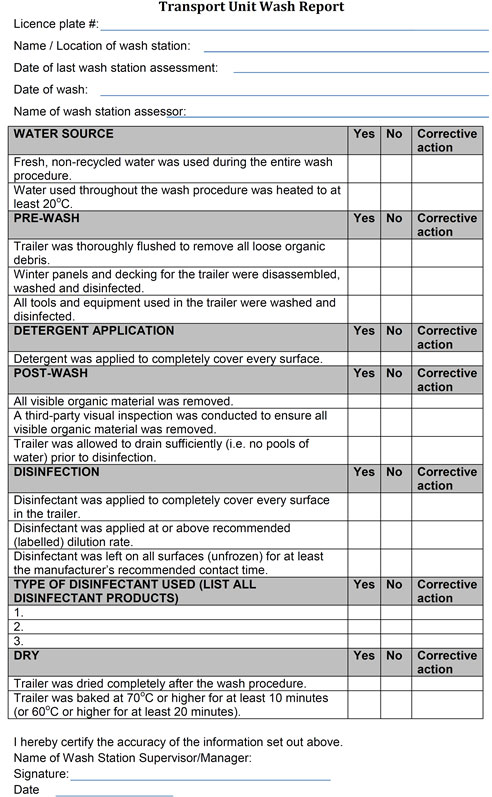
Description of image – Annex 1: Transport unit wash report
The Transport unit wash report contains fields to collect the following information:
- Licence plate #
- Name / Location of wash station
- Date of last wash station assessment
- Date of wash
- Name of wash station assessor
The report allows you to select yes, no or corrective action for a number of options found under headings as follows:
- Water source
- Fresh, non-recycled water was used during the entire wash procedure.
- Water used throughout the wash procedure was heated to at least 20°C.
- Pre-wash
- Trailer was thoroughly flushed to remove all loose organic debris.
- Winter panels and decking for the trailer were disassembled, washed and disinfected.
- All tools and equipment used in the trailer were washed and disinfected.
- Detergent application
- Detergent was applied to completely cover every surface.
- Post-wash
- All visible organic material was removed.
- A third-party visual inspection was conducted to ensure all visible organic material was removed.
- Trailer was allowed to drain sufficiently (i.e. no pools of water) prior to disinfection.
- Disinfection
- Disinfectant was applied to completely cover every surface in the trailer.
- Disinfectant was applied at or above recommended (labelled) dilution rate.
- Disinfectant was left on all surfaces (unfrozen) for at least the manufacturer's recommended contact time.
- Type of disinfectant used (list all disinfectant products)
- Dry
- Trailer was dried completely after the wash procedure.
- Trailer was baked at 70°C or higher for at least 10 minutes (or 60°C or higher for at least 20 minutes).
The bottom of the report includes the following:
I hereby certify the accuracy of the information set out above.
Name of Wash Station Supervisor/Manager:
Signature:
Date
Annex 2a: Trip information sheet
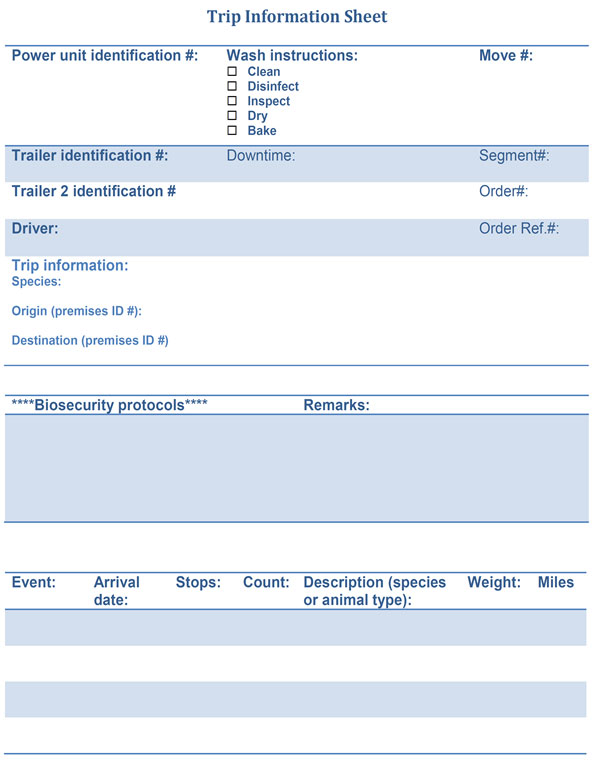
Description of image – Annex 2a: Trip information sheet
The Trip information sheet contains fields to collect the following information:
- Power unit identification #
- Wash instructions:
- Clean
- Disinfect
- Inspect
- Dry
- Bake
- Move #
- Trailer identification #
- Downtime:
- Segment#
- Trailer 2 identification #
- Order#
- Driver
- Order Ref.#
- Trip information:
- Species
- Origin (premises ID #)
- Destination (premises ID #)
- Biosecurity protocols
- Remarks
- Event
- Arrival date
- Stops
- Count
- Description (species or animal type)
- Weight
- Miles
Annex 2b: Trip information sheet example
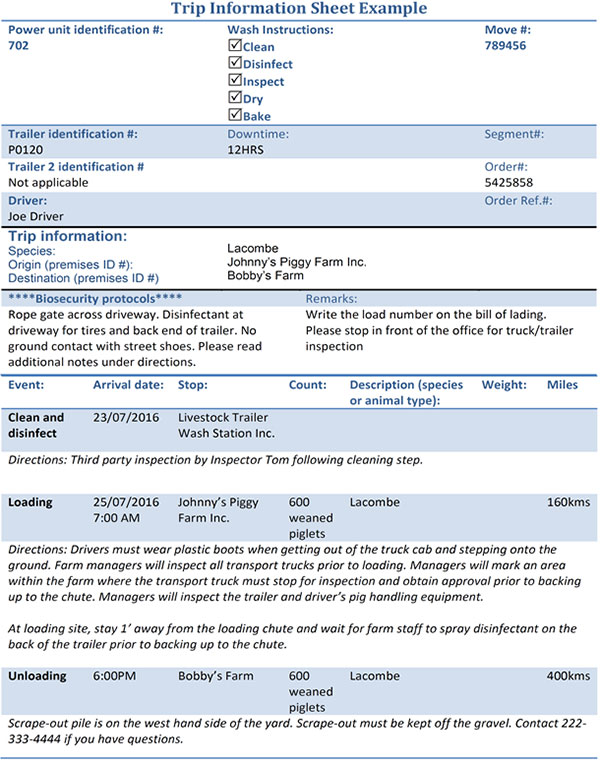
Description of image – Annex 2b: Trip information sheet example
The Trip information sheet example shows the completed sheet as follows:
- Power unit identification #: 702
- Wash instructions, with the following boxes checked:
- Clean
- Disinfect
- Inspect
- Dry
- Bake
- Move #: 789456
- Trailer identification #: P0120
- Downtime: 12 hours
- Segment#: blank
- Trailer 2 identification #: Not applicable
- Order#: 5425858
- Driver: Joe Driver
- Order Ref.#: blank
- Trip information:
- Species: Lacombe
- Origin (premises ID #): Johnny's Piggy Farm Inc.
- Destination (premises ID #): Bobby's Farm
- Biosecurity protocols: Rope gate across driveway. Disinfectant at driveway for tires and back end of trailer. No ground contact with street shoes. Please read additional notes under directions.
- Remarks: Write the load number on the bill of lading. Please stop in front of the office for truck/trailer inspection
- Event: Clean and disinfect
- Arrival date: 23/07/2016
- Stops: Livestock Trailer Wash Station Inc.
- Count: blank
- Description (species or animal type): blank
- Weight: blank
- Miles: blank
- Directions: Third party inspection by Inspector Tom following cleaning step.
- Event: Loading
- Arrival date: 23/07/2016 7:00 AM
- Stops: Johnny's Piggy Farm Inc.
- Count: 600 weaned piglets
- Description (species): Lacombe
- Weight: blank
- Miles: 160kms
- Directions: Drivers must wear plastic boots when getting out of the truck cab and stepping onto the ground. Farm managers will inspect all transport trucks prior to loading. Managers will mark an area within the farm where the transport truck must stop for inspection and obtain approval prior to backing up to the chute. Managers will inspect the trailer and driver's pig handling equipment.
At loading site, stay 1' away from the loading chute and wait for farm staff to spray disinfectant on the back of the trailer prior to backing up to the chute.
- Event: Unloading
- Arrival date: 6:00PM
- Stops: Bobby's Farm
- Count: 600 weaned piglets
- Description (species): Lacombe
- Weight: blank
- Miles: 400kms
- Scrape-out pile is on the west hand side of the yard. Scrape-out must be kept off the gravel. Contact 222-333-4444 if you have questions.
Annex 3: Biosecurity best practices for cleaning and disinfection
This section provides guidance and identifies the biosecurity best practices when:
- scraping out
- choosing a wash station
- cleaning and disinfection
- keeping records of biosecurity protocol
3.1 Scrape-out
Scrape-out, a part of the dry cleaning step, is the first step of cleaning and disinfection. Scrape-out locations are areas that can be a high-risk source of contamination for the transport unit and driver, they may be accessible to all types of transportation units and contain scrape-out material from animal populations of varying disease statuses.
Scrape-out of the transport unit is important because:
- it minimizes the risk of spreading disease that may be present in the manure, bedding and other secretions left in the transport unit.
- it is easier to remove organic matter that is stuck to the surfaces of the transport unit when loose material has been removed first.
- many commercial wash stations will not allow vehicles with livestock or poultry manure into their facilities.
Whenever possible, scrape-out:
- At destination following unloading to minimize the risk of spreading disease.
- As soon as possible at a designated scrape-out site because it's difficult to remove manure once it has dried or is frozen to the transport unit.
Prevent contamination of the power unit and transportation unit by following the biosecurity guidance outlined in subsection 2.5.2 – Entering and exiting the power unit.
Drivers should consider the following when choosing or going to a scrape-out location:
- the scrape-out location complies with provincial and municipal environmental legislation.
- avoid driving through potential sources of contamination. For example:
- avoid driving through used bedding, manure, standing water or mud.
- drive slowly when accessing the scrape-out location to prevent the undercarriage of the transport unit from being contaminated.
When scraping out:
- remove deck planks and knock off all manure and bedding.
- remove crates and cages.
- remove the bulk of the organic materials using a shovel while following a systematic process.
- work from top to bottom and front to back.
- remove bags of unused bedding and store them in a location far from clean vehicles and livestock.
3.2 Prepare the transport unit for washing
The pre-wash preparation focuses on taking apart and removing all of the pieces and equipment that are washed and disinfected independently of the main trailer.
Remove:
- All objects from the trailer and storage compartments (clothing, boots, tools, equipment, shovels and handling tools)
- Remove winter panels
- Decking
- Crates or cages
- Dollies
- Rubber mats
For poultry trailers, open up curtainsFootnote 7.
Transport units and equipment associated with the transportation of animals should be made of, or covered with materials that can withstand repeated cleaning and disinfection. Damaged areas of the transport unit or areas constructed of permeable material should be replaced or repaired to facilitate cleaning and disinfection. If replacement is not possible, then additional inactivation steps such as thermal assisted drying or baking may are recommended.
3.3 Pre-wash rinse
Following scrape-out, smaller loose organic matter will still be present in the trailer. To effectively wash the transport unit, it is essential to first rinse the unit to flush out all loose organic matter. The removal of organic matter during the rinse step will improve the effectiveness of the detergent or degreaser applied during the wash step.
Biosecurity best practice
- Use clean water.
- Before applying a detergent or degreaser, remove loose organic matter using a low-pressure and high-volume flush.
- On vertical or sloped surfaces, always rinse from top to bottom.
Caution
The use of a high pressure washer during the rinse step is not recommended since it tends to spread particles rather than flush them out.
When rinsing the transport unit, it is recommended to:
- use clean water – water that does not contribute to the level of contamination or pathogen load.
- keep the transport unit on a slight incline (e.g. 2%) to allow water and organic matter to flow out of the back of trailer during the rinse step.
- use a high volume hose, rinse the exterior and interior of the trailer with clean water to remove any remaining organic material.
- rinse the transport unit in a way that prevents the re-introduction of organic material from areas that have already been cleaned (see Figure 8). Always work from the:
- exterior to the interior of the transport unit;
- top to the bottom.
- front to the back; and
- rinse the floor around the transport unit and the hose to prevent organic matter from being re-introduced into the transport unit during the inspection and disinfection steps.
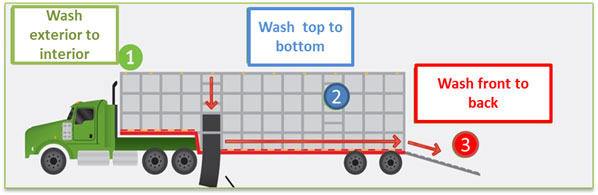
3.4 Washing
The presence of a biofilm and organic matter impedes the effectiveness of the disinfectant. The use of a detergent or degreaser helps remove organic matter and disrupts any biofilms present in the transport unit. Always follow manufacturer's instructions when using a detergent. For guidance on selecting an appropriate detergent and disinfectant combination, consult a specialist; this could be a veterinarian, product representative, agricultural technical specialist and/or an industry associations. When selecting a detergent or degreaser, it is often a balance between capacity, compatibility, cost and corrosiveness of long-term repeated use.
The application of a detergent or degreaser is most effective when the bulk of organic material has been removed during scrape-out and rinsing. Washing is not complete until all organic matter has been completely removed from the transport unit. It may be necessary to wash the transport unit several times to remove all organic matter.
When washing a transport unit always:
- follow the manufacturer's instructions when preparing and using the detergent or degreaser.
- ensure that you are using the recommended concentration and that the water is within the recommended temperature range.
- apply the detergent or degreaser and;
- ensure that all surfaces have been covered;
- work from the outside to the inside;
- on vertical or sloped surfaces, work from bottom to top (see Figure 8 and 9) and front to back
- use low to medium water pressure and/or brush to loosen any remaining organic material.
- If compatible with the detergent or degreaser, use a suitable anti-freezing agent to minimize the risk of freezing.
- wash the undercarriage and wheels to remove organic material.

3.5 Post-wash rinse
If loose, visible organic material is still present in the transport unit following the wash step, then an additional rinse step using a high volume (low pressure) hose is recommended to flush out the remaining organic matter (see Pre-wash rinse – subsection 3.3).
3.6 Inspect
Disinfection is only effective when organic matter has been completely removed from the transport unit. Prior to disinfection, always inspect the transport unit to ensure that all organic matter has been removed. If organic matter is noticed during the inspection step then repeat the washing step. In addition, ensure that there is no pooling of water in the transport unit since pooled water will reduce the effectiveness of the disinfectant. Washing the transport unit on a slight incline (e.g. 2%) will help ensure that there's no pooling of water.
Biosecurity best practice
- Inspect the transport unit prior to starting disinfection to ensure that all organic matter has been removed.
- Repeat the wash step if organic matter is still present.
During inspection:
- ensure that the person doing the inspection is wearing clean clothes and footwear.
- ensure the trailer is well lit.
- use a spot light for low light areas within the trailer (see Figure 10), for examples for corners, cracks, storage compartments, inside of an open tubes, etc.

- move gates or doors so that all areas are visible.
- inspect any items that were washed separately from the transport unit such as deck planks, crates, dollies, rubber mats, curtains, cages, dividers etc.
- use a visual inspection checklist to ensure that no areas are missed (refer to Annex 5a for the general visual inspection checklist and Annex 5b for an example of a visual inspection form used for swine transport unit).
3.7 Disinfection
The consultation to identify the detergent should include the identification of a disinfectant. There are several considerations when selecting a disinfectant:
- effective against pathogens of concern (viruses, bacteria or fungi) that may cause disease in the type of animals transported;
- ability to significantly reduce the pathogen load or inactivate 99.9 % of the pathogens;
- cost;
- corrosiveness of long term repeated use;
- outside temperature;
- effective on the surface materials present;
- personal protective equipment required to use the disinfectant;
- safe for humans, animals and the environment;
- management of effluent from the disinfection step;
- application type (see Table 2).
| Types of applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Foaming | High efficiency – less product is required to cover greater surface areas Achieves sufficiently longer contact time (adheres) Complete coverage can be easily seen |
Requires specialized equipment (foamer) |
| Spraying | Does not require specialized equipment. | May require multiple application to achieve (wet) contact time |
| Fogging | Ensures that the disinfectant reaches all areas | Requires special equipment and infrastructure |
Ensure that the transport unit surfaces are visibly clean, without pooled water and dry (if possible) prior to applying a disinfectant. Once a disinfectant has been selected, follow the manufacturer's instructions to ensure that you are using the manufacturer's recommended water temperature, concentration, amount and contact time.
Concentration is the amount of disinfectant per litre of water. Disinfectants can be mixed by hand or using equipment. If equipment is used to prepare the disinfectant, then it must be maintained and calibrated on a regular basis as per the manufacturer's direction. For some disinfectants the efficacy is progressively reduced once they are diluted or mixed, therefore it is important dilute or mix immediately prior to use.
When applying the disinfectant it is important to apply enough to completely cover all surface areas. Always apply disinfectants systematically to ensure that no surfaces have been missed. The advantage with coloured or foaming disinfectants is that it's visually apparent when surfaces have been covered.
Contact time is the length of time a disinfectant must remain wet on a surface in order to be effective. Various factors (type of surface, application method, humidity, air flow and temperature) can drastically affect the evaporation rate. It may be necessary to reapply the disinfectant multiple times in order to obtain the recommended contact time. Foaming disinfectants that adhere to surfaces are more likely to remain wet and achieve the recommended contact time when compared to spraying.
Biosecurity best practice
- Antifreeze agent must be safe for animals, people and the environment.
Cold weather conditions (temperatures below 0° Celsius), result in most disinfectants freezing. Once a disinfectant freezes it is not possible to achieve the recommended concentration and contact time to effectively reduce the pathogen load or inactivation of pathogens. To use liquid disinfectants in freezing temperatures, an antifreeze agent is needed to prevent the liquid from freezing. The amount of antifreeze agent to be mixed with disinfectant may depend on the environment temperature and affect the contact time (see Table 3).Several compounds are classified as antifreeze agents for example; methanol (MeOH), calcium chloride (CaCl2), ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, some agents have pathogen inactivation capacities. The antifreeze agent must be safe for humans, animals and the environment.
Propylene glycol is most commonly used since it does not impact the efficacy of most disinfectants. Consult a disinfectant product representative to identify compatible antifreeze agents, concentrate level, dilution, amount of antifreeze and recommended contact time.
| Disinfectant dilution rate | Amount of disinfectant concentrate(ml) | Water | Propylene glycol | Temperature (degrees Celsius) | Contact time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:40 | 25 ml | 2.8 L (70%) | 1.2 L (30%) | 0 to -10 | 40 |
| 1:40 | 25 ml | 2.4 L (60%) | 1.6 L (40%) | -11 to -15 | 60 |
| 1:40 | 25 ml | 2.4 L (60%) | 1.6 L (40%) | -16 to -20 | 80 |
| 1:20 | 50 ml | 2.8 L (70%) | 1.2 L (30%) | 0 to -10 | 20 |
| 1:20 | 50 ml | 2.4 L (60%) | 1.6 L (40%) | -11 to -15 | 30 |
| 1:20 | 50 ml | 2.4 L (60%) | 1.6 L (40%) | -16 to -20 | 40 |
3.8 Reassembly
The interior of the transport unit, any parts that were removed and equipment must also be disinfected prior to reassembly. Once equipment has been reassembled, apply another layer of disinfectant to the exterior of the trailer. It is important to ensure that personnel involved in the reassembly of the trailer are wearing clean clothing and footwear so that they do not contaminate the trailer.
3.9 Undercarriage, wheels and wheel well cleaning and disinfection
When cleaning and disinfecting a transport unit, it is recommended to include the undercarriage, wheels and wheel wells. The cleaning and disinfection biosecurity best practices outlined above also apply to the undercarriage, wheels and wheel wells. Specialized equipment, such as an undercarriage wash station or long wash wand can facilitate the process.
If the cleaning and disinfection protocol includes driving over an undercarriage wash station after the rest of the transport unit has been cleaned and disinfected, then put in place measures to prevent organic matter or wash water from recontaminating the areas that have already been cleaned and disinfection. Splash guards located just above the undercarriage wash can help mitigate this risk.

3.10 Dry phase
Even after cleaning and disinfection, pathogens can be concealed in the smallest of cracks, joints and pitted metal. Some pathogens can replicate in warm and moist environments.
The transport unit should be dried in a clean area and on a slight incline (e.g. 2%) to encourage water to flow out of the transport unit. Drying can occur naturally or by using ventilation and heat treatment in a drying bay. In the winter, it is recommended that transport units be dried in a heated building.
Ideally, drying bays should:
- be located in the clean area or zone away from contaminated transport units;
- have restricted access;
- located in an area that is not accessible to dirty or contaminated vehicles, equipment and staff;
- only allow transport units that have been cleaned and disinfected into the drying bay;
- be kept clean.
3.11 Heat treatment
Heat treating a transport unit is a pathogen inactivation step that can be used. The temperature and time that must be achieved for heat treatment to be effective is pathogen specific. For example, PEDv in feces can be effectively inactivated when exposed to high temperature of 71°C for 10 minutes (Thomas et al, 2015). If heat treatment is used as an inactivation step, ensure that the required inactivation temperature is reached and maintained for the appropriate amount of time throughout the transport unit.
During the heat treatment, use probes and timers to ensure that the temperature and time required to inactivate pathogens has been consistently achieved throughout the transport unit. Probes must be placed in a location where it is most difficult to heat (for example, the nose of the trailer or the area furthest away from the heat source).
3.12 Cleaning the interior of the power unit
Care should be taken to keep the power unit clean at all times. Strict biosecurity protocols should be followed by those who have access to the power unit, to ensure that it is kept clean. Pets should never be allowed into the power unit.
Biosecurity best practice
- Never allow pets to enter the power unit.
Biosecurity protocols for cleaning and disinfection of the power unit and frequency will be based on the level of risk. The protocol for cleaning the interior of the power unit should consider following:
- use disinfectant wipes to clean all surfaces (see Figure 12).
- pay particular attention to high contact surfaces such as door handles, the steering wheel, seat belt, accelerator, break, clutch and gear shift.
- remove all floor mats.
- clean and disinfect the floor mats.
- vacuum areas around and under the floor mats.
- change or clean and disinfect seat covers.

Description of figure 12:
Figure 12: Illustration of common contact areas in the power unit that require additional attention when cleaning and disinfecting. Photo credit: Ontario Swine Health Board Truck Wash Handbook.
Figure shows cleaning and disinfection of common contact areas of the power unit, for example; gear stick, steering wheel, radio, CD player, door handle, foot rest, accelerator and brake pedals, floor and storage compartments, etc. using a disinfectant spray, clean cloth, brush or vacuum cleaner.
Annex 4a: Example of a cleaning and disinfection protocol for livestock transport units at a wash station
- Scrape-out before bringing the trailer for cleaning and disinfection.
- Clean and cover the outside entrance pad with lime prior to bringing the trailer into the wash bay.
- Remove all chase boards, shovels, rattle paddles and slappers.
- Remove deck planks.
- Remove winter covers.
- Wash the outside of the trailer including wheels, storage compartment and undercarriage with hot water.
- High volume flush the deck planks and inside of the trailer.
Note: Use hot water if the trailer is frozen.
- Apply detergent by foaming to all surfaces outside and for the manufacturer's recommended contact time. If applicable, wash the deck planks with hot water starting with the edges, then the flat surfaces, then flip the planks and repeat the process.
- Wash the inside of trailer with hot water.
- High volume cold rinse the wash station floor (to reduce recontamination of trailer).
- High volume cold rinse the deck planks and inside of the trailer.
- Wash station personnel inspects the trailer for cleanliness.
- High volume cold rinse of the wash station floor and all hoses, wash equipment, etc.
- Put winter boards in the trailer.
- Apply disinfectant by foaming to all surfaces inside and out.
- No further entry is allowed.
- Store trailer in an inclined position.
- Dry trailers.
- Use manufacturer's recommended concentration for detergent and disinfectant.
- The detergent and disinfectant concentrations are checked and calibrated 1x/month.
Power unit
- Remove all floor mats, boots and prods.
- Wash the exterior including wheels and undercarriage.
- Apply detergent using a foamer to all surfaces, floor mats and boots (soak for 15 minutes).
- Hot water wash the exterior, boots and floor mats.
- Using disinfectant wipes:
- clean and disinfect prods.
- wipe down interior surfaces, as needed.
- Vacuum interior as needed (2-3x/week).
- Apply disinfectant using a foamer to wheels and wheel wells, floor mats and boots.
- Replace all equipment and add clean coveralls.
The driver is responsible for the cleanliness of the power unit
Annex 4b: Example of a truck and crate cleaning and disinfection standard operating procedure in a poultry slaughter establishment
Truck and crate cleaning and disinfection protocol in the live end of a poultry slaughter establishment
Purpose
To minimize the risk of cross-contamination when reloading live birds on the truck.
Responsibility
The employees at the live end of the slaughter establishment are assigned truck washing duties and are responsible to the live receiving leadhand. A truck wash bay checklist is completed to document the completion of duties and inspection for adequacy of cleaning. The live receiving leadhand checks the truck before releasing and initials the form confirming his review. The offal monitor is assigned to clean and wash crates and modules.
Method
After the truck is unloaded, it is taken to the wash bay. The truck is then rinsed with low pressure and 37.8–71.1° Celsius (100–160°F) potable water. The trailer is washed with detergent and rinsed with potable water until it is visibly clean. The underside and tires are included. The same protocol is repeated on the other side.
All surfaces of the trailer and power unit are disinfected including the undersides and tires. The sanitation supervisor checks the disinfectant concentration and contact time on a daily basis and records the level on the "Chemical Concentration and Temperature Checklist". During winter months, upon completion of cleaning and disinfection, and inspection, close the curtains of the trailer to prevent snow and ice buildup inside the trailer.
The waste from crates and modules are dumped into inedible waste container. The crates and modules are rinsed with hot water, foamed with disinfectant mixture and rinsed with hot potable water prior to re-use.
Frequency
- Every truck of live birds after they are unloaded.
- After each use of crates and modules.
Critical limit
Transport vehicles and crates and modules must be visibly clean. Transport vehicles must have all surfaces disinfected.
Deviation procedure
If trucks cleaning and disinfection is not adequate as per the leadhand, the procedure has to be repeated until they are visibly clean.
The sanitation supervisor adjusts the concentration of disinfectant chemical when it is less than 500 ppm or over 1000 ppm and records any adjustments made.
Verification
The truck wash bay checklist is reviewed by the Quality Assurance department, weekly. If there are any outstanding issues, the quality assurance manager is contacted to review procedures and have issues resolved.
Related records
- Truck wash bay check list
- Inedible premises check
Live Poultry Receiving Department: Truck wash bay checklist–Daily
Verifier's name
Date:
Monitor's name:
Date:
Record all findings and deviation procedures in the checklist (see Table 4).
Note: Pressure must be between 600–1000 PSI with water temperature of 37.8–71.1° Celsius (100–160° Fahrenheit).
Critical limits: Disinfectant MUST be applied at manufacture's recommended concentration and contact time.
Trailers must be visibly clean; NO feathers, NO fecal matter.
Trailers must be in good repair and have no broken parts, damaged floors or doors that won't close etc.
Deviation procedure:
- If disinfectant is not applied, notify the supervisor for corrective action.
- If the trailer is not clean, then rewash.
| Trailer # | Disinfectant applied Yes/No | Clean Yes/No | Good repair Yes/ No | Correction required Yes/No | Who was notified? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | |||||
| 2. | |||||
| 3. |
Annex 4c: Example of a cleaning and disinfection protocol for equine trailers at a wash station
- 1. Remove feed, bedding and manure at destination according to the premises waste management plans.
- Use a shovel to remove the bulk of the waste.
- Use a broom to remove as much of the organic matter as possible.
- 2. Drive the trailer for washing to the wash station. Place the trailer onto the wash pad.
- 3. Remove all leads, shovels, buckets, brooms, ties, chest and rear guards, dividers and floor mats (where possible) from the trailer and place them onto the floor of the wash pad so they can be cleaned and disinfected separately.
- 4. Using the high volume hose (low pressure), spray the entire trailer and try to remove as much organic matter as possible. Work from outside to inside, top to bottom and front to back. Follow this order:
- Spray the outside of the front of the trailer and work your way back.
- Spray wheels, axels, mud flaps, and the under carriage and the back door.
- Open the loading ramp and rinse the interior walls and ceiling of the trailer as you move back towards the loading ramp.
- Rinse the floor working from the front all the way back towards the loading ramp.
- Rinse floor mats, leads, shovels, buckets, brooms, ties, chest and rear guards.
Note: Use warm water if the trailer is heavily soiled or frozen. Use of high pressure (pressure washer) is not recommended as it distributes organic matter and infectious agents into the air and adjacent surfaces.
- 5. Using the sprayer and brush, apply the premixed detergent and scrub all surfaces to loosen stuck organic matter. Apply the detergent to a 24" section from bottom to top and then use a hard bristle brush and scrub the section until all of the organic matter has been loosened from the surface. Work in this order:
- Start with the outside of the front of the trailer and work your way back
- Apply detergent and brush the wheels, axels, mud flaps, and the under carriage and the back door.
- Wash the interior walls of the trailer starting with the front of the trailer and working your way back.
- Working from front to back, wash the ceiling, floors and loading ramp.
- Wash floor mats, leads, shovels, buckets, brooms, ties, chest and rear guards.
- 6. Using the high volume hose and warm water, rinse the entire trailer to remove all detergent and organic matter from the exterior and interior of the trailer.
- 7. Rinse the wash bay floor out from the trailer towards the drains.
- 8. Apply detergent to your boots and scrub them clean.
- 9. Rinse your boots and the brush that was used to scrub the trailer and hose to remove all organic matter.
- 10. Let the trailer sit for 20 minutes to allow water to drain from the trailer.
- 11. Using additional light such as a strong flash light, inspect the exterior and interior of the trailer to ensure its visibly clean and that there are no pools of water on the floor of the trailer.
Note: Pay particular attention to hard-to-reach areas such as hinges, corners, windows, tie rings and latches. If organic matter is visible then repeat steps 5–11 on affected areas until they are visibly clean.
- 12. Using the disinfectant sprayer, apply disinfectant to the trailer. Work from bottom to top and in this order:
- Start with the outside of the front of the trailer and work your way back towards the wheels on each side of the trailer.
- Spray the wheels, axels, mud flaps, and the undercarriage
- Spray the back of the trailer and the back door.
- Spray the interior of the trailer starting with the front of the trailer and working your way back.
- Spray all sides of the floor mats, leads, shovels, buckets, brooms, ties, chest and rear guards.
- Spray the wash bay floor and hose.
Note: Pay attention to the length of time that surfaces remain wet with the disinfectant. In hot and dry environments it may be necessary to respray the entire trailer with disinfectant in order to achieve the manufactures' recommended contact time. In sub-freezing weather conditions, anti-freeze agent can be added while preparing disinfectant solution.
- 13. Allow the trailer and equipment to dry completely before placing the floor mats, leads, shovels, buckets, brooms, ties, chest and rear guards back into the trailer.
- 14. Complete the trailer wash bay checklist.
Trailer cleaning and disinfection record sheet:
Ensure that the detergents, disinfectant and antifreeze agent are prepared as per manufacturers recommendations. Follow safety instructions on the product label.
Person who performed the cleaning and disinfection:
Date:
Name of the wash station:
Detergent Information:
Product name:
Concentration:
Application method:
Was the trailer inspected and found to be visibly clean following the wash procedure?
- Yes
- No
Disinfectant information
Product name:
Concentration:
Application method:
Contact time:
Annex 5a: General visual inspection checklist
Front of trailer
- Side walls
- Ceiling
- Floors
- Gates and latches
- Deck rails
- Ramps
Midsection of trailer
- Sidewalls
- Ceiling
- Floors
- Gates and latches
- Deck rails
- Decking
- Horse dividers
- Feeders
Back of trailer (top to bottom)
- Sidewalls
- Ceiling
- Floors
- Tools
- Gates and latches
- Deck rails
- Ramps
Outside of trailer
- Back
- Backdoor
- Undercarriage
- Wheel wells
- Wheels and tires
- Side steps
- Side doors
- Side panel
- Nose
- Coroplast panels and storage box
Inside the power unit
- Steering wheel
- Door handles
- Floor mats
- Seat cover
- Stick shift
- Dashboard
- Radio
Annex 5b: Example of a visual inspection form used for swine transport units
Check each area for cleanliness and whether or not it is dry. Circle appropriate answer. Indicate the location of any areas of concern on schematic and annotate with photo #.
| Clean | Dry | |
|---|---|---|
| Power unit exterior | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Tire rim | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Storage boxes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Floor board | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Seat | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Steering Wheel/Dash/Console | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Clean | Dry | |
|---|---|---|
| Trailer exterior | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Tire rim/undercarriage | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Storage boxes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Rubber bumpers | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Outside gates | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Internal chute (if applicable) | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Clean | Dry | |
|---|---|---|
| Walls | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Floors | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Ceilings | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Gates (both sides) | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Winter panels (both sides) | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Clean | Dry | |
|---|---|---|
| Sort boards | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Rattle paddles/Shakers | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Shovels/Brooms | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Prods | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Equipment | Yes | No | Yes | No |
Areas of concern
Please photograph any areas of concern and indicate location on schematic with photo # and comment.
Exterior
Interior – Forward view
(Viewing from back to front)

(Viewing from front to back)

Examples – Areas of concern
Please photograph any areas of concern and indicate location on schematic with photo #.
Interior – Backward view (i.e. Viewing from front to back)

Description of image - Interior – Backward view
There are three panels. From left to right, the first panel shows a diagram of the inside of a transport trailer (front to back) with an area of concern on the inner side of the door indicated with a circle with an arrow point to the words, "#2 & #3 Dirty."
The second panel, Photo 2, is a photograph of the inner side door of a transport trailer. The area of concerned circled with an arrowing pointing to the last panel. The last panel, Photo 3, is a close up of the area of concern.

Annex 6: Biosecurity guidance for choosing a wash station
The following general criteria should be considered for choosing a wash station for cleaning and disinfection;
- Access pathways
- Ideally clean transport units do not take the same route as dirty transport units.
- Pathways are maintained and are kept free of manure and other organic matter.
- Pathways are graded and made with a surface material that allows for year-round drainage.
- Site organization
- There is physical and functional separation of clean and dirty areas to ensure that there is no cross-contamination between dirty and clean transport units.
- There are designated storage areas for clean versus dirty transport units.
- Vehicles (flow and parking), equipment (flow and storage) and staff (flow and duties) are organized to ensure that there is no cross contamination between clean and dirty areas.
- Scrape-out locations are completely separated from the wash site and pose no risk of cross-contamination of the wash site or of cleaned and disinfected transport units leaving the site.
- There is physical and functional separation of clean and dirty areas to ensure that there is no cross-contamination between dirty and clean transport units.
- Wash bays/Washing areas
- Designed in a way that prevents wash water from contaminating other areas and equipment on the site.
- Floors are bermed to prevent water from flowing and contaminating areas outside of the wash bay.
- Walls or curtains are used to prevent contaminated wash water from splashing out of the washing area.
- Floors are sloped to provide good drainage and direct water towards a wastewater collection system.
- The floor and walls or curtains are made from a material that can be cleaned and disinfected.
- Wash bays are cleaned and disinfected between transport unit washes. See Annex 4a: Example of a wash bay protocol for swine and ruminant transport Units.
- Wash area is drive-through so that clean trailers do not have to take the same route as dirty trailers.
- Kept at a temperature above freezing year round.
- Designed in a way that prevents wash water from contaminating other areas and equipment on the site.
- Water
- Quality
- Water that does not contribute to the level of contamination or pathogen load and available in sufficient quantity to perform the clean and disinfection process.
- Using recycled wash water without treatment is a risk.
- Hardness (presence of ions of calcium and magnesium may interfere with the effectiveness of detergents and degreasers).
- Neutral pH water is recommended since alkaline and acidic water will impact the efficacy of detergents and disinfectants.
- Water that does not contribute to the level of contamination or pathogen load and available in sufficient quantity to perform the clean and disinfection process.
- Capacity to achieve the manufacturer's recommended water temperature for the detergent and disinfectant.
- Detergents or disinfectants are less effective when water temperature is outside of the recommended range.
- Quality
- Effluent collection systems
- Has the capacity required for the site (there is no backup of dirty water that can contaminate wash bays or washing areas, access pathways or storage areas).
- Stores effluent in a biosecure manner until it can be disposed or treated.
- Wash water, manure and organic matter are managed and disposed of in accordance with municipal, provincial and federal legislation and regulation.
- Use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) (see Figure 13 as an example)
- Wear PPE that provides effective protection for the process and chemicals used.
- PPE recommendations can often be found on the detergent and disinfectant manufacturer's label.
- Another source of recommendations is the chemical Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS). An MSDS is a document that contains information on the potential hazards (health, fire, reactivity and environmental) and how to work safely with the chemical product.
- Most importantly, do not re-contaminate the transport unit after final pathogen inactivation step.
- Wear PPE that provides effective protection for the process and chemicals used.

Annex 7a: Disclosure of transport history
This disclosure is being provided to:
| Farm owner/manager: | |
| Of farm/site: | |
| On the date: |
I, ![]() , of the transport company
, of the transport company ![]() hereby certify that the following (transport) trailer with licence plate number
hereby certify that the following (transport) trailer with licence plate number ![]() and power unit with licence plate number
and power unit with licence plate number ![]() have undergone the wash procedures on the date
have undergone the wash procedures on the date ![]() , at the time
, at the time ![]() , and at the location
, and at the location ![]() as stipulated in the attached Transport Unit Wash Record documents.
as stipulated in the attached Transport Unit Wash Record documents.
I further certify that these previously identified trailer and power unit, in the period between the completion of these wash procedures and arrival at you farm/site, have neither:
- Visited any premises that handle or house livestock or poultry;
- Been parked alongside unwashed power units or trailers used in the transport of livestock or poultry; nor,
- Been parked or used in a way that puts them at a high risk of becoming contaminated with livestock or poultry pathogens.
Check one
- I have also attached the Trailer/power unit Travel History document to this disclosure.
- I have not included a Trailer/power unit Travel History document with this disclosure.
I make no claims certifying that the identified power unit and trailer pose zero risk to biosecurity in terms of the spread of livestock or poultry pathogens, only that the procedures indicated in the attached paperwork have been undertaken to minimize said risk.
Name of transporter/driver: ![]()
Name of transport company: ![]()
Signature: ![]()
Date: ![]()
Annex 7b: Transport unit travel history

Description of image – Annex 7b Transport unit travel history
Transport unit travel history document has fields to collect the following information:
- Licence plate number:
- Last animal handling/production location attended by transport unit (not including wash stations)
- Location type
- Farm
- Assembly yard
- Slaughter establishment
- Auction mart
- Events
- Competition
- Fairs
- Other
- Country: Canada / United States
- Date of visit
- Time of visit (am/pm)
- Last use of transport unit equipment for the movement of animals
- Type of animals
- Date of visit
- Time of visit (am/pm)
- I hereby certify the accuracy of the information set out above.
- Name of transporter/driver
- Name of transport company
- Signature
- Date
Annex 8: Example protocols for entering and exiting the power unit and trailer
Example protocol for entering and exiting the power unit:
There are a variety of protocols that can be used to prevent the interior of the power unit from becoming contaminated. One way that this can be accomplished is by having dedicated footwear for the power unit (driving shoes) and by having separate footwear for exiting the power unit. Consider the following protocol:
- Prior to leaving the power unit:
- remove power unit designated footwear.
- open the door and swing your feet out of the truck.
- put on footwear designated for activities outside of the power unit.
- step out of the power unit.
- When entering the power unit:
- remove footwear as you are stepping into the power unit.
- place footwear into a sealed container.
- use hand sanitizer prior to touching anything inside the power unit (door handle, steering wheel, stick shift, etc.).
- put on power unit designated footwear.
Example protocol for entering and exiting the trailer:
There are a variety of protocols that can be used to prevent the interior of the trailer from becoming contaminated. This protocol has been provided as an example (see Figure 14).
When entering the trailer:
- Retrieve a biosecurity kit from a clean location (for example; from a storage cubby or plastic storage box) and place it outside the access door to the trailer.
- Open the biosecurity kit and place the lid topside down.
- Remove shoes and while stepping onto the biosecurity kit lid.
- While taking care to ensure that of the contents of the biosecurity kit do not touch the ground, put on:
- clean coveralls;
- a pair of clean boots; and,
- disposable gloves.
- Step out of the biosecurity kit and directly into the trailer.

When exiting the trailer:
- Step out of the trailer and directly in to the biosecurity kit.
- Remove coveralls, gloves and place them directly into in the biosecurity kit. Take care to ensure that the coveralls and gloves do not come into contact with the ground.
- As you step out of your footwear, step onto the biosecurity kit lid.
- Step off of the biosecurity kit lid and place your foot into your shoes.
- Place the lid back onto the biosecurity kit and return the kit to its storage compartment.
- Follow the protocol for re-entering the power unit as described above.
Annex 9: Example of transport boot protocol to follow when entering and exiting the power unit at high-risk stops
Use either rubber overshoes or disposable boot covers when exiting your power unit at the border. Examples of high-risk areas are truck stops with livestock trailers, farms, repair shops, weigh scales and clearly contaminated areas where manure is visible.
- When having to exit the power unit, decide whether rubber overshoes or boot cover should be worn.
The rule of thumb is: If you need to be out of your power unit for an extended period or have to walk any distance, use rubber overshoes. For quick out and in events, use disposable boot covers.
- As you exit the power unit, slip on appropriate boot cover and move onto the top step. Prior to exiting the power unit, make sure that your disposal container is in easy reach to make re-entering more efficient and biosecure.
- On your return to the power unit, remove boot covers or rubber overshoes while stepping onto the bottom step. Do not allow your exposed footwear to come into contact with the ground. In this way you will limit the contamination of your steps.
- Place used boot covers or rubber overshoes into the disposal container.
- Use hand sanitizer after removing boot covers or rubber overshoes before touching any interior surface of the vehicle. Wipe any surface that might have touched when re-entering the vehicle (e.g. the steering wheel or door handle).
- This procedure should be used at the border or any other identified high-risk area on the trip to and from the collection point.
- Rubber overshoes are washed and dried with work clothes on your return to the shop.
Annex 10: Bibliography
Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada. "Canada's red meat and livestock industry at a glance." 2016.
Bowes, Victoria. "After the Outbreak: How the British Columbia Commercial Poultry Industry Recovered After H7N3." Avian Diseases (2007): 313–316.
Canadian Pork Council. "Traceability and Identification Program: Pig Trace Canada." March 2016.
Engele , K and Whittington, L. "Economic Costs of PEDv". Prairie Swine Centre semi-annual newsletter. Winter 2014
Livestock Market Interruption Strategy Steering Committee. "Livestock Market Interruption Strategy." 2016.
Lowe, James and Phillip Gauger. "Role of transportation in spread of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus infection, United States." Emerging Infectious Diseases (2014): 872–874.
Neumann, E. "Assessment of the economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome on swine production in the United States." Journal of American Veterinary Medical Association (2005): 385–392.
Paarlberg, PL. "Updated Estimated Economic Welfare Impacts of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDv)". Working Paper #14-4, Dept of Agricultural Ecnomics, Purdue University, April 7, 2014
Pasma T, Furness MC, Alves D, Aubry P. "Outbreak investigation of porcine epidemic diarrhea in swine in Ontario." The Canadian Veterinary Journal 57.1 (2016): 84–89.
Potential Economic Impacts of a Foot and Mouth Disease Outbreak in BC Livestock Waste Tissue Initiative. Calgary: Serecon Management Consulting Inc., 2010.
Sellers, R.F. and S.M. Daggupaty. "The Epidemic of Foot-and-Mouth Disease in Saskatchewan, Canada, 1951–1952." Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research (1990): 457–464.
Serecon Management Consulting Inc. "Domestic Livestock Movement Demographic Study." 2015.
Smyth GB, Dagley K, and J. Tainsh. "Insights into the economic consequences of the 2007 equine infleuza outbreak in Australia." Australian Veterinary Journal (2011): 151–158.
Thomas PR et al. (2015). Evaluation of time and temperature sufficient to inactivate porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in swine feces on metal surfaces. J Swine Health Prod.;23(2):84–90
Yeske, Paul et al. "What did we learn from the packing plant survey and what can we do in the future?" n.d. (2014)
Annex 11: Acknowledgements
| Representative | Organization/Affiliation |
| Dr. Cornelius Kiley CFIA Co-Chair |
Canadian Food Inspection Agency |
| Mark Beaven Industry Co-Chair |
Canadian Animal Health Coalition |
| Dr. Lucie Verdon | Council of Chief Veterinary Officers designate (Québec) |
| Dr. Jagdish Patel | Council of Chief Veterinary Officers designate (Alberta) |
| Erica Charlton | Canadian Hatchery Federation Canadian Poultry and Egg Processors Council |
| Stephane Beaudoin | Canadian Livestock Transportation Certification Program |
| Jorge Correa | Canadian Meat Council |
| Dr. Graham Clarke | Canadian Renderers Association |
| Haidee Landry | Equestrian Canada (Equine Canada) |
| Martin Pelletier | Équipe québécoise de contrôle des maladies avicoles Équipe québécoise de santé porcine |
| Susan Fitzgerald | Ontario Livestock and Poultry Council Poultry Service Association |
| Dr. Doug MacDougald | South West Vets |
| Rick Peters | Steve's Livestock Transport Ltd |
| Dr. Kuldeep Chattha | Canadian Food Inspection Agency |
Other contributors from the CFIA include Josée Laframboise, Dr. Patricia Pentney, Dr. Lorne Jordan, Dr. Daniel Schwartz, Olivier Fortin, Sandra Bowler and other administrative staff.
