On this page
- About this document
- Glossary
- National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard
- Development of this document
- Self-Evaluation Checklist
About this document
Who is this document for
The National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard forms the basis of a comprehensive voluntary program designed to provide applicable guidance for owners or managers of all poultry production types in Canada. It has been developed as a tool for all people and businesses handling and keeping poultry, including large-scale supply-managed producers, backyard flock owners and other domestic bird keepers.
This On-Farm Biosecurity Standard is supplemented by a General Producer Guide that provides guidance to producers on how the Target Outcomes may be achieved.
The Standard and associated Producer Guide are designed to support poultry producers in the development of farm-specific biosecurity plans that do not already participate in a provincial association or On-Farm Food Safety (OFFS) program (such as the non- regulated commercial and non-commercial poultry industry). They have also been designed to be complementary with, and enhance, existing On-Farm Programs.
The OFFS programs developed by industry formally address many of the elements of biosecurity and will be the primary avenue for implementation where OFFS programs exist.
This program is based on clear, scientifically justified principles. It details a range of measures intended to prevent disease-causing agents from entering or leaving a premises housing poultry.
Product on the Canadian market originates from both domestic and imported suppliers. Regardless of the source, the same standards should, ideally, apply to the production of all products being sold in Canada.
Why is biosecurity important
There is no standard definition of the word Biosecurity, but it has become the accepted term used to describe the measures needed to protect against the introduction and spread of diseases.
It is in every poultry keeper's best interest to ensure that they are aware of the risks and do what they can to limit the chances of disease developing or spreading.
Birds that are infected with a pathogen may or may not show clinical signs of disease. However infected birds can shed the organism (through their feces, through aerosols, urates and other bodily fluids) into the environment. If disease is left unchecked, other birds can become infected and the organism can accumulate in the environment.
Chronically infected birds/flocks provide an opportunity for the organism to replicate and in some cases undergo genetic changes. These changes may make the organism less or more likely to cause disease in birds, other animals and humans.
Because pathogenic organisms are microscopic, they are not visible to the naked eye. Despite this, they can be found in large numbers in visible material such as: dust, water droplets suspended in the air, and fecal contamination. An infective dose of pathogenic organisms can be contained in a particle of dust. Such a small amount of contaminated material can be hidden on equipment, clothing, footwear, or hands, allowing the disease to be carried from one flock to another.
Disease outbreaks both in Canada and overseas clearly demonstrate the serious impact that avian diseases can have on business, individual livelihoods and local communities. The impact may range from the destruction of tens of thousands of poultry and multi-million dollar losses, to the cancellation of poultry shows and temporary restrictions on the movements of animals, products and by-products. The period during which emergency controls are in place may vary depending on how rapidly a disease can be successfully controlled.
Some diseases, known as zoonoses, (for example those caused by organisms such as Salmonella) can infect both poultry and humans. Good biosecurity is therefore an important element in the prevention of human illnesses.
Everybody who keeps poultry must share responsibility for protecting their business or hobby by reducing the risks associated with the spread of diseases.
An effective biosecurity program is based on the understanding and the vigorous application of the adopted measures to ensure exclusion (preventing introduction of the disease) and containment (when introduced, preventing disease from spreading).When a component of the program has a weakness, or where biosecurity measures are not fully implemented, it provides a route by which disease might enter the flock or remain undetected within the flock.
The clear benefits from practicing good biosecurity include the following:
- having healthy poultry
- minimizing the potential for significant costs and losses in revenue
- protecting human health
- protecting the health of wild birds by containing poultry diseases that might affect them
- protecting your ability to move poultry and poultry products without restriction
- protecting other industries such as feed suppliers
- protecting export markets
Development of this document
The Avian Biosecurity Advisory Committee (ABAC) was created with a membership of representatives from all potential users of this document. The committee identified areas of practical effective controls using an objective, impartial science-based approach.
A technical sub-committee derived six main principles and associated recommendations for biosecurity measures. (See Annex A.)
These principles:
- focus on prevention of avian influenza and other disease spread through respiratory transmission (other types of disease transmission were also included within the review)
- address gaps in existing On-Farm Food Safety systems
- are based on scientific analysis of efficacy
- have a high level of cost benefit return to encourage compliance
- are applicable to any level of poultry production
- are readily auditable
Utilizing a science-based risk and cost/benefit analysis, background work for this standard identified and prioritized those biosecurity interventions with the greatest impact on reduction of risk of spread of contagious disease.
How should this document be used
With such a broad target audience not all of these principles will be applicable or practical for every situation. Keeping this in mind, the National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard has been organized into three sections representing the foundations of a smoothly operating biosecurity system. These are defined as:
- Access Management
- Animal Management
- Operational Management
Each of the three foundation sections is further divided into subsections and Target Outcomes.
Each Target Outcome represents a goal that all keepers of poultry, regardless of the size of their flock, should try to implement to protect their flocks from introduction and spread of avian diseases.
The National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard is the main document. Each section is summarized, listing the Target Outcomes with a brief explanatory text. It is supported by a second document, the General Producer Guide to the National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard.
The General Producer Guide has been developed, with significant contributions from representatives of the different poultry production types, as an information resource to assist poultry producers when developing biosecurity plans for their farming operations. It demonstrates the flexibility required for a variable and complex poultry industry. To that end, the General Producer Guide is not a full and complete listing of all examples that can be used to meet the Target Outcomes. Other "Guide" documents with more production type-specific producer guidance can be developed in the future.
Every keeper of poultry should focus on achieving a level of control in each of the components on their property. However, for those who are new to the concept of biosecurity, those with limited resources, or where it is not practical or applicable to fully achieve each of the target outcomes, the guideline document will provide a set of examples of measures that can be taken to meet the Target Outcomes.
Near the beginning of the document, there is a Glossary providing definitions of certain terms used within the text.
At the end of the document is the original document developed by ABAC, "Main Principles and Associated Recommendations," which has been used as the basis for this standard.
A self-evaluation checklist is also included which can be used to quickly record the Target Outcomes being effectively controlled and those that need further action.
Biosecurity: a cycle of activities
The implementation of biosecurity principles on a farm or facility can be viewed as a cycle of activities which includes:
- assessing the biosecurity risks
- developing a plan that addresses the risks
- implementing biosecurity measures and procedures
- monitoring flock health, keeping records of illnesses and treatments, and gathering disease and pest information to evaluate the plan and identify new risks
- reassessing the risks and responses on an on-going basis to ensure continuous improvement
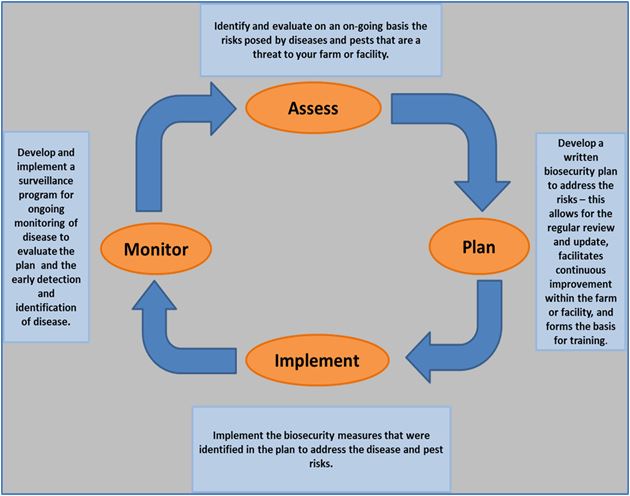
Description of Figure 1 – Cycle of biosecurity activities
Figure 1 is an illustration of the cycle of activities that should be completed to develop and implement a biosecurity plan. The cycle of biosecurity activities has four items in the centre with arrows pointing between them in clockwise direction. The first item at the top of the cycle is Assess. Moving clockwise, the second item is Plan, the third item is Implement and the fourth item is Monitor. There is a text box by each of these items in the cycle (four in total). Above the word Assess there is a box with the following text: Identify and evaluate on an on-going basis the risks posed by diseases and pests that are a threat to your farm or facility. To the right of the word Plan there is a box with the following text inside: Develop a written biosecurity plan to address the risks – this allows for the regular review and update, facilitates continuous improvement within the farm or facility, and forms the basis for training. Below the word Implement is a text box with the following text inside: Implement the biosecurity measures that were identified in the plan to address the disease and pest risks. To the left of the word Monitor is a text box with the following text: Develop and implement a surveillance program for ongoing monitoring of disease to evaluate the plan and the early detection and identification of disease.
Assess: The risks posed by the introduction of pests and diseases that threaten flock health on your farm are identified and evaluated in consideration of the components of a biosecurity plan. The identification and evaluation of risks will allow for current biosecurity issues within a farm to be addressed.
Plan and implement: A written on-farm or facility biosecurity plan is highly recommended, regardless of the size or type of facility. A written plan allows for regular review and update, facilitates implementation and continuous improvement within the operation, and forms the base for training.
Monitor and reassess: It is important that the design, effectiveness and implementation of a biosecurity plan be assessed not only on a routine basis but also when changes in farm practices or biosecurity issues occur. Production practices should be reviewed frequently to ensure that implemented measures are effective in relation to pest and disease prevention and control.
Developing your farm biosecurity plan
Developing a farm biosecurity plan involves achieving the right balance between disease risk and prevention. Your biosecurity plan will be unique to address the specific risks to your farm and production activities. Work with your veterinarian and industry experts on developing a plan.
Step 1: Prepare a diagram of the farm
Create a detailed farm diagram and identify potential pathways for disease and pest transmission from people, equipment, vehicles, and wildlife that can transmit disease.
Step 2: Identify the risks
Identify the poultry diseases that are concerns and how they are transmitted. Consider:
- diseases that have previously occurred on the property, those present in the local poultry population, and endemic to the region
- the health of poultry flocks from which new or replacement poultry are sourced
- diseases present in the wild bird population including both resident and migratory birds
Step 3: Review management practices and complete the self-assessment tool in the Producer Guide
Many poultry management practices pose some degree of biosecurity risk. Identify your daily care and management practices and any less frequent activities (for example vaccination and repair services) that might result in the transmission of pathogens. Review your farm diagram – does your farm design and layout and your management practices affect your ability to manage disease risks?
Complete the biosecurity self-assessment provided in the biosecurity guide. Identify areas where biosecurity practices are being effectively managed and those where improvements can be made.
Step 4: Identify biosecurity goals and best practices
Using the biosecurity standard and guide, identify biosecurity goals and best practices that can be implemented to address the biosecurity gaps.
Step 5: Develop an implementation strategy
While all biosecurity risks need to be addressed, some will be more critical than others. Prioritize the biosecurity tasks and establish a timeline for their completion.
Step 6: Review the effectiveness of the biosecurity plan and continuous improvement
The effectiveness of the biosecurity plan is measured by the adoption of its biosecurity practices, their integration into daily routines and the impact to the health status of flock. When necessary, design and implement improvements to the biosecurity plan.
Principles of disease transmission
Understanding the basis of infectious disease is necessary for their prevention and control. Infectious diseases in poultry result from a complex interaction of three factors referred to as the disease triad:
- an animal that is susceptible to disease (the host)
- a pathogen such as a bacterium, virus, fungus or parasite capable of causing disease (the agent)
- an opportunity for the host and agent to come into contact (the environment)
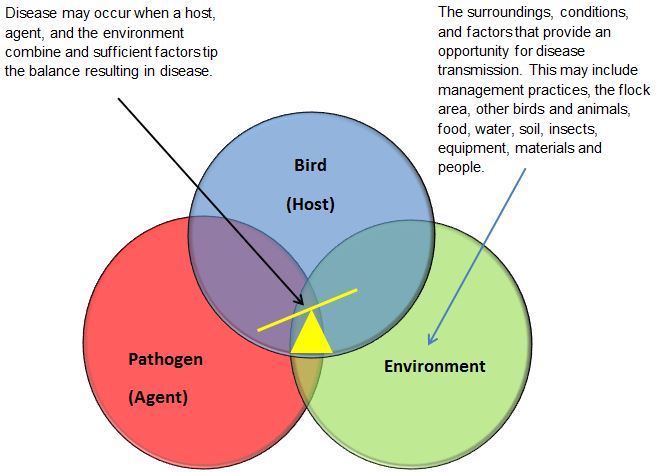
Description of Figure 2 – The disease triad
This diagram illustrates the relationship between a bird (the host), a pathogen (the agent), and the environment. Disease may occur when a susceptible animal, a pathogen, and an environment favourable for disease development are present and there is sufficient time for exposure and then multiplication of the agent in the animal. There are many factors that influence whether disease will occur including the health of the animal, adequate nutrition, external stresses, the number of pathogens present and the ability of the pathogen to cause disease. No one element is responsible for the expression of the disease. It is the interaction of the 3 elements (the presence of a pathogen, a susceptible host and the environmental conditions) that determine whether it tips the scale to favour the expression of a disease.
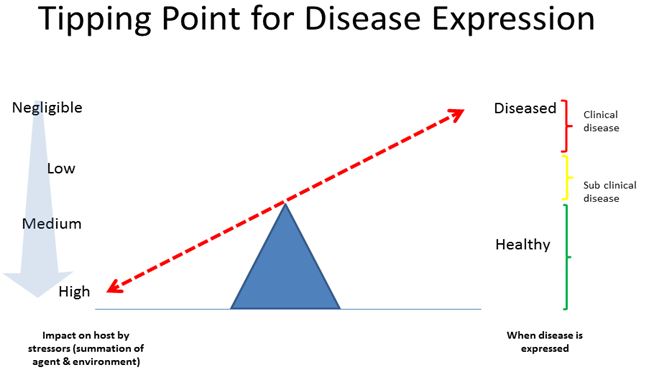
Description of Figure 3 – Tipping point for disease
The image has both a left and a right margin. Below the left margin is a title. The text reads: Impact on host by stressors (summation of agent and environment). To the left of the left margin is an arrow, that gets wider as it runs from the top to the point at the bottom. On the left margin is a scale from. From top to bottom the text reads: Negligible, Low, Medium, High.
Below the right margin is a title. The text reads: When disease is expressed. On the right margin is a scale. The text reads from top to bottom: Diseased, Healthy, Diseased is further divided, from top to bottom as Clinical Disease, Subclinical Disease. These are indicated by three vertical co-linear coloured lines: red (clinical disease, top), yellow (sub-clinical disease, bottom) and green (healthy, bottom).
In the centre of the image is a triangle pointed upwards serving as a fulcrum on which is balanced a double ended red dotted arrow running from bottom left margin (High) to top right (Clinical Disease).
The cumulative impact of potential stressors (such as exposure to pathogens, changes in social structure, inadequate nutrition, poor ventilation, and significant light and temperature changes) on poultry over a period of time can overwhelm their ability to resist infection resulting in disease. The disease may be sub-clinical (poultry are infected yet appear healthy) or clinical (poultry are infected and appear sick) depending on the degree of the impact of the stressors, characteristics of the disease agent and the health status of poultry prior to exposure.
Three broad approaches to prevent and control infectious diseases include:
- decreasing exposure of animals to pathogens: Preventing contact between animals and pathogens can prevent infection and disease from occurring. If exposure does occur, there must be a sufficient number of viable organisms (an infectious dose) that can bypass the animal's defence systems and then multiply to cause disease. Many of the biosecurity practices focus on reducing exposure, including separating healthy animals from animals that are sick or of undetermined health, minimizing contact with contaminated equipment, managing insects and pests that may transmit pathogens and cleaning and disinfecting equipment.
- decreasing susceptibility of animals to disease: There are factors that can be managed to reduce susceptibility to disease including: providing proper nutrition, managing underlying disease, reducing stress, implementing effective parasite control, and the appropriate use of antibiotics and other medications. There are other factors that affect an animal's susceptibility to disease that cannot be influenced to a significant degree such as age and genetics.
- increasing resistance to disease: Vaccination is the primary method used to improve resistance to certain, specific infectious diseases.
Glossary
- Additional Biosecurity Measures
-
A level of biosecurity to be practiced to mitigate for situations where recommended practices cannot be followed (i.e. recommended may be an "all in/all out" system). Where this is not possible (i.e. as in the case of a multi-age premises) additional biosecurity precautions need to be implemented.
- Anteroom
-
An area or room that immediately precedes the Restricted Access Zone (RAZ) and provides a transition from the Controlled Access Zone (CAZ).
- Approved
-
When used in reference to chemicals such as rodenticides, means approved by the appropriate regulatory authority for the specific usage mentioned in the text.
- Barn
-
Any structure that encloses poultry flocks including sheds, runs, etc.
- Beneficial practice
-
A management practice, technique or technology that, when adopted, results in improvement and increased sustainability of the operation.
- Biosecurity program
-
A risk reduction program that conforms to Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) national standards and is designed to prevent and control the introduction and spread of pathogens.
- Controlled Access Point (CAP)
-
Visually defined entry point(s) through which all traffic, such as workers, equipment, feed trucks, etc. will enter the Controlled Access Zone (CAZ) and/or the Restricted Access Zone (RAZ).
- Controlled Access Zone (CAZ)
-
The area of land and buildings constituting the poultry production area of the premises that is accessible through a securable controlled access point.
- Clean
-
Free of any visible accumulation of organic matter and debris or other residues.
- Debris
-
Any material that may be capable of harbouring disease-causing organisms or pests such as discarded equipment or machinery, manure, dead poultry or parts of dead poultry, egg white, egg yolk, egg shells, feathers and soil.
- Disinfection
-
The application of a physical or chemical process to a surface for the purpose of destroying or inhibiting the activity of disease-causing micro-organisms.
- Downtime
-
A period of time between flocks, starting with a barn or flock area being emptied of poultry and ending with the placement of new poultry. It allows for the natural reduction in numbers of disease-causing micro-organisms within the barn or flock area. The effective period can be reduced by cleaning and disinfecting at the beginning of the period.
- Endemic Diseases
-
Diseases that are constantly present within a region or population.
- Enhanced Biosecurity
-
At times when a disease outbreak is suspected on the premises or has been identified in the vicinity, extra biosecurity measures may be required and increased emphasis placed on existing biosecurity procedures.
- Essential Visitors
-
A person who enters the Restricted Access Zone (RAZ), and has a necessary role in the farm operation, other than personnel concerned with day-to-day poultry production on the premises. Visitors include veterinarians, service and delivery people, suppliers and regulators.
- Foreign Animal Diseases
-
Infectious diseases that normally do not occur in the country either because they have never been present there or because they were eradicated and then kept out by government control measures or agricultural practices.
- Flock
-
A group of poultry managed as a distinct population.
- Flock Area
-
Area/range that unconfined (outdoor) poultry occupy.
- Fomite
-
Any inanimate object or substance capable of carrying infectious organisms. This may include but is not limited to equipment, farm vehicles and articles of clothing or shoes.
- Lock
-
A secure fastening device that requires a key, code or key fob to open.
- Non-Essential Visitors
-
People and their equipment who do not require access to the Controlled Access Zone (CAZ) and Restricted Access Zone (RAZ).
These include but are not limited to guests, friends and family. - Pathogenic
-
Capable of causing disease.
- Pathogens
-
Biological agents, such as a bacteria or virus which have the potential to cause diseases.
- Pests
-
Includes insects, spiders, ticks, rodents, wild birds and other animals that pose a nuisance to poultry.
- Potable
-
Suitable for drinking.
- Poultry
-
All birds reared or kept in captivity for breeding, the production of eggs or meat for consumption, for production of other commercial products, for restocking supplies of game birds or for breeding these categories of birds.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
-
Specialized clothing and equipment worn by an individual to provide a protective barrier against exposure and injury from chemical, physical or biological hazards. Personal protective equipment also reduces the transmission of pathogens to poultry from contaminated clothing, equipment and dirty hands.
- Premises
-
A parcel of land with a continuous property boundary and defined by a legal land description or, in its absence, by geo-referenced coordinates, on which or on any part of which poultry are grown, kept, assembled or disposed of.
- Producer Guidance
-
Examples and beneficial practices to facilitate achievement of the standard.
- Protocols
-
A code of conduct or defined procedure to be followed.
- Reportable Disease
-
A disease that must be immediately reported to the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA). Reportable diseases in poultry are Notifiable Avian Influenza, Newcastle Disease (velogenic), Pullorum Disease (Salmonella pullorum), and Fowl Typhoid (Salmonella gallinarum). These diseases are also "Foreign Animal Diseases" in Canada.
- Restricted Access Zone (RAZ)
-
An area inside the Controlled Access Zone (CAZ) that is used, or intended to be used, to house poultry including semi-confined and range production and where personnel and equipment access is more restricted than the CAZ. The RAZ is sometimes referred to as the Production Area or Restricted Area (RA) in other poultry production documents and guides.
- Spiking Males
-
Sexually mature male poultry introduced into a breeding flock in order to maintain fertility by boosting mating frequency.
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
-
Documented procedure based on generally accepted good practices that describe in detail the steps followed to meet an objective (for example a SOP that details the barn cleaning and disinfection procedure).
- Target Outcome
-
The goal that all keepers of poultry, regardless of the size of their flock, should aim for if they are to protect their flocks from the introduction and spread of avian diseases.
National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard
The following basic biological principles are the foundation of the national avian on-farm biosecurity standard described in this document that result in an effective Biosecurity program.
Pathogens are controlled through implemented biosecurity practices that try to ensure what is inside stays in and what is outside stays out.
Why does biosecurity work
- Access to the "inside" is restricted with the establishment of zones. Visual and/or physical boundaries are created that define the premises buffer zone or "Control Access Zone" (CAZ) and the internal production/housing area or "Restricted Access Zone" (RAZ). Movement of people/animals/equipment/materials across these zone boundaries is controlled.
- Good biosecurity practices break the cycle of infection pressure (flock flock). These include spatial breaks (distance/segregation/isolation), temporal breaks (sequencing/downtime) and physical breaks (cleaning/disinfection). Monitoring the health status of your flock and reacting to early signs of disease facilitates breaking the cycle of infection and allows biosecurity practices to be scaled up.
- Good biosecurity reduces carriage across zone boundaries such as biosecurity procedures for mortality & manure management that reduce the opportunities for organisms to get "out". Procedures involving cleaning, wearing appropriate clothing or personal protective equipment, the use of a clean source of inputs and pest control reduce the opportunities for organisms to get "in" and reduce contact between "in" and "out".
Note:
A General Producer Guide has also been developed and is presented in a separate document. The Producer Guide is an information resource to assist poultry producers when developing biosecurity plans for their farming operations. It provides current information on a variety of beneficial biosecurity practices as examples of different approaches producers could take in order to meet the target outcomes of the biosecurity standard.
Section 1 Access Management
1.1 Designation of Zones
Access to/exit from the barn, flock area and premises is controlled through the establishment of protective zones and controlled access points.
1.1.1 Target Outcome
Recognizable zones and controlled access points are in place.
It is important to ensure that everyone who works/lives on a premises or comes onto a premises for any purpose is clear about where they are allowed to go. This is best achieved by setting up protective zones around the areas where poultry are kept or handled. For these zones to be effective, they need to be visible or defined and have clearly identified access points.
The best approach is to create two zones:
- An outer area commonly referred to as a Controlled Access Zone (CAZ) which encompasses the entire area where poultry are kept or handled.
- An inner more restricted area where poultry are housed or intended to be housed, located inside the CAZ, to which access is more tightly controlled. For the purposes of this document it will be referred to as the Restricted Access Zone (RAZ). The RAZ is also referred to as the Production Area or Restricted Area (RA) in other poultry production documents and guides. The RAZ may include the inside of a barn, a barn and range area, pasture and any other area identified by the producer as requiring an elevated biosecurity level.
Controlled access points (CAPs):
- are established to manage access to the CAZ and the RAZ
- should provide or lead to an area that is equipped with supplies for conducting the biosecurity requirements (for example designed to facilitate hand washing, change of clothes and boots)
Examples of CAPs are a gate to the CAZ and the door of a poultry barn or a gate to an outdoor range that can be secured.
To provide the necessary space and infrastructure for implementing the biosecurity procedures:
- ante-rooms (preferably) or transition areas should be established at the CAP for entering the RAZ, particularly when barns/buildings are present, and when renovating and/or building new barns
- a transition area should be established at the CAP for entering the RAZ of range and pasture production. The transition area should provide: a hard surface that can be kept clean, storage for biosecurity clothing and materials and space to perform biosecurity procedures including the ability to sanitize hands
Transition areas need not be elaborate or complex. Concrete pavers or a gravel surface and totes for biosecurity supplies such as clothing, boots and hand sanitizer may be sufficient for some flocks.
1.1.2 Target Outcome
Visual indicators are in place to define the Controlled Access Zone (CAZ) and Restricted Access Zone (RAZ).
Having put the zones and access points in place it is essential that they be easily identified. This can normally be achieved with a combination of signs and barriers.
Whatever method is used, a key factor is the ability to ensure regular access to the CAZ can be closed /blocked if needed.
It is important to have a physical or visual barrier separating the CAZ from the RAZ at which point additional measures such as footwear changing and hand cleaning can take place. This can be in an enclosed area or anteroom which can be kept clean and prevent access by pests and other animals. Transition areas as described in Section 1.1.1 can be used for moving between the CAZ and RAZ of range/pasture production.
1.2 Entry/Movement/Exit Controls
1.2.1 Target Outcome
People working on the premises are knowledgeable of and understand the importance of and rationale behind the CAZ, RAZ and CAPs.
Owners or keepers of poultry need to ensure that everyone understands not only where and what the zones are but also the reason why the zones are in place. This requires communication, training and supervision of people on the premises. See sections 3.6.1 and 3.6.2
People who understand the purpose of a biosecurity measure are more likely to adopt the practice as part of their daily routine and ensure that any contractors or visitors coming onto the premises abide by these measures.
It is important that the same knowledge is shared with family members, people who are on the premises but do not work with poultry, and any temporary workers.
1.2.2 Target Outcome
Access to the CAZ and RAZ is controlled by appropriate measures and routine procedures. Tools/equipment/facilities necessary to accomplish the established procedures are available, functional and maintained for their required purpose.
Diseases can be brought in or spread on clothing, footwear, hands, vehicle tires or dirty equipment. To minimize these risks every premises needs to have clearly defined control measures in place for accessing the CAZ and RAZ.
- Restrict access to the CAZ by establishing a CAP. The CAP is the clearly defined entry point that can be closed with a barrier. This barrier may include a gate, chain or other device. Restricted entry is communicated through biosecurity signage
- Control access to the RAZ through a physical barrier which may include an ante-room, transition area, a barn door or gate and appropriate signage. Controlling access to this area is critical as this is where diseases can be stopped from gaining access to the flock or being transmitted from the flock to other flocks
- Limit access to the CAZ and the RAZ to essential personnel and service providers required for flock production
- Accompany visitors when entry to the premises is required
- Provide facilities, equipment and materials to sanitize hands, and clean and disinfect footwear and equipment, and perform clothing and boot changes as necessary between zones based on the established routine biosecurity protocols for daily operations
- Establish biosecurity procedures for entry of personnel and essential visitors based on the relative risks of disease transmission
- Maintain a visitor log
Maintain a visitor log. Record movements on and off the premises or at the level of the RAZ.
Requiring visitors to sign in provides the opportunity for evaluating visitor biosecurity risks and discussing biosecurity requirements for access to the site or at the level of the flock. Additionally, knowing who has been on the premises provides the information necessary to follow up and identify other potentially infected premises quickly. Ideally where people have been and where they are going next. The faster the disease is contained, the quicker producers and industry can get back to business.
The best way to ensure that everyone understands the requirements is to have written instructions that clearly describe the steps to be followed for access to the CAZ and RAZ. This provides a consistent template for communication and training. Refer to the farm diagram, created during the development of a biosecurity plan, when discussing biosecurity requirements. Elements of a farm diagram may include a map of the property and locations of:
- premises boundaries
- farm buildings (barns, equipment, miscellaneous etc.), flock areas, CAZ(s), RAZ(s), CAP(s)
- office, parking
- feed, feed supplements and bedding storage
- manure/compost storage
- mortality storage
- water treatment and inline medicators
- other areas as necessary
Section 2 Animal Health Management
2.1 Animal Introduction/Movement/Removal
2.1.1 Target Outcome
Each placement or removal of poultry is recorded and carried out with appropriate scheduling, isolation or segregation to minimize the introduction or spread of disease. People, equipment and vehicles are managed to ensure they do not pose a risk of introducing or spreading disease.
Every time poultry are moved onto or from the premises, or between barns/flock areas, there are associated risks for the introduction and spread of infectious diseases. It is therefore important to schedule these movements to keep risks to a minimum.
Proper scheduling:
- enables the segregation or isolation of poultry or flocks within individual barn units/flock areas
- regulates traffic flow within and between premises
- may reduce the risks associated with activities such as catching or placement of new poultry that occur in close proximity to the resident flock when live poultry will remain on the premises
People catching or placing poultry, where live birds remain, should wear clean clothing and boots prior to entering the RAZ.
As outlined in the Poultry Service Industry Biosecurity Guide, service sector personnel are responsible for being aware of and complying with the producer's site-specific biosecurity plan or adhering to their company's biosecurity standards if higher than those requested by the producer.
Movements should be planned and recorded so, if an infectious disease is suspected, flocks can be quickly traced and isolated if required.
"All in/all out" placement of single-age poultry within the barns/flock areas presents the least risk. Under this system a new flock is introduced into a barn/flock area or premises within a short time frame. Facilities are emptied, cleaned and disinfected or otherwise managed to reduce pathogen load (for example barn heating, litter treatment and downtime) before the introduction of the next flock.
In flocks where "all in/all out" placement does not apply, the risks are greater and additional precautions are needed as outlined in target outcome 2.1.3.
It is important that all new poultry brought onto the premises are from a source that has an active disease surveillance and risk mitigation program in place:
- source poultry from a hatchery that operates under a disease control program or from flocks that have current health records and no evidence of infectious disease
- ensure that poultry introductions have equivalent health status and vaccination history (levels) as resident flocks
Poultry that are to be introduced into barns with multi-age flocks should be kept separate for a quarantine period before introduction. Consult your veterinarian or poultry specialist to identify an appropriate time period.
2.1.2 Target Outcome
The downtime between flocks is optimized in each barn/flock area.
Downtime is a period of time that starts with a barn/flock area being emptied of poultry and ends with the placement of new poultry. The period allows for the natural reduction in numbers of disease-causing micro-organisms (pathogens) within the barn/flock area.
Downtime between flocks within a barn or flock area should be maximized to allow adequate time for this pathogen reduction to occur.
Pathogen load is reduced in the absence of a host. The longer a barn or flock area is left empty between flocks, the less likely it is that disease organisms will remain a threat. Pathogen load is also significantly reduced with the removal of organic material and a thorough cleaning and disinfection process. Cleaning and disinfection surfaces poultry come into frequent contact with is particularly important as well as surfaces that pose a risk for residual contamination including: barn walls and flooring, waterers, feeders, heaters, ventilation systems (fans) and equipment used for cleaning and disinfection. It is important to prevent re-contamination of the barn/flock area following barn cleanout (cleaning and disinfection) and prior to placing poultry. When a full cleaning and disinfection is not performed other strategies to manage pathogen loads can be used including heating barns and treating litter.
To be effective, the whole barn or flock area should be clearly separated from other barns or flock areas (that still contain live poultry). This could potentially include adjoining barns between which there is a shared service area such as an egg packing room. If so, the egg packing room should be included in the cleaning process at the same time as the barn that has been emptied.
If there is not a break between flocks, or barns/flock areas are not emptied of poultry, an effective downtime should occur at least once a year as a minimum. If annual downtime is not performed, additional precautions should be taken as detailed in target outcome 2.1.3
2.1.3 Target Outcome
More stringent additional biosecurity measures are implemented either at the barn, flock area or premises level where "all in/all out" scheduling and downtime is not practical.
Where "all in/all out" scheduling or maximized downtime as per section 2.1.2 is not possible, particular and constant focus on the application and enforcement of daily in-barn or flock area biosecurity procedures for both farm personnel and visitors is warranted.
Additional biosecurity measures are required to mitigate the potential disease risks from movements (e.g. poultry, people, equipment and vehicles) between premises and/or barns and flock areas within a premises. This is particularly important on farms with multi-age flocks, multi-species premises, and when there are new introductions and/or returning birds to allow for the separation/quarantining of poultry that are to be added to an existing flock and for the maintenance and hygiene of barns that contain multi-age flocks.
Critical areas include:
- managing and controlling access to RAZ
- ensuring clothing and footwear cleaning and disinfection or changes when entering and leaving the RAZ
- hand sanitation
- managing traffic flow and scheduling of activities on the site
2.2 Ongoing Monitoring of Health Status and Response
Know the health status of the flock and be prepared to react.
In order to recognize an important disease condition and effect appropriate and prompt action, it is critical to know the disease status of the flock. In the event of a reportable disease, early diagnosis and disease surveillance is critical in order to contain the pathogen.
2.2.1 Target Outcome
Individuals who monitor poultry are knowledgeable and experienced in monitoring flock health, the recognition of disease conditions, and timely response protocols.
It is not expected that keepers of poultry or their staff will be able to identify the signs of specific diseases. The diagnosis of diseases should be left to veterinarians and laboratories.
However, it is important that personnel are suitably experienced or trained in order to be able to identify any changes in behaviour, appearance, mortality patterns or productivity within the flock that may indicate an infectious disease is present.
If deviations from the norms are identified, people must know what actions to take and within what time frame. Early intervention reduces the size and scope of a disease event, reducing the number of infected poultry, the pathogen load in the barn/flock area/environment, and opportunities for pathogens to be carried from the site.
2.2.2 Target Outcome
Daily procedures for observation, and culling if necessary, are followed.
Early detection is vital to prevent the spread of disease, so a minimum of a daily walk through the flock is essential. This gives the opportunity to identify poultry that are demonstrating abnormal behaviour or signs of sickness.
Increase flock monitoring after higher risk activities such as placements, and vaccination crew or catching crew visits, and following higher risk periods such as seasonal risks (e.g. migratory birds close to the farm) and during local outbreaks.
The advantage of this approach is that sick poultry can be culled and removed from the flock and signs of disease can be spotted before increased mortality and decreased feed or water consumption are apparent. It will also ensure that all mortalities are removed from the flock daily.
Euthanasia and biosecurity considerations
Procedures for managing birds that are sick are in place to ensure their welfare while minimizing the risk of disease transmission. The NFACC Code of Practice for the Care and Handling of Hatching Eggs, Breeders, Chickens and Turkeys (June 2016), requires that "sick or injured birds and birds that exhibit obvious signs of pain must be promptly treated or euthanizedFootnote 1 by competent personnel". The code indicates that "To alleviate pain and suffering when there is no reasonable prospect for recovery, euthanasia of birds is necessary".
Similarly, the NFACC Code of Practice for the Care and Handling of Pullets and Laying Hens (2017) indicates: "sick or injured birds that are suffering and unlikely to recover must be euthanized without delay".
Wearing appropriate personnel protective equipment while performing the euthanasia of sick poultry can minimize contamination of clothing and hands, exposure of personnel and reduce the transmission of pathogens within and between flocks.
Assign trained personnel to euthanize poultry and securely store and transport the poultry to the storage and disposal area as per section 3.1.2 or securely package for submission to a diagnostic laboratory as per section 2.2.4
Following euthanasia of sick poultry, it is a best practice that all equipment used during this procedure be cleaned and disinfected and personnel should wash their hands and don clean PPE before returning to other duties.
2.2.3 Target Outcome
A daily mortality log is maintained for each flock.
Mortality records are a key tool in assessing the health of a flock. The keeping of records on a daily basis allows for the tracking of mortality numbers by day, establishment, or production cycles. A steady or sudden increase in mortality numbers is a clear indication that an infectious disease may be present.
Ideally mortality records should be cross-checked with feed and water consumption and/or production records to aid in the identification of causes of increased mortalities.
2.2.4 Target Outcome
Unusual morbidity or mortality triggers contact with a veterinarian and disease diagnosis action. Suspicion of diseases that are contagious, of economic importance, or reportable, triggers a "disease response plan" that provides guidance to individuals on the appropriate procedures to follow.
If record-keeping and/or observation indicates that the numbers of mortalities and culls are unusually high or carcasses have unusual signs of disease, or if significant factors such as a noteworthy drop in feed and/or water consumption or in production are identified, veterinary advice should be sought.
If an infectious disease is suspected or officially diagnosed, keepers of poultry and staff should have an action plan in place so the necessary procedures can be followed without confusion or delay.
Measures may include self-quarantine and an enhancement of routine biosecurity procedures.
Critical components of a disease response plan and self-quarantine include:
- obtaining a veterinary diagnosis
- informing farm personnel and service providers of the situation
- strictly controlling and restricting farm and flock access to only those people necessary for animal care and wellbeing
- temporarily halting the movement of poultry, eggs, manure, culled birds, and mortality and postponing deliveries
- performing enhanced biosecurity procedures including cleaning and disinfecting all equipment and performing clothing, boot changes, and hand washing on entry and exit to the CAZ and RAZ
- initiating treatment and communicating disease information/diagnosis as necessary to appropriate parties: (e.g. poultry boards and government)
- continuing to practice enhanced biosecurity and flock monitoring as per veterinary advice post diagnosis until the situation resolves
- contacting a federal veterinarian in the event of a suspected reportable disease
Collection of carcasses and/or samples for diagnostic purposes
Selection and submission of relevant samples is important to ensure that they provide the best possible information to assist in obtaining a disease diagnosis. Any movement of potentially infected birds or samples from birds to a diagnostic laboratory must prevent contamination of the samples and the potential transmission of pathogens off site.
- Contact your veterinarian to request a flock health inspection to obtain a tentative diagnosis. If samples are required for further diagnostic evaluation, request your veterinarian to collect and submit samples to a diagnostic laboratory. Your veterinarian will know what samples are required and the procedures for collecting and submitting
- If your veterinarian is unavailable or you have been instructed to submit samples, contact the laboratory to obtain the sample submission protocols and submission forms
- Consider submitting blood, swabs or tissues from live and recent mortality to reduce the risk of transmitting disease; the samples can provide good diagnostic value for certain diseases and be easily packaged for transport
Section 3 Operational Management
3.1 Mortality and Manure Management
Procedures for waste management are present on each premises.
Mortality Management
3.1.1 Target Outcome
Daily procedures are followed with respect to dead poultry including collection and removal from the RAZ.
Effective mortality management procedures should include an action plan that directs the day-to-day handling of dead poultry found on the premises.
An infectious disease may be introduced into the flock without any clinical signs becoming apparent during its early incubation period. Low pathogenic diseases that result in no discernible or mild clinical signs may be present.
Assume any dead poultry (including sick birds which have been culled) could be infected with a pathogen. Handle appropriately to ensure that any potential pathogens are not spread beyond first the barn/flock area and then the premises level.
- Mortality should be promptly collected and removed from contact with the flock. Removal from the RAZ should occur as soon as possible and at least daily
- Mortality that is not immediately removed from the RAZ, should be contained in leakproof, containers that prevent access by pests and poultry until removal at the end of the day
- To minimize potential exposure and spread of disease, people collecting mortality should wash and sanitize hands before resuming other activities within a barn/flock area. When there are concerns of zoonotic disease, disposable gloves are recommended
- It is a best practice to change PPE (for example boots and outer clothing) when moving between zones to minimize common contact between zones. This is particularly important when moving between barns or re-entering a barn following mortality collection and removal from the RAZ
- Suitable containers for collecting and transferring mortality include but are not limited to:
- a leakproof pail or tote with a tight fitting lid
- a labelled, closed cart designated for this purpose
- a plastic leakproof bag
3.1.2 Target Outcome
A dead poultry storage system, which protects the carcasses from scavengers and pests until final disposal, is utilized on the premises.
Dead poultry being transferred to the storage area and final disposal location should be moved in sealed containers so that no feathers, fluids or other parts of the carcass are able to escape and contaminate surfaces.
Each premises should have a properly designed dead bird isolation/storage system which fully contains carcasses. Dead birds are covered and protected from scavengers and pests through to final disposal (examples include chest freezer; closed transportable container; and an enclosed facility securely located from the flock, feed and water sources).
3.1.3 Target Outcome
Carcass disposal, including any on-farm disposal (incineration, composting and burial), is done in accordance with provincial or municipal guidelines. If a rendering service is utilized then the pickup is performed to minimize any biosecurity risk.
Effective mortality management procedures would include an accepted method of carcass disposal; ensure compliance with provincial and municipal guidelines.
Establish plans and procedures for managing the collection and disposal of routine levels of mortality and elevated mortality; this is frequently a requirement under provincial farm plans.
The movement of carcasses between poultry premises for disposal poses a risk for spreading disease and should be minimized.
Manure Management
3.1.4 Target Outcome
Manure is suitably handled and stored to minimize the risk of transferring disease organisms to poultry flocks.
Manure can be a high-risk source of pathogens; therefore, there should be a clear management strategy for its handling and storage.
Pathogens in manure can be spread by air, in dust, or on people, equipment and vehicles.
The safest practice is for manure to be composted on-site and disposed of away from poultry flocks. The composting process should be managed to ensure appropriate mixing and heating to inactivate pathogens prior to disposal.
Where manure is stored and spread on the premises, it should be stored and managed in a manner that does not allow for its accidental reintroduction into the RAZ.
All methods of manure handling, storage and disposal should meet the requirements of federal and provincial legislation.
3.2 Premises, Building, Equipment and Vehicle Cleaning and Disinfection
3.2.1 Target Outcome
A cleaning and disinfection program is in place that applies to premises, buildings, equipment and vehicles.
It is advisable to apply a consistent approach to cleaning and disinfection on the whole premises. It is more difficult for diseases to become established or spread in a generally clean environment, where buildings, equipment and vehicles are routinely cleaned and when necessary disinfected.
Cleaning and disinfection of barns and flock areas, to the extent possible, following flock cycles can help break the cycle of infection. When a full cleaning and disinfection is not achievable other strategies to manage pathogen loads can be used including heating barns and treating or composting litter.
Cleaning and disinfection (and personal sanitation such as hand washing, boot and clothing changes) take on increasing importance:
- when "all in/all out" placement of single-age poultry and maximizing downtime between flocks cannot be achieved
- when entering RAZs while birds are present and the birds will remain in production and on range/pasture production
- when entering sites where a RAZ incorporates multiple barns while birds are present and the birds will remain in production
- during and following disease outbreaks
The methods and degree of cleaning and disinfection can vary to meet the needs and situation. Written instructions will ensure that all individuals are clear about the procedures for cleaning and disinfection and will encourage consistency.
Written instructions should take into account seasonal climate changes and the challenges they pose.
3.3 Facility Maintenance
3.3.1 Target Outcome
A program for facility maintenance is in place.
Well-maintained buildings and storage facilities play a significant role in successfully achieving several of the other target outcomes listed in this standard by:
- preventing access by pests and other animals and installing wild bird deterrents
- cleaning-up feed spills immediately
- ensuring that stored feed, bedding, and litter in the barns are not affected by rain
- being easier to clean and disinfect
In addition, maintenance procedures should ensure that poultry are kept in the best possible environment. Poorly maintained ventilation systems, for example, may help to create an environment that is favourable for the rapid buildup and spread of disease within a flock.
Facility maintenance also includes maintaining boundaries and barriers around the biosecurity zones.
- Prevent the accumulation and pooling of water in the CAZs and RAZs, particularly the areas around barns and range areas, and the generation of leachate from manure and mortality storage areas
- Pathways and laneways for vehicles, equipment and people should be hard surfaces that can be maintained clean
- Maintain the area around barns free from debris and vegetation and mow and/or maintain regularly
- When trees and shrubs are present (when used as shelter belts or on free range premises to provide shade), they should be selected to minimise wild bird attraction
3.4 Water/Feed/Bedding Management
Water Management
3.4.1 Target Outcome
A water management program is in place to ensure that water is potable and meets local guidelines for poultry consumption.
The water system (water source, storage, delivery and treatment systems) can be a source of pathogens. Contamination may occur from pests, wildlife and other sources through direct or indirect contact. Prevention and control measures can minimize if not eliminate this risk.
Sources of water that are susceptible to pathogen contamination include bodies of surface water (e.g. reservoirs, ponds, lakes and rivers), groundwater aquifers and rainwater collection systems. Surface water systems pose a significantly higher risk for the introduction of infectious organisms and undesirable substances and are not recommended for use without a functioning treatment system.
Manage water systems to ensure water quality; this may include, cleaning, disinfecting, and flushing systems and testing water quality.
Waterers, particularly those used in range and pasture production, should be designed and sited to minimize access to and contamination from pests.
Feed Management
3.4.2 Target Outcome
Feed is obtained and stored in a manner that minimizes the risk of contamination by pathogens.
Feed that has not been properly stored presents a risk to the flock. Feed that is exposed to or contains pests, may be contaminated with pathogens which will then be transferred to the flock. Feed which has become damp also provides an ideal environment for the rapid development of harmful organisms.
It is important to ensure that feed is handled and stored properly on the premises and purchased from a reliable source that has a Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) plan or similar systems in place.
To reduce the attraction for wild birds, ensure feed storage cannot be accessed by wild birds and feed spills are immediately cleaned up.
Feeders, particularly those used in range and pasture production, should be designed and sited to minimize access and contamination by pests.
Bedding
3.4.3 Target Outcome
Bedding is obtained and stored in a manner that minimizes the risk of contamination by pathogens.
Fresh bedding material that has not been properly stored and protected from contamination, particularly by wild bird and rodent pests, presents a risk to the flock. Bedding storage protects bedding from water, access by pests and other potential sources of contamination. The same principles as those applied to feed should be applied to bedding.
3.5 Pest Control Program
3.5.1 Target Outcome
An integrated pest control program is present.
Pests (particularly insects, rodents and wild birds) can serve as a source and mechanism for spread of pathogens. Poultry exposure can be direct or indirect (contamination of feed, water, equipment and materials).
An integrated program of pest control relies on an effective management of the production environment, the maintenance and modernization of the facilities, and direct control methods (mechanical and chemical) to prevent introduction and spread of contagious disease organisms by pests.
Poultry keepers with range and/ or pasture production need to use a variety of methods to manage/control wild birds.
Garbage Management
3.5.2 Target Outcome
Garbage is effectively and safely disposed of.
If household and farm-related garbage is not effectively stored and disposed of, it can be a risk to the poultry flock by attracting pests and predators which can introduce disease either directly or indirectly by moving potentially contaminated garbage around the premises.
Garbage should be disposed of regularly and safely (in accordance with federal and provincial laws) and stored in a manner that prevents access by pests and predators.
3.6 Biosecurity Program and Training
3.6.1 Target Outcome
All people working on the premises are knowledgeable of, and understand the rationale behind and importance of, biosecurity and biosecurity protocols.
It is important for all people to receive training/briefing before starting to work with poultry so they have a general understanding about all aspects of the process and not just their own tasks.
People who understand the purpose of a biosecurity measure are more likely to adopt the practice as part of their daily routine. They are more likely to ensure any visitors and service contractors act in accordance with the farm biosecurity practices.
3.6.2 Target Outcome
All people working on the premises have reviewed the applicable biosecurity-related instructions as needed, based on their assigned tasks.
The best way to ensure people (including family members if applicable) are clear on how to complete their assigned tasks is to have written procedures that are reviewed with the people doing the work and updated when necessary.
A Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is a documented procedure based on generally accepted good practices. It must be easy to read while describing the steps followed to meet an objective (for example an SOP that details the barn cleaning and disinfection procedure). SOPs should be followed at all times.
Additional provision for extra or more rigorous biosecurity measures in the event of a disease outbreak either on the premises or within the region should be included.
Keepers of poultry who do not employ staff and carry out all the activities on the premises themselves should still document their procedures. This will help make sure the target outcomes in this document are being addressed and it can serve as a guide for farming procedures when temporary assistance is required.
Annex A – Main Principles and Associated Recommendations Identified by the Technical Sub-Committee
The Avian Biosecurity Advisory Committee (ABAC) was mandated to identify practical, effective controls utilizing science-based analysis and objective literature. The membership of ABAC has representatives from the whole spectrum of potential users of this document.
This science-based document recommends practices to reduce the risk of transmission and maintain effective control of Avian Influenza or other highly contagious respiratory pathogens. For more detail on how this document was developed, please see the endnote.Footnote 2
Often prevention and intervention methods need be done in a logical sequence to be effective. Adopting one recommendation without first doing another may render the action unsuccessful. Further, barn level recommendations and premises level recommendations are closely linked and the success of one is dependent on the other.
The following guidelines have been prioritized based on published infectious disease literature (i.e. principle 1 has the greatest potential for reducing risk of transmission and maintaining effective control of Avian Influenza compared to principle 2, etc.). Nevertheless, all principles are important.
Principle 1: Procedures for mortality management are present on each premises.
The introduction and presence of an infectious agent is difficult to identify in the early incubation period before development of clinical signs or in a low pathogenic agent with an absence of clinical signs. Assume any dead bird could be infective and handle appropriately to ensure that any potential pathogens are not spread beyond first the barn and then the premises level.
Effective mortality management procedures should include the following: a physical container or structure for proper carcass isolation/storage on removal from the production area, an accepted method of carcass disposal and an action plan that directs the day-to-day handling of dead birds found on the premises.
Recommendation 1: Each premises should have a properly designed dead bird isolation/storage system which fully contains carcasses. Dead birds are covered and protected from scavengers and insects through to final disposal (examples include chest freezer, closed transportable container, enclosed facility remote from barn).
Recommendation 2: Each premises should have appropriate carcass disposal. This may include on-farm disposal (incineration, composting and burial, according to provincial or municipal guidelines). If a rendering service is utilized, then the pickup point must be external to Controlled Access Zone (CAZ).
Recommendation 3: With respect to dead birds found in the barn, each premises should have daily procedures to follow that include timely collection, removal from production area, storage and disposal as described above.
Principle 2: Know the health status of your flock and be prepared to react.
To recognize an important disease condition and effect appropriate and prompt action, it is critical to know the disease status of your barn. In the event of a foreign animal disease, early diagnosis and disease surveillance is critical in order to contain the pathogen. Monitoring flock health should include: at least the daily observation of the flock and culling if necessary, maintaining a mortality log, recognition and prompt action in the event of suspicious clinical signs or unacceptable mortality followed by prompt diagnostic action and activation of an "emergency response plan."
Recommendation 1: Each barn should maintain a daily mortality log.
Recommendation 2: Disease diagnosis action should be triggered in the event of any unusual morbidity or mortality. Each producer should establish a working relationship with a poultry veterinarian trained in poultry disease diagnosis. Poultry veterinarians are trained in disease recognition and the appropriate methods of sample submission to a certified veterinary diagnostic laboratory.
Recommendation 3: All producers should know and understand the "emergency response plan" that directs employees on the appropriate procedures to follow in the event of morbidity or mortality highly suspicious of contagious economically significant or notifiable diseases. This will include but is not limited to immediately contacting the premises veterinarian, self-imposed barn/premises isolation/containment, self-declaration and notification of appropriate officials, maintaining the current visitor log for traceback purposes, etc.
Recommendation 4: All premises employees should be trained in monitoring flock health, recognition of conditions that should trigger a response, and timely response protocols.
Recommendation 5: Producers should participate in an ongoing national surveillance program.
The surveillance program should be designed to reflect the premises' risk level. This may include ensuring started stock is disease-free, testing after high-risk activities (e.g. visit from vaccination crew), frequency of testing associated with seasonal risk or location risk. A national surveillance program must be statistically valid, be cognizant of biosecurity and marketing concerns in design, and encourage compliance by effective and appropriate compensation.
Principle 3: Each introduction or removal of birds from a barn or premises is carried out with appropriate scheduling, isolation or segregation to minimize introduction or spread of disease.
Proper scheduling enables segregation or isolation of birds within individual barn units, regulates traffic flow within and between premises, and reduces proximity risks between barns where loading or unloading activities are occurring and live birds remain on a premises. An "all-in/all-out" approach and appropriate "downtime" between flocks should be targeted for disease control where possible.
Recommendation 1: Each barn should have a bird arrival and bird dispersal schedule with associated records. "All in/all out" management should be a target - introduction and dispersal should be completed in a short time (within seven days).
Recommendation 2: Each barn should maximize the downtime between flocks where possible. Ideally, this should be at least 14 days to allow adequate time for pathogen reduction. Each premises should maximize a downtime where possible.
Recommendation 3: If recommendations 1 and 2 cannot be achieved on-premises, then enhanced biosecurity measures must be implemented either at the barn or premises level as the situation dictates. At the barn level, for activities such as partial flock shipment over a period greater than seven days, introduction of spiking males, heavy tom production, or movement to another barn for further growth, enhanced measures may include but are not limited to: crate cleanliness, full cover-ups for catching crews, and enhanced cleaning procedures and sanitation using appropriate products at optimum concentrations. At the premises level, if for example there is more than one barn per premises with each barn at a different stage of production, enhanced biosecurity measures should be taken between barns to enable barn segregation. These may include but are not limited to: washing and/or hand sanitation, change of clothing and boots, control of human traffic and/or fomite movement.
Principle 4: Ensure that access to the barn and premises is controlled through the establishment of protective zones and controlled access points.
Control of people and pets is important in reducing the risk of carriage of a pathogen into a barn or onto a premises. Controlled access to the barn can be achieved. Controlling access to a premises is more difficult. In commercial situations, the Controlled Access Zone (CAZ) commonly refers to the area around the barns. The Restricted Area (RA) generally refers to barn interiors or production area.
Recommendation 1: Barn access should be controlled via the controlled access point (CAP). Only essential personnel should enter a barn. Pets should be prohibited from entering a barn. Ideally, in order to facilitate compliance, this would include an appropriately designed and well-maintained barn entrance or anteroom with clearly visible signage, locked doors and hand-washing/hand sanitizing facilities.
Recommendation 2: Premises access must be controlled. Only essential personnel should enter the CAZ and visitor parking must be outside the CAZ. Only essential vehicles should enter the CAZ. In order to facilitate compliance, each premises should have a visually defined CAZ (signage, ropes, stakes, or fencing) and the entrance to the CAZ should be capable of being closed. This may be accomplished by a single laneway that can be blocked or a physical gate.
Recommendation 3: Procedures are in place to minimize potential carriage between the CAZ and RA. There must be no common footwear contact between the CAZ and the RA (i.e., boot changes, sanitation, or plastic boots). There must be a means to sanitize hands prior to entering or leaving the restricted area. Appropriate protective clothing (clean or restricted to barn cover-ups and boots) should be worn in the barn. Barn clothing and boots should be supplied for visitors.
Recommendation 4: Each premises must have established procedures for employees entering a barn and moving to other barns within a premises. Employees should be trained and understand the reason behind and importance of these procedures. These procedures should include but not be limited to: hand sanitation, not being in contact with other birds within a 24-hour period, and appropriate boot sanitation and change of clothing.
Principle 5: Drinking water for birds should be free from significant pathogens and meet water quality standards for livestock/poultry consumption.
Recommendation 1: Water should not be from open ponds or other open sources. Water must be treated if necessary. For range production, covered water sources or closed water systems should be used.
Principle 6: Measures are used to prevent introduction and spread of contagious disease organisms by pests.
Recommendation 1: Integrated pest control should be in place (insects, wild birds, rodents).
This may include but is not limited to: covered feed bins, closed feed systems, screened openings, routine baiting program, gravel strip outside building foundation, emptying of feed lines/boots/hoppers at cleanout, CAZ kept free of debris and long vegetation.
Recommendation 2: For range production, alternate measures can be used, including: sufficient covered or roofed space to house all poultry at risk times (seasonal), and well-maintained fencing against livestock, pets and predators.
Development of this document
The Technical Committee of the Avian Biosecurity Advisory Committee was mandated to identify areas of practical, effective controls with respect to Avian Influenza. This was done utilizing science-based analysis that was objective, impartial and avoided preconceived assumptions or beliefs, identified gaps and allowed a cost/benefit analysis with the aim of improving implementation and compliance.
The Technical Committee work had a focus on highly contagious respiratory pathogens such as Avian Influenza. The approach taken for this work considered each unit level of operation separately (barn, premises, etc.), presence and nature of disease agent and routes of transmission.
A detailed list of scenarios, risk introduction and exit and interventions was developed. Based on extensive literature review parameter values, effectiveness, risk indexes, index interpretation, severity and acceptable levels were identified. Auditable parameters associated with each intervention were identified and compared to existing OFFS programs.
The Halvorson Risk Index tool was selected for use in the analysis of the possible interventions to calculate relative risk level pre-intervention and post-intervention and calculated reduction efficacy for each intervention. The list of interventions was sorted from most to least effective risk reduction.
The CMi survey risk score index was used where possible to corroborate the results from the above analysis. (CMi is an external consulting firm that is experienced and recognized in the field of biosecurity).
The Technical Committee produced a document listing 6 main principles for on-farm Avian Influenza biosecurity in priority order, with several associated recommendations (also in priority order) as minimum guidelines. These are targeted for effectiveness and also response stratified. These principles and recommendations are based on scientific analysis of efficacy and have high level of cost benefit return to encourage compliance. Because they are based on agent/host interaction, rather than production system, the principles are also applicable to any level of poultry production.
Revision of the Standard in 2018
The National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard, first published in 2009, has been revised and re-released in 2018 based on an increased awareness and understanding of the risks and management of infectious diseases in the poultry industry. The revised standard provides poultry producers, backyard flock owners and industry with additional guidelines and best practices on reducing the spread of disease, including but not limited to the following topics:
- assessing disease risks
- developing a farm biosecurity plan
- routes of disease transmission and approaches to disease control
- establishing biosecurity zones and managing movements of people, equipment and vehicles
- developing disease response and self-quarantine protocols
Funding to support the revision was provided under the Growing Forward 2 initiative. The National Avian Biosecurity Advisory Comittee (ABAC), previously established in 2006, was reconvened to revise the standard. ABAC provided broad representation of poultry stakeholders and was comprised national and provincial producer organizations, federal and provincial governments, academia and poultry producers. Recent scientific literature on poultry diseases, disease outbreaks, and disease risk mitigation measures were reviewed and guidelines and best practices identified and incorporated. The revised document was approved by ABAC in January of 2018 and letters of non-objection provided by the four national poultry producer associations (Chicken Farmers of Canada, Turkey Farmers of Canada, Canadian Hatching Egg Producers, and Egg Farmers of Canada) by March of 2018.
Self-Evaluation Checklist
Self Audit ( or )
Section 1 Access Management
1.1 Designation of Zones
- 1.1.1 Recognizable zones and controlled access points are in place
- 1.1.2 Visual indicators are in place to define the Controlled Access Zone (CAZ) and Restricted Access Zone (RAZ)
1.2 Entry/Movement/Exit Controls
- 1.2.1 People working on the premises are knowledgeable of and understand the rationale behind and importance of the CAZ, RAZ and CAPs
- 1.2.2 Access to the CAZ and RAZ is controlled by appropriate measures and routine procedures. Tools/equipment/facilities necessary to accomplish the established procedures are available, functional and maintained for their required purpose
Section 2 Animal Health Management
2.1 Animal Introduction/Movement/Removal
- 2.1.1 Each placement or removal of poultry is recorded and carried out with appropriate scheduling, isolation or segregation to minimize the introduction or spread of disease. People, equipment and vehicles are managed to ensure they do not pose a risk of introducing or spreading disease
- 2.1.2 The downtime between flocks is optimized in each barn/flock area
- 2.1.3 More stringent additional biosecurity measures are implemented either at the barn, flock area or premises level where "all in/all out" scheduling and downtime is not practical
2.2 Ongoing Monitoring of Health Status and Response
- 2.2.1 Individuals who monitor poultry are knowledgeable and experienced in monitoring flock health, the recognition of disease conditions and timely response protocols
- 2.2.2 Daily procedures for observation, and culling if necessary, are followed
- 2.2.3 A daily mortality log is maintained for each flock
- 2.2.4 Unusual morbidity or mortality triggers contact with a veterinarian and disease diagnosis action. Suspicion of diseases that are contagious, of economic importance, or reportable triggers a "disease response plan" that provides guidance to individuals on the appropriate procedures to follow
Section 3 Operational Management
3.1 Mortality and Manure Management
- 3.1.1 Daily procedures are followed with respect to dead poultry including collection and removal from the RAZ
- 3.1.2 A dead poultry storage system, which protects the carcasses from scavengers and pests until final disposal, is utilized on the premises
- 3.1.3 Carcass disposal, including any on-farm disposal (incineration, composting and burial), is done in accordance with provincial or municipal guidelines. If a rendering service is utilized, then the pickup is performed to minimize any biosecurity risk
- 3.1.4 Manure is suitably handled and stored to minimize the risk of transferring disease organisms to poultry flocks
3.2 Premises, Building, Equipment and Vehicle Cleaning and Disinfection
- 3.2.1 A cleaning and disinfection program is in place that applies to premises, buildings, equipment and vehicles
3.3 Facility Maintenance
- 3.3.1 A program for facility maintenance is in place
3.4 Water/Feed/Bedding Management
- 3.4.1 A water management program is in place to ensure that water is potable and meets local guidelines for poultry consumption
- 3.4.2 Feed is obtained and stored in a manner that minimizes the risk of contamination by pathogens
- 3.4.3 Bedding is obtained and stored in a manner that minimizes the risk of contamination by pathogens
3.5 Pest Control Program
- 3.5.1 An integrated pest control program is present
- 3.5.2 Garbage is effectively and safely disposed of
3.6 Biosecurity Program and Training
- 3.6.1 All people working on the premises are knowledgeable of, and understand the rationale behind and importance of, biosecurity and biosecurity protocols
- 3.6.2 All people working on the premises have reviewed the applicable biosecurity-related instructions as needed, based on their assigned tasks
