Table of Contents
- About this document
- General Producer Guide - National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard
- Section 1 - Access Management
- Section 2 - Animal Health Management
- Section 3 - Operational Management
- Glossary
- Annexes
- Annex A - Self-Evaluation Checklist
- Annex B - Sample Standard Operating Procedures - Procedures for Barn Entry and Exit
- Annex C - Producer Self-Quarantine Protocol
- Annex D - Barn Cleaning and Disinfection in Inclement Weather
- Annex E - Footwear Sanitation
- Annex F - Sample Standard Operating Procedures - Using Footbaths
- Annex G - Sample Standard Operating Procedures - Footbath Maintenance
- Annex H - Sample Mortality Log
- Annex I - Disinfectants
- Annex J - Impact of Federal Disease Control and Response Measures - Producer Considerations for Premises Design and Procedures
About this document
Who is this document for?
This General Producer Guide has been developed as an information resource for the National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard to assist poultry producers with the development of biosecurity plans for their farming operations. Biosecurity planning and implementation reduces the risk of infectious disease transfer within and among poultry flocks. Enhancing your farm's biosecurity protects both individual and industry-wide economic interests. Further, it reduces the risk to public health that may result from certain poultry diseases.
The General Producer Guide and the National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard form the basis of a comprehensive program designed to provide applicable guidance for owners or managers across all the poultry sectors in Canada. This Guide has been developed as a tool for all people and businesses that handle and keep poultry, including large scale supply-managed producers, backyard flock owners, and other domestic bird keepers. It provides guidance to producers on how to achieve the Target Outcomes of the National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard.
The Standard and the associated Producer Guide are designed both to support the development of farm-specific biosecurity protocols for sectors that do not participate in a provincial association or On-Farm Food Safety (OFFS) program - such as the non-regulated commercial and non-commercial sectors - and to complement and enhance existing on-farm programs. The OFFS programs, developed by industry, formally address many elements of biosecurity and will be the primary avenue for implementation, where applicable.
This Guide is based on clear, scientifically justified principles. It details a range of measures that could be implemented to prevent disease-causing agents from entering or leaving a premises that houses poultry.
The importance of biosecurity
There is no formal definition for the word "biosecurity", but it has become the accepted term used to describe the measures needed to protect against the introduction and spread of diseases.
It is in the best interest of poultry keepers to ensure that they are aware of the risks and that they implement procedures to limit the chances of disease developing or spreading. When a bird is infected with a pathogenic organism, there may or may not be obvious signs of clinical disease. Nevertheless, this pathogen can be reproduced in the bird's body, which then sheds the organism into the environment through body excretions, including feces, urates from the kidneys, and aerosols from the respiratory system. The organisms contained in these excretions contaminate the surfaces in the surrounding environment, which then carry the infection to the next bird. If another bird becomes infected and the pathogens are in sufficient quantity to overcome a susceptible bird's immune system, the bird becomes infected and the cycle continues. As the pathogenic organism passes through more and more birds, its numbers in the environment multiply rapidly.
Additionally, pathogenic organisms can change over time to become more or less capable of causing disease. Circulating unchecked within a flock or between flocks of different generations, organisms have greater opportunity to undergo genetic alterations, and thus potentially cause more significant disease in poultry or other animal species, including humans.
Because pathogenic organisms are microscopic, they are invisible to the naked eye. Despite this, they can be found in large numbers in visible material, such as dust, water droplets suspended in the air, and fecal contamination. A dust particle can contain an infective dose. In fact, such a small amount of contaminated material may be hidden on equipment, clothing, footwear, or even hands, allowing the disease to be carried from one flock to another.
Past disease outbreaks, both in Canada and overseas, clearly demonstrate the serious impact that avian diseases can have on business, individual livelihoods, and local communities. The impact may range from the destruction of tens of thousands of birds, to the cancellation of shows or sporting events. The period during which emergency controls are in place may vary depending on how rapidly a disease can be successfully controlled.
Some diseases, known as zoonoses, can infect both poultry and humans. Good biosecurity is therefore an important element in preventing human illnesses.
Those who keep poultry must share responsibility for protecting their business or hobby by reducing the risks associated with the spread of diseases.
Practising good biosecurity has clear benefits as follows:
- healthy birds
- minimized potential for significant costs and losses in revenue
- protection of human health
- unrestricted movement of birds
- protection of other industries, such as feed suppliers, and
- protecting export markets
The use of this document
The General Producer Guide has been organized to follow the organization of the Standard document. It is divided into three sections (the same as in the Standard), representing the foundations of a smoothly operating biosecurity system:
- Access Management
- Animal Management
- Operational Management
In each section, each Target Outcome of the Standard is followed by current information on a variety of biosecurity-related practices as examples of the measures that producers can implement to meet the target outcome. The Guide demonstrates the flexibility required for a variable and complex poultry industry. It is not a full and complete listing of all examples that can be used to meet the Target Outcomes. Many examples relate to large commercial-scale industry, but also apply to other sectors. Optimal or highly effective biosecurity measures are provided in text boxes labelled "Ideally". They represent an ideal for those producers who wish to implement more rigorous biosecurity measures. Other guides, with more sector-specific producer guidance, may be developed in the future.
Biosecurity is best achieved when all of the foundations and their components are in place and are being managed properly. Weak building blocks or poorly implemented biosecurity measures provide a route by which disease might enter the flock or remain undetected within the flock.
All keepers of poultry should focus on achieving a level of control in every component on their property. For those new to the concept of biosecurity, those with limited resources or where it is not practical or applicable to fully achieve all target outcomes, the Guide provides examples of measures to take to mitigate the risks on a day-to-day basis.
A Glossary at the end of the document provides definitions of terms used. There are also a number of annexes, one of which is a self-audit checklist. This checklist can be used to quickly record the Target Outcomes that are being effectively controlled and those that need further action on your premises.
General Producer Guide - National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard
This document provides producer guidance on meeting Target Outcomes of the National Avian On-Farm Biosecurity Standard. These general guidance notes were developed with significant contributions from representatives of the various poultry sectors. They are not a full and complete listing of all methods that can be used to meet the Target Outcomes but do include some existing beneficial practices and other examples to facilitate meeting the Target Outcomes, while providing the flexibility required for a variable and complex poultry industry.
Some specific examples may be presented in boxes. Additional guidelines, in the "Ideally" boxes, may be more difficult and/or expensive procedures to implement, but will improve your biosecurity program. You should consider implementing these additional procedures - especially in scenarios of increased risk (i.e. a disease challenge in the area).
Section 1 - Access Management
1.1 Designation of Zones
1.1.1 Target Outcome - Recognizable zones and access points are in place.
Producer Guidance
Zones and access points may be defined as follows:
Controlled access zone (CAZ): The area of land and buildings constituting the poultry-production area of the premises that is accessible through a securable controlled access point.
Restricted access zone (RAZ): An area inside the CAZ that is used, or intended to be used, to house poultry, including semi-confined and range production, and where personnel and equipment access is more restricted than in the CAZ. Within the RAZ, the unrestricted movement of people, birds, and equipment may occur. The RAZ is sometimes referred to as the "production area" or "restricted area" (RA) in other poultry production documents and guides.
Controlled access point (CAP): A visually defined entry point(s) through which workers, equipment, feed trucks, etc. will enter the CAZ and/or the RAZ.
The CAZ
Recommendations for establishing a CAZ
- Draw, in the initial design phase, a map of your property.
- Ensure that, when deciding on boundaries, the CAZ is large enough to provide a functional buffer zone around the poultry housing units, but remains small enough to allow traffic that is not directly involved with poultry production to travel around the CAZ (not through the CAZ).
- Include all buildings and structures used directly in the production of poultry.
- Note: The shape and size of the CAZ will vary among sites.
- Require personnel and equipment to pass through an appropriate primary CAP when entering or exiting the CAZ.
- Exclude personal residences and non-applicable structures (machine shops and storage sheds, etc.) if they are not used for production equipment and materials. This allows visitors who access a personal residence and personnel who need to enter unrelated machine shops and storage facilities to do so without entering the CAZ.
- Park unnecessary vehicles outside the CAZ.
The RAZ
Recommendations for establishing a RAZ
- Establish the area that is housing the poultry as a RAZ.
- Recognize that the barn entrance to the RAZ is the last line of defence in preventing the entry or exit of disease-causing organisms. Ideally, the RAZ is a physical enclosure that segregates the birds from the external environment and possible exposure to disease agents from outside. A RAZ that includes outside areas (outside pens, laneways for vehicles or equipment, etc.) is at a higher risk for exposure to disease.
- Consider facility operations and your areas of concern regarding internal spread of disease-causing agents when designing a RAZ. Everything within a RAZ can be considered of equal risk status, because of unrestricted movement of people, birds, and equipment within this zone.
- Applies normally to an individual barn, a compartment or floor within a barn, a series of connecting barns for birds that are raised indoors, or an enclosed outdoor area where birds are raised.
- Consider each barn as a separate RAZ in a multi-barn site. Within a single CAZ, having biosecurity procedures among barns is a good practice for reducing the possibility of spreading disease-causing agents from barn to barn.
- Note that, for barns with more than one floor, for barns which are physically joined by a common anteroom, or for barns that contain multi-aged flocks, a single RAZ or several separate internal RAZs may be appropriate. If rooms, compartments, or floors of the barn share a common air space - that is, wall dividers do not extend fully to the ceiling, and/or ventilation is shared - creating separate RAZs may be of little value in preventing disease transmission.
- Establish a visually defined entrance, requiring all necessary traffic, human or otherwise, to pass through an appropriate primary CAP. This includes a transition area or anteroom where the biosecurity procedures can occur for movement between the CAZ and RAZ.
- Note: For some production methods and premises configurations, multiple RAZs may not be operationally feasible. Options, including collective RAZs, are detailed in the diagrams below, with the following understanding:
- If multiple buildings and/or ranges operate without restrictions on movements between the buildings/ranges, at least one RAZ should exist around the entire complex with entry and exit controls.
- This option would be less effective in reducing the possibility of disease spread into/out of the complex, and has no controls to reduce the risk of disease spread within the complex.
- Have your veterinarian or local association help configure a RAZ that would be defined in such a way that is practical, while at the same time, minimize the possibility of disease introduction or spread.
- Ensure that the people who enter your premises are not sick, have not been in contact with sick poultry, livestock, pets and/or people, especially those exhibiting clinical signs related to influenza virus.
The three concepts depicted below provide options for laying out these zones, though other scenarios may better fit your operation.
Concept 1 One controlled access zone with one restricted access zone
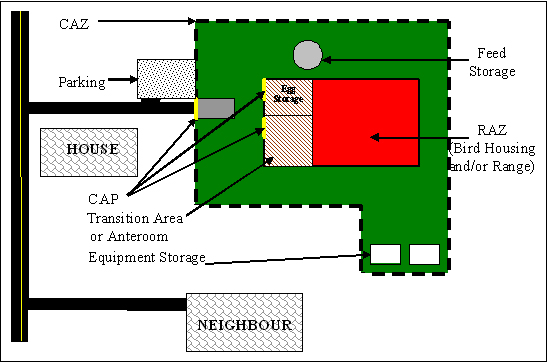
Description for - Concept 1: One controlled access zone with one restricted access zone
A CAZ (green) and a RAZ (red) for a simple farm site, comprised of only one barn and/or range and limited outbuildings. A CAP (yellow) provides access to each zone, and parking outside of the CAZ limits the volume and frequency of traffic movement. A transition area at the front of the barn allows room for people who work on the premises to perform boot and clothing changes, hand washing, and other personal duties. Egg pickup personnel can access the egg storage room (pink) via an anteroom or through a separate exterior door.
CAZ = controlled access zone RAZ = restricted access zone CAP = controlled access point
A CAZ and a RAZ for a simple farm site, comprised of only one barn and/or range and limited outbuildings, can be easily established. The CAZ incorporates all the farming activities, whereas the RAZ is the barn and/or range. A CAP provides access to each zone, and parking outside of the CAZ limits the volume and frequency of traffic movement.
A transition area at the front of the barn allows room for people who work on the premises to perform boot and clothing changes, hand washing, and other tasks. It may also provide room for dry storage or egg collection activities, depending on the needs of the farm site. For egg production, egg pickup personnel can access the egg storage room via the anteroom or through a separate exterior door.
Concept 2 One controlled access zone with multiple restricted access zones
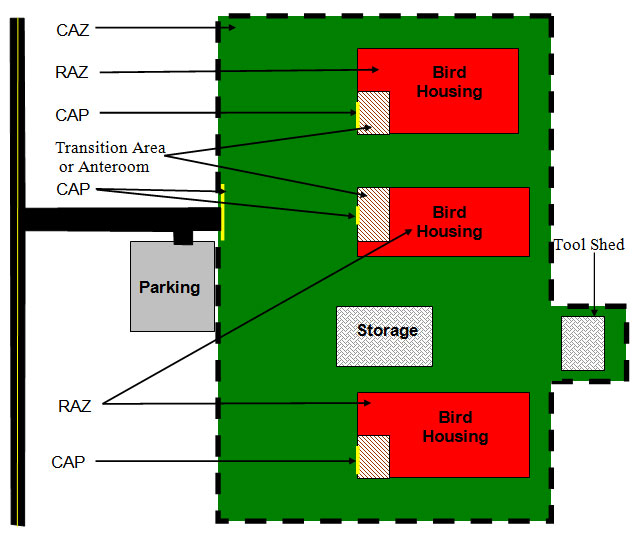
Description for - Concept 2: One controlled access zone with multiple restricted access zones
A larger and more complicated site may contain multiple barns and/or ranges (red), along with equipment and storage buildings (grey), in a single CAZ (green). A separate RAZ and CAP (yellow) have been established for each barn and/or range. Transition areas at the front of each barn and/or range allow personnel to apply appropriate sanitary measures. One CAP provides access to the single CAZ. Parking is established outside the CAZ to reduce unnecessary traffic movements.
CAZ = controlled access zone RAZ = restricted access zone CAP = controlled access point
A larger and more complicated farm site may contain multiple barns, along with equipment and storage buildings. A separate RAZ and CAP have been established for each barn. Transition areas within the barn allow personnel to apply appropriate sanitary measures. One CAP provides access to the single CAZ. Parking is established outside the CAZ to reduce unnecessary traffic movements within the CAZ.
Concept 3 One controlled access zone with a restricted access zone, containing multiple buildings and/or ranges
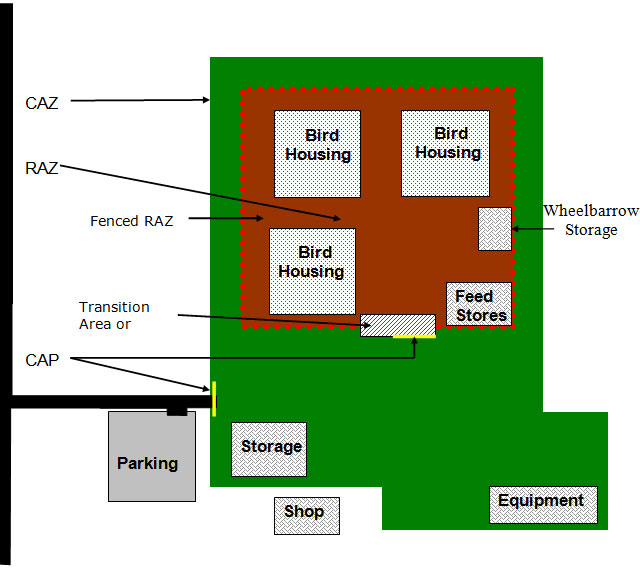
Description for - Concept 3: One controlled access zone with a restricted access zone, containing multiple buildings and/or ranges
A more complex site may contain multiple barns and/or ranges, along with equipment and storage buildings. One CAP (yellow) provides access to the single CAZ (green). The one RAZ (red) inside is not ideal for disease control; however, if the operation includes common equipment and personnel who are moving unrestricted between buildings, it may be the only alternative. Entry into the RAZ is controlled by a CAP (yellow). This could be an anteroom setup for personnel and with cleaning and disinfecting capabilities for larger equipment. Parking is established outside the CAZ to reduce unnecessary traffic movements.
CAZ = controlled access zone RAZ = restricted access zone CAP = controlled access point
A more complex farm site may contain multiple barns and/or ranges, along with equipment and storage buildings. One RAZ, as in this example, is not ideal for disease control; however, if the operation includes common equipment and personnel who are moving unrestricted among buildings, one RAZ, including all buildings and the area inside in which unrestricted movement occurs, may be the only alternative. In this setup, control of disease spread into and out of the complex is less effective than if each barn was a separate RAZ. Further, there is no control of disease spread between the barns. All barns would be of equal biosecurity status (i.e. as if they were all one barn). Entry into the RAZ is controlled by a CAP. This could be an anteroom setup for personnel and with cleaning and disinfecting capabilities for larger equipment. One CAP provides access to the single CAZ. Parking is established outside the CAZ to reduce unnecessary traffic movements within the CAZ.
1.1.2 Target Outcome - Visual indicators are in place to define the controlled access zone (CAZ) and the restricted access zone (RAZ).
Producer Guidance
Recommendations for demarcating the CAZ
- Visually define the entrance (i.e. the CAP). This can be accomplished with signage and visual markers.
Ideally:
- The boundary of the CAZ would be readily distinguishable.
- Boundaries, such as the edge of a cultivated field, driveway, roadway, or the property edge, are used if possible. Boundaries might be distinguished by one or more of the following:
- landscaping (grass cutting, gravel, pathways);
- tree lines, posts, or other visual markers;
- fencing;
- signage.
Recommendations for demarcating the RAZ
- Establish a readily visible boundary. Typically, this would constitute the walls of the housing unit, but could be fencing or other physical barriers if the RAZ were to include more than the structure that is housing animals.
- Visually define the entrance (i.e. the CAP). This can be accomplished with signage and visual markers.
1.2 Entry, Movement, Exit Controls
1.2.1 Target Outcome - People who work on the premises are knowledgeable of and understand the importance of and rationale behind the CAZ and the RAZ.
Producer Guidance
The people who access or work within the zones require a briefing to identify the measures in place regarding access control to the zones and why it is important that they be followed. People who work on the premises should have this covered as part of their training and/or briefing (according to Target Outcomes 3.6.1 and 3.6.2) before starting work. This Guide and the Standards document could be used as training aids. An annual review for people working on the premises would be beneficial.
Individuals who frequent the premises, but do not work within the zones, should understand the importance of avoiding an unintentional compromise of biosecurity. They should know not to enter the zones without being supervised or without having further training. They also need to take responsibility for any accompanying non-essential visitors.
1.2.2 Target Outcome - Access to the CAZ and RAZ is controlled by appropriate measures and routine procedures. Tools/equipment/facilities necessary to accomplish the established procedures are available, functional and maintained for their required purpose.
Producer Guidance
The Controlled Access Points
The purpose of a CAP is to ensure CAZ and RAZ entry and exit is through a place where appropriate procedures can be applied to personnel, vehicles, equipment, and materials that may carry disease-causing agents to minimize disease spread. This may include cleaning and disinfection measures and/or clothing changes. The goal is to reduce pathogen transmission, primarily by mechanical means (common contact), enabling the CAZ and RAZ to be of a higher (more protected) health status than that of the outside environment.
Recommendations for establishing a CAP for the CAZ - physical structures, tools, equipment
- Create one primary CAP to the CAZ.
- Consider both the entrance and the exit as primary access points for premises that have a U-shaped access point, as they see the common flow of traffic on the premises.
- Limit the number of CAPs to ensure adequate maintenance and monitoring.
- Devise a method of blocking the entrance to the CAZ when needed (i.e. in a disease response situation) - a single laneway blocked by a wagon or other obstacle, for example.
Ideally:
- There is a lockable gate, chain, or other device that restricts access of vehicles and people.
- The barrier is kept closed, except when vehicles and personnel are entering or leaving.
- Post effective signage for CAPs (e.g. "Biosecurity is in effect in this area").
- Signage might also state that permission is required to proceed (with contact information provided) or that staff accompaniment is required.
- It is recommended that signage outside the CAZ inform personnel of the procedures to follow for admittance, and include identification of the parking area.
Ideally:
- The surface of the CAP would be hard, impervious, and easy to clean with a broom, shovel, or pressure washer. Concrete or asphalt is ideal. Crushed rock is preferred over bare earth, but cannot be easily cleaned. Other options could be considered.
- Wash water would run off toward areas that provide natural filtration (grassy areas with vegetation) and would comply with applicable environmental regulations.
- CAPs would be equipped with cleaning and decontamination equipment. This includes materials that are adequate for the effective cleaning and decontamination of vehicular and foot traffic, as necessary. For example:
- water (preferably hot);
- equipment to wash hands (sanitizer) and footwear (brushes);
- paper towels and garbage disposal;
- dedicated footwear (rubber boots) and outwear (coveralls);
- equipment or tools to remove caked-on material;
- pressure washers with the ability to apply detergent and disinfectant (when necessary);
- equipment to clean the decontamination station.
- CAP equipment (i.e. disinfectant, clothing, etc.) must be protected from the elements. A room, shed, or other structure at the CAP can be used for this purpose. For smaller operations, CAP equipment may be stored in large totes or bins.
Recommendations for movement control at the CAP to the CAZ
- Allow only essential personnel and vehicles to enter the CAZ.
- Ensure that vehicles are visibly clean and free of organic material.
- Take care to ensure that all traffic on the premises drives slowly to avoid disturbing dust.
Ideally, access to/exit from the CAZ would be controlled by the following:
- Supervised entry;
- Agreements with feed, veterinary, and other service providers on entry and premises biosecurity protocols, delivery schedules, etc.;
- Vehicles and/or equipment as follows:
- For vehicles and equipment that are to remain in the CAZ, it may be sufficient that they are visibly clean and free from organic debris. Washing and disinfecting wheels and wheel wells is still a prudent measure.
- At most access points, during summer and winter, cleaning may be accomplished with minimal equipment: a broom, shovel, and hand sprayer may be effective for the types of vehicles and dry roadway surfaces encountered. (A review of the frequency, type, cleanliness, and use of the vehicles and equipment entering the farm site would be required to implement this option.)
- The sharing of equipment between premises and operations is not recommended.
- Vehicles and equipment that have been directly exposed to poultry and/or manure from other premises will require full cleaning and disinfection. Optimally, this should be performed prior to vehicles and equipment leaving the premises where the exposure occurred to reduce the transmission of disease agents off-site. If this is not feasible, vehicles and equipment should be cleaned at the closest commercial wash station. On arrival at the next premises, minimal cleaning and disinfection would be required.
- Vehicles and equipment that have visited other premises without direct exposure to poultry and/or manure require contact surfaces (e.g. tires) cleaned and disinfected.
- Upon detection of serious contagious diseases within the local poultry population, all vehicles and equipment entering the CAZ should be cleaned and disinfected prior to entry and upon exit. When a disease alert has been issued, producers should request guidance on protocols from their veterinarian, poultry board or organization, and provincial or federal governments.
Ideally, all personnel would be required to wear CAZ-specific boots and clothing, or to use disposable coveralls and booties.
- Boot cleaning and/or the wearing of booties may be all that is necessary for visitors who are wearing clean clothing and who are moving through the CAZ directly to a RAZ where clothing and boot changes will be necessary, or who will be in the CAZ for a brief period and have not visited, nor will be visiting, any other agricultural premises that same day.
Note: All visitors pose a risk to premises for disease carriage, but some visitors pose a higher risk than others. However, without requesting detailed information, risk cannot be adequately assessed. Always consider that visitors may be arriving from or going to other premises.
Recommendations for establishing a CAP for the RAZ - physical structures, tools, equipment
- Ensure that there is one primary CAP to the RAZ. If a secondary CAP is required, ensure it is adequately maintained and monitored.
- Use secure barriers (i.e. locked doors) to ensure the access through CAPs is restricted.
Install visible signage at all CAPs to a RAZ, stating that it is a biosecurity restricted area, and to avoid entering unless authorized. Signage posted at the entrance should state "No Entry - Biosecurity in Effect," "Permission to Enter Required Past This Point", or wording with a similar meaning.
- Provide a transition area, preferably with an impervious, cleanable floor (e.g. concrete) and a roof, where transition area procedures can be applied to personnel and equipment entering and leaving the RAZ. An anteroom as a transition area is highly recommended.

Equip the CAPs with RAZ-specific footwear and clothing plus equipment and materials for cleaning and/or decontamination foot traffic (also equipment and vehicles if applicable).
Recommendations for movement control at the CAP to the RAZ
- Limit access to the RAZ to only those individuals required for flock production or to essential visitors who have received instruction in appropriate biosecurity measures.
- Sanitize hands prior to entry and exit, before and after handling poultry, and especially after handling mortalities. Adequate hand sanitization is best accomplished by hand washing with soap and water, or if hands are suitably clean, a hand sanitizer or a pre-packaged alcohol hand wipe.
- Ensure that there is no common footwear contact between the CAZ and the RAZ.
- Changing into specific barn footwear is ideal. Wearing disposable plastic overshoes is acceptable.
- If this is not practical, boot dipping in well-maintained footbaths is a less desirable alternative option. (See Annex E for information on footwear sanitation.)
- Clean and disinfect equipment that enters the RAZ.
Note: Annex B provides a detailed set of barn access (entry and exit) procedures for personnel.
Ideally, at the access to/exit from the RAZ:
- Barn doors or range gates would be kept locked;
- The names and dates of essential visitors who enter the RAZ would be recorded; and
- Personnel would put on premises-specific clothing or appropriate protective clothing, such as disposable coveralls.
Additional considerations for personnel and visitors
Ensure those who enter your premises are not sick, and have not been in contact with poultry, livestock, pets, and/or people that are sick, especially those exhibiting clinical signs related to influenza virus.
People who have had contact with poultry or poultry workers from other farm sites during the preceding 48 hours need to ensure they have washed (preferably showered) and changed into clean clothing before entering the RAZ where live poultry are kept. Any clothing that is worn off-farm or when visiting other premises is not acceptable as premises-specific clothing.
People should not access barns other than the ones in which they are working.
Traffic flow of trucks or equipment should be regulated to limit the proximity of activities to other barns.
Non-essential visitors
People and their equipment that have no requirement to access the CAZ and RAZ include, but are not limited to, guests, friends, and family. If there is no necessity for production purposes, these visitors should not be allowed access into the CAZ and the RAZ.
Essential visitor:
Any person who enters the CAZ or RAZ, other than personnel concerned with day-to-day poultry management on the premises.
Biosecurity measures that may be required of essential visitors - such as veterinarians, service and delivery people, suppliers and regulators - may include, but are not limited to the following:
- The owner or manager ensuring that all visitors and personnel entering or leaving the RAZ follow the designated biosecurity rules;
- Wearing RAZ-specific clothing and boots;
- The owner and/or a farm employee accompanying visitors who enter the CAZ and the RAZ (otherwise, the owner and/or farm employee must be confident that the visitor is aware of, and will implement, the farm's biosecurity procedures); and
- Signing and filling out the premises log book (with name, date, time of arrival, and contact information).
Ideally:
A more comprehensive visitor log is the preferred option and may also include the following:
- organization for which the visitor works;
- vehicle licence plate;
- purpose of visit;
- date of last contact with poultry;
- *location of previous premises visited; and
- *next premises to be visited.
*These details are particularly important during a disease outbreak. The more information provided, the easier it is to trace movements that are a disease transmission risk.
Catching crew, vaccination crew, and other comparable service providers
When live poultry remain in the RAZ, biosecurity measures that may be imposed for RAZ access include, but are not limited to the following:
- ensuring adequate equipment cleanliness;
- providing barn-specific equipment;
- all members of the crew wearing clean clothing or disposable cover-ups;
- all members of the crew cleaning and disinfecting boots or wearing disposable booties.
Egg pickup service providers:
- Access the egg storage room, using an exterior door to the location that eggs are stored via the anteroom.
- Clean, sanitize, and dry the equipment that is used for egg storage and transport prior to entry onto the premises.
The producer should strive to minimize the potential cross-contamination between the egg storage room and the rest of the production facility at all times. After eggs are picked up, the producer should ensure that the storage room is kept clean and tidy. The producer can sweep and spot clean areas, if necessary, to ensure that there is no accumulation of dust or egg residue.
Ideally:
- Boot cleaning and disinfection may be all that is necessary for egg pickup service providers moving, for a short period of time, into the egg storage room that is part of the CAZ.
- Washing and disinfecting the egg storage room can take place at the time of annual clean-out or prior to placing new birds. Note: For hatching eggs, the Canadian Hatching Egg Quality (CHEQ) Program recommends that egg room floors be cleaned weekly.
Section 2 - Animal Health Management
2.1 Animal Introduction, Movement, Removal
2.1.1 Target Outcome - Each placement or removal of poultry is recorded and carried out with appropriate scheduling, isolation or segregation to minimize the introduction or spread of disease.
Producer Guidance
- Schedule movement of poultry to minimize potential exposure to other poultry on the premises.
Ideally:
All in/all out - All poultry within a new flock are placed in an empty RAZ within seven days. When the flock is removed from the RAZ, the process is again completed within seven days.
"All in/all out" scheduling should occur, keeping the completion time of poultry arrival and shipment as short as possible, first within each barn and ideally within the entire premises.
- Consider taking additional precautions when "all in/all out" scheduling is not practised, as outlined in the guidance for Target Outcome 2.1.3. Specifically: poultry introduction, movement, and return; multi-species operations; multi-aged operations; inter- and intra-premises movement; and premises unit configurations and isolations.
- Source poultry from a hatchery that operates under a disease control program or from flocks that have current health records and no evidence of infectious disease. Flock health, vaccination, and veterinary inspection records should accompany all new poultry brought onto the premises.
- Keep poultry that are introduced or re-introduced into an existing flock separate for a quarantine period before introduction.
- Make available historical records of placement, introduction, and removal, and outline future scheduling. Records should be kept regardless of the shipment and movement practices on the premises.
Ideally:
Records should be kept for a minimum of one year, unless a longer period is specified by provincial or On-Farm Food Safety (OFFS) program requirements.
2.1.2 Target Outcome - The downtime between flocks is optimized in each barn.
Producer Guidance
Definition:
Downtime: The time between flocks starting with a barn being emptied of birds and ending with the placement of new birds. It allows for the natural reduction in numbers of disease-causing micro-organisms within the barn. The effective period can be reduced by cleaning at the beginning of the period.
For each barn or production area, optimize downtime as follows:
- The text box below suggests a minimum downtime after the flock has been removed. It assumes flock removal is followed by dust blow-down and manure cleanout (dry cleaning). The addition of washing and disinfecting to the process may allow for an overall reduced downtime.
- If a reduced downtime period is unavoidable, add washing and disinfection to the process as soon as possible after shipment to allow for maximum downtime after being thoroughly cleaned and dry.
- Cold (particularly freezing temperatures), wet, or seasonal conditions can affect the practicality of washing, disinfection, and downtime. In these situations, slight alterations in routine cleaning and disinfection procedures or other options should be considered to meet production needs without compromising biosecurity. (Annex D provides information on cleaning barns in inclement conditions.)
Ideally:
- Have a downtime of 14 days after the flock has been removed to significantly reduce pathogen load.
- Dry clean after removing the birds, to reduce pathogen load further.
- Add washing and disinfection after dry cleaning to minimize pathogen load and, if necessary, allow for some reduction in the overall downtime (i.e. 7 to 10 days total downtime).
- If manure is not removed, schedule a downtime of at least 21 days. Composting the manure inside the barn or heat-treating by heating the barn (to 105°F/40°C for two days) will further reduce pathogen load and risk to the next flock.
- Schedule for the entire barn to be empty approximately once a year, with a full cleanout and downtime of 14 days (and if possible, keep the entire premises empty of live poultry for 14 days).
2.1.3 Target Outcome - More stringent additional biosecurity measures are implemented either at the barn or premises level where "all in/all out" scheduling and downtime is not practical.
Producer Guidance
Areas where Target Outcomes 2.1.1 and 2.1.2 will not be met and which present an increased possibility of pathogen introduction:
- multi-age barns;
- multi-species operations;
- returning birds;
- staggered or phased live poultry introduction or removal into an established flock that includes the following:
- partial flock shipment over a period greater than 7 days (e.g. heavy tom production [turkeys larger than 13.3 kg]);
- introduction of spiking males into breeding flocks;
- movement to another barn for further growth or egg production; and
- proximity to shipping activities.
Note: Repeated crew or transportation equipment and/or container contacts increase the risk of pathogen introduction to any remaining poultry; therefore, additional precautions are warranted.
The additional biosecurity measures that may be taken in association with moving or introducing poultry may include, but are not limited to the following:
- transporting all poultry that are moved from one barn to another or one flock to another in clean crates;
- ensuring that poultry introductions have equivalent vaccination history (levels) as resident flocks;
- scheduling all activities within the barns or between barns to start with the youngest poultry and to end with the oldest in any barns that contain multiple ages of poultry (with the exception of any quarantined birds, which would be attended last);
- increasing the monitoring of the flock after higher risk procedures (e.g. vaccinations, handling, and returning birds); and
- isolating (a separate RAZ) from resident flocks for 30 days:
- all new poultry, if not shown to be disease free through participation in a testing or certification program;
- returning show birds; and
- all poultry that have been treated with a live vaccine.
The biosecurity measures that require extra attention to ensure adequate biosecurity between subsequent flocks may include, but are not limited to the following:
- cleaning or disinfection procedures for personnel and equipment;
- manure movement, handling, storage, and spreading;
- completing all necessary repairs to the barn structure and equipment;
- cleaning floor of transition area, or cleaning barn anteroom, if applicable;
- removing dust and other debris from the barn exterior;
- pest control procedures;
- cleaning and disinfecting the barn after any disease outbreak prior to repopulation; and
- review of flock health, vaccination, and treatment programs with your veterinarian.
Note: Biosecurity measures may be applied to the premises level when there is more than one barn and when each barn is at a different stage of production.
The measures that should be taken to clearly separate each barn into separate isolation units include, but are not limited to the following:
- applying biosecurity measures between barns to enable barn segregation;
- regulating the flow of both pedestrian and vehicular traffic (in direction and/or timing) to provide the best order of operation to reduce possible cross-contamination and proximity to live poultry;
- paying particular attention to manure and mortality handling and route of travel to avoid cross-contamination to other barns still in production; and
- limiting the movement of equipment between barns, and cleaning and disinfecting all equipment that is moving between barns.
2.2 Ongoing Monitoring of Health Status and Response
2.2.1 Target Outcome - Individuals who monitor poultry are knowledgeable and experienced in monitoring flock health, the recognition of disease conditions, and timely response protocols.
Producer Guidance
- People who work on the premises should be sufficiently trained and experienced to recognize sick and under performing birds.
- People who work on the premises should be suitably trained and briefed to take necessary actions in cases where disease is suspected.
- Training people in the basics of good flock management practices will assist in their recognizing conditions that can predispose or contribute to flock illness. (See Annex D.)
The options for improving skills are as follows:
- attending seminars and/or workshops organized by government, veterinarians, or the poultry industry;
- descriptions and/or photographs of typical symptoms placed in anterooms, restrooms, etc.; and
- supervision by more experienced personnel.
Note: Target Outcome 3.1.1 outlines further guidance on training.
2.2.2 Target Outcome - Daily procedures for observation, and culling if necessary, are followed.
Producer Guidance
- Conduct a walk-through of the barn and/or range area at least once daily, taking note of poultry behaviour and attitude, and the presence of culls or sick birds as follows:
- In barns, walk along both sides and down the centre, ensuring that you look in corners, nest boxes, and covered areas.
- In range areas, walking in an "S" or "X" shaped pattern can ensure good coverage of the flock.
Note: It is highly recommended that this be done two or more times daily.
- Keep still at various points in the barn to allow the flock to settle, easing the observation of sick birds or unusual behaviour. This will also allow the observer to hear unusual sounds made by poultry with breathing difficulties.
- Ensure that lighting in the barn is adequate to allow all of the flock to be observed clearly.
Ideally:
Flock monitoring should be responsive to increased risk levels, and occur as follows:
- during and after introduction of new stock;
- following high-risk activities (e.g. visit from vaccination crew);
- during seasonal or location risk; or
- during a local outbreak, etc.
2.2.3 Target Outcome - A daily mortality log is maintained for each flock.
Producer Guidance
- Mortalities should be collected daily and the number recorded.
- As a minimum, mortality records should include the total number of dead birds found each day and should include birds that have been culled due to sickness symptoms.
Ideally:
It is recommended that mortality records are maintained as part of a more comprehensive flock health management record, elements of which include but are not limited to the following:
- daily observations of flock condition;
- daily morbidity and mortality counts;
- lists of all vaccines and medications given at the hatchery and the farm;
- lists of all diseases and syndromes that were diagnosed, medicated, or not;
- input and deliveries, including feed, suppliers, and chicks;
- output records (e.g. egg production);
- flock movements;
- feed and water consumption rates; and
- end of flock data.
2.2.4 Target Outcome - Unusual morbidity or mortality triggers contact with a veterinarian and disease diagnosis action. Suspicion of diseases that are contagious, of economic importance, or reportable triggers a "disease response plan" that provides guidance to individuals on the appropriate procedures to follow.
Producer Guidance
- Cull and remove from the flock those birds that are showing symptoms of sickness.
- Review feed and water consumption and, if necessary, collect feed and water samples.
- Initiate a call to a veterinarian for any evidence of disease symptoms, sudden rises in mortalities and/or sick birds, or unacceptable drops in feed and/or water consumption or egg production.
Ideally:
A veterinarian should be consulted if any of the following clinical signs are observed:
- loss of appetite;
- decreased egg production, and/or soft or misshapen eggs;
- lack of energy (depressed behaviour);
- diarrhea;
- coughing or sneezing (respiratory distress);
- swelling of tissues around eyes and neck;
- purple wattles and combs;
- abnormal neurological behaviour (muscular tremors, depression, drooping wings, twisting of heads and necks, lack of coordination, complete paralysis, etc.); or
- elevated mortalities.
All farms should:
- use the services of a veterinarian trained in poultry disease diagnosis;
- use the services of a veterinarian who has relevant post-graduate training and who demonstrates a current knowledge and understanding of poultry disease; or
- have access to technical services that are supported by veterinary expertise.
Records should be maintained when the veterinarian provides advice or recommendations on the health and welfare of the birds on the farm.
For example:
- The contact name and number of the veterinarian or veterinary clinic is available.
- The visitor log shows records of veterinary visits.
- The flock sheet, feed, and production records show any medications prescribed to birds.
- Diagnosed infectious or production-related diseases, copies of diagnostic reports, and prescriptions are kept on file, etc.
Disease response plan
- The owner and/or manager should be aware of his or her role in the Provincial Emergency Response Plan. This information may be obtained by contacting your veterinarian or a provincial board office (for supply-managed producers), or by attending an information session on this topic.
- If there is strong evidence of a highly infectious disease, producers should contact their veterinarian. Supply-managed producers should also contact their Provincial Board Office and follow any guidance provided.
- If a contagious disease of economic importance is suspected, enhanced biosecurity protocols should be initiated, and preparations for self-quarantine started. (See Annex C.)
An example of a disease diagnosis action plan:
Suspicious clinical signs or an unacceptable increase in unexplained mortalities is/are detected.
There is a self-imposed barn or premises isolation or containment (Annex C).
Access to the premises is restricted.
A veterinarian is called.
A contagious disease of economic importance is suspected.
(If a reportable disease is suspected, the veterinarian must notify the Canadian Food Inspection Agency [CFIA]).
Appropriate samples are collected for lab analysis and confirmation.
Self-declaration and notification of appropriate officials occur.
The current visitor log is reviewed for trace-back purposes.
Upon the suspicion of disease of economic importance, a self-quarantine or isolation protocol (Annex C) may include, but is not limited to the following:
- implementing enhanced biosecurity measures between barns and limiting access to the premises (particularly the CAZ);
- limiting movement between barns and off the premises;
- contacting a veterinarian and providing birds or samples, as needed, under veterinary consultation and following any veterinary advice;
- discussing the situation with family members and employees;
- postponing bird movements, vaccinations, etc.;
- reviewing flock health and mortality records;
- reviewing all visitor logs and delivery slips; and
- informing the necessary farm visitors, such as feed delivery, to schedule the affected farm as the last call of the day.
Section 3 - Operational Management
3.1 Mortality and Manure Management
3.1.1 Target Outcome - Daily procedures are followed with respect to dead birds including collection and removal from the production area.
Producer Guidance
Mortality management includes the activities below, all being performed in a biosecure manner:
- prompt collection of mortality;
- removal of mortality from contact with the flock; and
- disposal of mortality (reduced exposure to the flock).
Recognizing that production systems vary greatly, mortality management may occur as one seamless process or in a set of steps as follows:
- Remove dead birds from the production area at least daily. Use rubber or disposable gloves for this activity.
- Conduct the gathering and removal of dead birds separately from other bird or product handling operations.
- Ensure that routine hand-washing takes place, followed by the use of a sanitizer after any handling of mortalities.
- Ensure written instructions are available to staff, detailing procedural steps for mortality management.
- Remove mortalities from the RAZ in covered containers. In some instances, mortalities may be disposed of in the RAZ by way of composting or incineration. (See section 3.1.3 for additional information.)
Examples of acceptable containers include, but are not limited to, the following:
- a pail with a tight-fitting lid;
- empty feed bags;
- plastic bags;
- a labelled, closed cart set aside, specifically for the collection and movement of dead birds, etc.
3.1.2 Target Outcome - A dead poultry storage system, which protects the carcasses from scavengers and insects until final disposal, is utilized on the premises.
Producer Guidance
- In some instances, mortality will be temporarily stored prior to final disposal.
- In mortality storage, the following are preferable:
- Mortalities should be stored frozen. Mortalities that are not frozen should only be stored for short periods of time.
- Storage should be located (sited) in a secure location away from the flock, feed, and water sources.
- Access to the storage location should be controlled (restricted).
- Storage should be in a manner that does not allow for escape of organic matter or exposure to the environment, and preferably in a sealable container.
- Storage areas should be kept free of pests, rodents, or other vermin.
- Carcasses should be disposed of as soon as possible.
- Care should be taken to avoid accidental spillage of material from the carcass when in transit to the freezer or from freezer to final disposal site.
- All containers used to collect mortalities should be cleanable or disposable.
3.1.3 Target Outcome - Carcass disposal, including any on-farm disposal (incineration, composting and burial), is done in accordance with provincial or municipal guidelines. If a rendering service is utilized then the pickup is performed to minimize any biosecurity risk.
Producer Guidance
Follow federal, provincial, and municipal rules at all times. They may limit options and placement.
- Avoid disposing carcasses near any food or water sources or poultry housing.
- Maintain biosecurity measures when disposing carcasses.
- Ensure that carcass disposal (no matter what method) takes place outside of the CAZ, with the exception of the collection of carcasses for rendering, freezing, or RAZ composting. (See subsequent sections, "Off-farm rendering" and "On-farm incineration.")
- Ensure, with the exception of off-farm rendering, that disposal sites are contained and demarcated. Some methods include fencing, signage and paint.
- Control access to carcass disposal site or area.
Off-farm rendering
- Store carcasses for rendering in a secure facility, and move to the access point or outside the CAZ when the rendering truck arrives or to a suitable container outside the CAZ for short-term holding, pending render pickup.
- Bring out the carcasses to the truck, upon arrival, in sealed, leak-proof containers.
- Clean and disinfect all containers, used to collect mortalities prior to their return into the CAZ and prior to re-entry into the RAZ.
On-farm incineration
- Keep incinerators clean and well maintained.
- Ensure that complete incineration occurs at every run.
- Avoid exceeding maximum capacity when running the incinerator.
- Do not locate newly installed incinerators on the same side of the barn as the air inlets.
Burial
- Cover carcasses with enough soil or other material (in accordance with local regulations) to prevent access from scavengers.
- Ensure that the burial site is in a location that is appropriate to soil type and water table.
Composters
- Design and operate composters, including composting performed in manure piles, in an effective manner. Producers should be aware of variables affecting the composting process that may require adjustment, including nutrient composition, added substrate, temperature, pH, volume (load), placement of carcasses, moisture levels, and the need to turn piles if temperatures are not achieved and sustained. (See Annex J.)
- Monitor temperatures to ensure that composting is working effectively.
- Maintain composters to minimize the attraction of flies, rodents, and other animals.
Note: In rare instances, where flock size, production type, and/or geography limit disposal options and flock disposal occurs inside the RAZ by way of incineration or composting, the disposal system must ensure containment of mortality and separation from the flock in a controlled area.
- Physically separate the disposal system from the flock in an adjacent room or by a wall or barrier. This prevents exposure of the flock to pathogens in dust, debris, organic material, secretion, or excretions etc., which may be released during the disposal process.
- Ensure that the disposal system is the right size for the production type, volume, and mortality rates.
- Plan for storage and/or access of substrates that may be required for the composting process.
- Provide sufficient room for cleaning and storage of any dedicated equipment.
- Ensure that separate mortality disposal systems are present for each RAZ.
- Pay additional attention to pest management, as mortality can be an attractant for pests (flies, rodents, birds, and scavengers), which can transmit disease to the flock.
- Recognize that mortality disposal systems inside the RAZ increase the risk of flock exposure to pathogens and require a higher level of management to ensure that disease transmission does not occur.
3.1.4 Target Outcome - Manure is suitably handled and stored to minimize the risk of transferring disease organisms to poultry flocks.
Producer Guidance
- Follow federal, provincial, and municipal rules at all times.
- When manure is stored in a pit under the production area, and live birds are to remain on site, consider this pit area as part of the CAZ. Any movement into the pit area requires biosecurity practices (i.e. change of footwear and clothing).
- Never use manure from an unknown or suspect source on the poultry farm. Avoid bringing any manure onto the farm, regardless of source.
Ideally:
- Manure is stored in a dry location and on a non-porous surface.
- Manure storage areas are controlled. These areas must be considered contaminated by contagious organisms. Limiting access to these areas will reduce disease transmission. They should be located away from barns to prevent transfer back into the barns by people, equipment, vehicles, or weather.
- Manure is composted before its removal from the premises or spreading onto land.
- Raw manure is not applied directly onto land. This is of significant concern if a disease outbreak has occurred recently in the barn.
3.2 Premises, Building, Equipment and Vehicule Sanitation
3.2.1 Target Outcome - A sanitation program is in place that applies to premises, building, equipment and vehicle sanitation.
Producer Guidance
- The basis of the premises biosecurity control measures for buildings, equipment, and vehicle sanitation should be a set of documented procedures that clearly specify the requirements to ensure that the appropriate standards of hygiene are maintained and that risk of contamination is minimized.
- These procedures should be followed at all times, with additional provisions if a disease outbreak occurs, either on the premises or within the region.
- Always complete cleaning of surfaces before disinfection. Dust, manure, and other debris can act as a barrier and protect pathogens from disinfectants; therefore, cleaning first is essential. In any cleaning situation, if dry cleaning is followed by washing, the efficacy is improved.
- Use only approved disinfection chemicals, at appropriate dilutions and not date-expired, when cleaning and disinfecting buildings or barns, equipment, and vehicles.
Ideally:
In a disease-response situation, washing and disinfection would become a necessity for all buildings, equipment, and vehicles. Cleaning processes would include vehicles coming onto the premises.
Barns
- Barns that have been emptied should be dry cleaned initially, followed by pressure washing and disinfection.
- Barn entryways, anterooms, egg rooms, and other service areas should be maintained clean and free of debris at all times.
- Barn exteriors, including the areas around fans and their housings, should be kept clean and free of debris.
- Where dirt floors exist, piling and composting of litter in the barn prior to removal, combined with heating the barn to 105°F/40°C) for two days, would reduce the risk of pathogen carry-over to the next flock. Every effort should be made to keep the rest of the barn clean.
Ideally:
- Surfaces in the barn are impermeable and can be cleaned, pressure washed or steam cleaned, and disinfected. (Disinfection is essential if a barn is being cleaned after a disease outbreak.)
- It is virtually impossible to clean or disinfect dirt floors. These should be avoided in the design of new barns.
- See Annex D for barn cleaning and disinfection in inclement weather.
Equipment
- Equipment should be selected for ease of cleaning.
- All equipment brought into the CAZ from outside should be clean, free from debris, and preferably disinfected. Disinfection is vital if equipment has had previous contact with manure or live birds, or if live birds remain on the premises.
- Equipment that is taken into a clean, disinfected barn should be cleaned and disinfected before entering the barn.
- Equipment moved between barns, within a single CAZ, should be free of visible contamination before being used in another barn.
Ideally:
- Most equipment used during production is dedicated to individual barns.
- Cleaning procedures for equipment and buildings include both dry cleaning and a wet cleaning process.
- Disinfection is performed following wet cleaning.
- Water lines should be flushed under high pressure and disinfected when barns are empty. It is recommended to flush lines on a regular schedule during production.
- Open drinkers in barns and range areas should be cleaned and disinfected regularly and left to dry before being reused.
Vehicles
- Ensure that all vehicles entering the CAZ are visibly clean.
- Clean vehicles that have had previous contact with poultry or manure off-site before entering the CAZ.
- Disinfect high-risk surfaces of vehicles before entry to and on exiting the CAZ. The high-risk areas are wheels, wheel wells, and surfaces that have been in contact with poultry or manure.
- Include the inside footrest area in the cleaning program when the driver or passengers have been to other sites with poultry present.
Ideally, or in response to a disease situation:
A cleaning program for vehicles would include the following:
- the physical removal of debris by washing with detergent and/or high pressure water;
- cleaning of the inside footrest area and steering wheel;
- disinfection of all outer surfaces of the vehicle;
- disinfection of wheel wells and tires before entry to and upon exiting the CAZ;
- appropriate disinfectant contact time before proceeding;
- vehicle washing area (concrete pad or other hard surface) cleaned of debris and disinfected between vehicles; and
- collection and containment of wash water and debris according to local/provincial regulations.
3.3 Facility Maintenance
3.3.1 Target Outcome - A program for facility maintenance is in place.
Producer Guidance
Poultry production areas and equipment should be maintained and kept functioning properly to ensure the best environment for continued health and ease of cleaning.
- Ensure that ventilation, feed, and water systems are functioning correctly.
- Cover feed bins, and keep in good condition.
- Keep storage areas in good condition.
- Keep barn sides, roofs, and doors in good condition.
- Design, maintain, and manage the premises to prevent feeding, shelter, or access for pest species.
- Prevent wild birds and animals from entering the barn, and deter them from range areas. Pay specific attention to restriction of potential access points, such as windows, doors, pipes, walls, attics, vents, inlets, fans, etc.
3.4 Water, Feed, Bedding Management
3.4.1 Target Outcome - A water management program is in place to ensure that water is potable and meets local guidelines for poultry consumption.
Producer Guidance
Water source
- Water provided to poultry should meet local guidelines for poultry consumption.
- Municipal supplies should be deemed to meet this requirement.
- Water from other sources should be analyzed yearly for bacterial content and other contaminating substances.
- More frequent water testing may be required if a previous analysis failed to meet recommended guidelines or if advised by a veterinarian or municipality.
Water storage
When water is stored prior to use by poultry or between flock placements:
- cover the container to prevent contamination;
- ensure that water is appropriately treated; and
- demonstrate that the water meets the minimum guidelines for poultry consumption, as advised by the local authority, by conducting annual laboratory test results.
Water delivery
- Keep water delivery systems clean by routine flushing, descaling, and disinfecting of water lines and drinkers.
- Design and maintain drinkers to prevent contamination of water at the point of use (i.e. ensure that they are not prone to litter or feed contamination).
Water treatment
- Water treatment systems may be installed if the water source is suspect, or as a routine prevention method.
- Surface water sources pose significantly higher risk for introduction of infectious organisms and are not recommended for use without a functioning treatment system.
- At any time a treatment system is in use, it should be well maintained with chemicals used as directed. Chemical usage should be monitored and recorded.
3.4.2 Target Outcome - Feed is obtained and stored in a manner that minimizes the risk of contamination by pathogens.
Producer Guidance
Obtaining feed
- Purchase finished feed from a source that can verify its safe origin, such as feed suppliers that follow established protocols under Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) or FeedAssure™ programs.
- Inform feed suppliers of premises' biosecurity procedures, and confirm their willingness to comply.
- Where practical, check feed condition and verify that it is pest-free on arrival. It is also good practice to keep feed samples, which can be tested if health problems later occur.
- Rotate newly purchased feed appropriately in order to use the oldest feed first.
- Avoid moving feed between farms.
- Take the necessary biosecurity precautions when moving feed from one premises to another. Only feed from the feed bin should be stored or moved off-farm. (Discard any feed within the Restricted Area [i.e. feed pans]). Other biosecurity measures may include the following: examination of feed for contaminates (mould, pests, manure, feces, etc.), examination of the transport vehicle, and personal cleaning and disinfection.
Feed storage
- Store feed in a dry, clean, and secure environment, away from wild birds and animals.
- Cover feed bins.
- Close feed systems.
- Empty feed lines, pans and troughs, boots, and hoppers at cleanout.
- Inspect feed routinely for moisture, spills, and pest activity.
- Quickly clean up and properly dispose of any feed spills.
3.4.3 Target Outcome - Bedding is obtained and stored in a manner that minimizes the risk of contamination by pathogens.
Producer Guidance
- Inform bedding suppliers of premises' biosecurity procedures, and confirm their willingness to comply.
- Where appropriate, check incoming bedding materials on arrival for deterioration or pests, and keep it dry prior to use.
Ideally:
Bedding will be stored in a weatherproof and pest-controlled environment.
3.5 Pest Control Program
3.5.1 Target Outcome - An integrated pest control program is present.
Producer Guidance
An effective integrated control program will ensure that the presence of potentially harmful pests, such as insects, rodents, and wild birds, is kept to a minimum.
General control methods for pests:
- don't attract;
- exclude (seal entry points);
- exterminate (bait or trap); and
- monitor for effectiveness and adjust.
These practices should be backed up by appropriate reduction methods, ongoing monitoring for pest activity, a response plan for signs of increased pest activity, and records of pest control activities, as follows:
- Ensure that the CAZ is free of debris, which might provide shelter for pests.
- Reduce or eliminate any features that could provide shelter, breeding grounds, roosts, nesting sites, or feed sources attractive to rodents and wild birds. For example:
- nearby standing water;
- spilled feed;
- nearby manure storage;
- unsealed mortality storage;
- open compost; and
- any accumulation of debris or tall vegetation.
- Exclude predators and pets from the RAZ.
Rodent-specific points
- Maintain a 1m-wide (3 feet) rodent barrier strip - using shale, gravel, bare earth, or extremely short vegetation - around each barn, and ensure that it is free of debris.
- If possible, maintain an additional 3.5m (12 feet) zone, outside the rodent barrier strip, free of debris and tall vegetation.
- Position bait stations and traps close to barn walls at entry points around the barn perimeter and inside the service area.
- Renew or replace rodent baits regularly, according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Ensure that rodenticides are approved, used in accordance with the label, and kept inaccessible to the flock.
Insect-specific points
- Position insect traps or electrocuting devices at insect entry points and in areas requiring specific control.
- Renew or replace insect-control products and devices regularly, according to manufacturer's instructions.
- Ensure that insecticides are approved for use near poultry.
Range-specific points
- Keep the range area free of debris that might shelter pests.
- Use closed or covered feeders and drinkers where possible. Moving feeders and drinkers regularly will help discourage pests.
- Have sufficient covered or roofed space to house all poultry at times of risk (an "enhanced biosecurity state").
Ideally:
The location will house poultry with sufficient space, no droppings will fall from overhead, and no small wild birds or rodents will have access. This could include housing with a solid roof and sides, but other materials, such as weld mesh, windbreak netting, and tarpaulins, are effective.
- Appropriate fencing, deterrent or scaring devices or traps (as per provincial guidelines) may be used for predator control.
Ideally:
- Construct fencing such that predators are unable to dig under the fence to gain entry or to climb over the top of the fence.
- Ensure that the fence is of sufficient mesh size to stop predators from climbing through.
- Some pests may be more problematic in some regions or operations, due to differences in geography, climate, or building structure.
- Additional pests not listed here may require control measures to ensure adequate biosecurity.
3.5.2 Target Outcome - Garbage is effectively and safely disposed of.
Producer Guidance
- Use garbage cans or bins with tight-fitting lids and that are lined inside with plastic bags to reduce odours (attractive to pests and predators) and to help keep the cans or bins clean.
- Provide garbage bins at the access points to the RAZ for disposable clothing and foot coverings.
- Keep garbage storage areas clean and maintained to limit insects, rodents, and scavengers.
- Position long-term garbage storage outside the CAZ.
- Dispose of garbage and household waste regularly, in accordance with provincial and municipal regulations.
3.6 Biosecurity Program and Training
3.6.1 Target Outcome - All people working on the premises are knowledgeable of, and understand the rationale behind and importance of, biosecurity and biosecurity protocols.
Producer Guidance
- Owners or keepers of poultry should ensure that all family and other workers are adequately trained before starting work, and that they have a general understanding of the processes of biosecurity, not just measures related to their own tasks.
- Someone who is properly trained will adopt biosecurity procedures as routine and provide suggestions for improvement. Equally important is ensuring that contractors and visitors abide by the control practices.
- The Standards document and this Guide can be used as reference material for such training. Provincial agriculture extension or poultry industry information seminars and workshops may also be available.
- A record of training should be kept for each worker.
Examples of training include the following:
- attending seminars or workshops;
- working under direct supervision;
- reviewing written instructions, or standard operating procedures (SOPs) - Target Outcome 3.6.2 provides further guidance;
- training using the Standard and this Guide as a template; and
- formal qualifications.
Examples of records include the following:
- title and/or certificate of attendance for seminars, workshops, courses attended;
- individual training records, detailing training given and dates; and
- a signed confirmation from each staff member that SOPs have been read and understood.
3.6.2 Target Outcome - All people working on the premises have reviewed the applicable biosecurity-related instructions as needed, based on their assigned tasks.
Producer Guidance
Development of Standard Operating Procedures
To ensure people understand how to complete their assigned tasks, written instructions or SOPs should be developed. These are step-by-step explanations of how to perform a task from beginning to end.
- SOPs relating to flock health management should be developed with the input of a veterinarian.
For example:
SOPs for mortality handling and disposal should include the following:
- times for daily mortality collection;
- mortality handling procedures, including hand sanitation;
- mortality transfer from the RAZ to storage or disposal site;
- procedures for the removal of birds for off-site disposal; and
- compost procedures, including pest control, time spent at and temperature of the compost site (if composting is disposal method used).
Reviewing SOPs with staff
- Review written instructions annually with staff as re-training or as a reminder to ensure continuous improvement and quality control.
- Provide all farm staff with copies of, or access to, the SOPs.
- Review SOPs prior to new staff starting work.
- When work commences, review SOPs again with the new staff and address any questions.
- Display SOPs or procedures, with accompanying rationale, at the entrance to the RAZ or in employee rest areas.
- Review SOPs prior to new staff starting work.
Ideally:
- SOPs will be reviewed annually for relevance and clarity of content.
- There will be SOPs including, but not limited to, the following:
- access procedures for CAZ and RAZ;
- moving between barns;
- building cleaning and disinfection procedures;
- vehicle and equipment cleaning and disinfection procedures;
- the pest control program;
- flock health monitoring and response;
- mortality handling;
- mortality disposal;
- manure management; and
- self-quarantine procedures (Annex C).
Glossary
Access point: A visually defined entry point(s) through which all traffic, such as workers, equipment, feed trucks, etc., will enter the CAZ and/or the RAZ.
Additional Biosecurity Measures: A level of biosecurity to be practised to mitigate situations where recommended practices cannot be followed. For example, where an "all in/all out" system is impossible (as in the case of a multi-age premises), additional biosecurity measures should be practised.
Anteroom: A room or area of a building which immediately precedes the restricted access zone (RAZ), providing a transition area from the controlled access zone (CAZ).
Approved: When used in reference to chemicals, such as rodenticides, it means approved by the appropriate regulatory authority for the specific usage mentioned in the text.
Beneficial practice: A management practice, technique or technology that, when adopted, results in improvement and increased sustainability of the operation.
Biosecurity program: A risk reduction program that conforms to Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) national standards and which is designed to prevent and control the introduction and spread of pathogens.
Clean: Free of any visible accumulation of organic matter and debris or other residues.
Complex: A collection of buildings and/or outdoor ranges that is or may be used directly for production.
Controlled access point: A visually defined entry point(s) through which all traffic, such as workers, equipment, feed trucks, etc., will enter the CAZ and/or the RAZ. It includes a transition area where procedures designed to minimize the spread of pathogens can occur.
Controlled Access Zone (CAZ): The area of land and buildings constituting the poultry production area of the premises that is accessible through a securable controlled access point. It excludes any residence and any other outbuildings that are not directly related to poultry production (e.g. machine sheds, storage sheds, workshops, etc.).
Debris: Any material that may be capable of harbouring disease-causing organisms or pests such as discarded equipment or machinery, manure, dead birds or parts of dead birds, egg white, egg yolk, egg shells, feathers and soil.
Disease response plan: A predetermined set of steps that is followed in the case of a significant disease occurrence. This response may be at the premises level by the production people, at the provincial level by the industry or provincial ministry, or at the national level in the case of reportable disease.
Disinfection: The application of a physical or chemical process to a surface for the purpose of destroying or inhibiting the activity of disease-causing micro-organisms.
Disposal (carcasses): Final removal of a bird carcass from the premises (by means of serviced rendering collection, composting, incineration, or burial).
Downtime: A period of time between flocks, starting with a barn being emptied of birds and ending with the placement of new birds. It allows for the natural reduction in numbers of disease-causing micro-organisms within the barn. The effective period can be reduced by cleaning at the beginning of the period.
Endemic Diseases: Diseases that are regularly reoccurring or whose causative agent is constantly present with a region or population.
Enhanced Biosecurity: At times when a disease outbreak is suspected on the premises or has been identified in the vicinity, additional biosecurity measures may be required, and increased emphasis placed on existing biosecurity procedures.
Essential Visitors: Any person required to enter the RAZ, other than personnel concerned with day-to-day poultry production on the premises. Visitors include veterinarians, service and delivery people, suppliers, and regulators.
Exotic Diseases: Infectious diseases that normally do not occur in the region, either because they have never been present there or because they were eradicated and then kept out by government control measures or agricultural practices.
Facility: Synonymous with "premises" (see below). May be used to refer to production areas on a premises.
Flock: A group of poultry managed as a distinct population.
Flock Area: Area or range that (outdoor) poultry occupy.
Fomite: Any inanimate object or substance capable of carrying infectious organisms. This may include but is not limited to equipment, farm vehicles and articles of clothing or shoes.
Isolation (or "segregation"): The status or practice of a bird, birds, or flock being kept physically separate from others (including direct and indirect contact). Usually performed for sick or returning animals.
Non-Essential Visitors: People and their equipment who do not require access to the CAZ and RAZ. These include, but are not limited to, guests, friends, and family.
Non-Premises Vehicles: Vehicles (cars, trucks, tractors, etc.) not owned or operated by the premises and not designated to the premises.
Pathogens: Biological agents, such as a bacteria or virus, that have the potential to cause diseases.
Potable: Suitable for drinking.
Poultry: All birds reared or kept in captivity for breeding, the production of eggs or meat for consumption, for production of other commercial products, for restocking supplies of game birds, or for breeding these categories of birds.
Poultry barn: Any structure that encloses poultry flocks, including sheds, runs, etc.
Premises (facility): A parcel of land with a continuous property boundary and defined by a legal land description or, in its absence, by geo-referenced coordinates, on which or on any part of which poultry are grown, kept, assembled, or disposed of.
Premises Vehicles: Vehicles (cars, trucks, tractors, etc.) owned and operated by the premises and primarily designated to the premises.
Producer Guidance: Examples and beneficial practices to facilitate achievement of the Standard.
Protocols: Effectively a code of conduct, defined procedure to be followed.
Range: A RAZ, allowing birds to roam freely within the confines of a perimeter.
Rendering: Using an off-farm service for the pickup and disposal of mortalities.
Reportable Disease: A disease that must be immediately reported to the CFIA. Reportable diseases in poultry are avian influenza, virulent/exotic Newcastle disease, pullorum disease (Salmonella pullorum), and fowl typhoid (Salmonella gallinarum). These diseases are sometimes referred to as "foreign animal diseases."
Restricted Access Zone (RAZ): An area inside the CAZ that is used, or intended to be used, to house poultry, including semi-confined and range production, and where personnel and equipment access is more restricted than within the CAZ. The RAZ is sometimes also referred to as the "production area" or "restricted area" (RA) in other poultry production documents and guides.
Spiking Males: Sexually mature male poultry introduced into a breeding flock to maintain fertility by boosting mating frequency.
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP): Documented procedure based on generally accepted good practices that describe in detail the steps followed to meet an objective (for example, a SOP that details the barn cleaning and disinfection procedure).
Storage (carcasses): Temporary placement of bird carcasses into a sealable, leakproof container until disposal.
Target Outcome: The goal that all keepers of poultry, regardless of the size of their flock, should aim for to protect their flocks from the introduction and spread of avian diseases.
Transition Area: An area where biosecurity procedures can occur for movement between the CAZ and the RAZ.
Annexes
Use of annexes
The information in the following annexes is not to be considered an official part of the General Producer Guide. The annexes have been provided for reference and example purposes only. The examples provided are not the only way to achieve the outcomes of the Guide; rather, they are intended to illustrate the flexibility and creativity that may be required given production variability.
Producers with any questions or concerns are advised to contact their national, provincial, or territorial boards. For further information, internet links have been provided at the end of each annex.
Annex A - Self-Evaluation Checklist
| Section 1 - Access Management | Self Audit or X |
|---|---|
| 1.1 Designation of Zones | |
| 1.1.1 Recognizable zones and access points are in place. | |
| 1.1.2 Visual indicators are in place to define the Controlled Access Zone (CAZ) and Restricted Access Zone (RAZ). | |
| 1.2 Entry, Movement, Exit Controls | |
| 1.2.1 People who work on the premises are knowledgeable of and understand the importance of and rationale behind the CAZ and the RAZ. |
| Section 2 - Animal Health Management | Self Audit or X |
|---|---|
| 2.1 Animal Introduction, Movement, Removal | |
| 2.1.1 Each placement or removal of poultry is recorded and carried out with appropriate scheduling, isolation or segregation to minimize the introduction or spread of disease. | |
| 2.1.2 The downtime between flocks is optimized in each barn. | |
| 2.1.3 More stringent additional biosecurity measures are implemented, either at the barn or premises level where "all in/all out" scheduling and downtime is not practical. | |
| 2.2 Ongoing Monitoring of Health Status and Response | |
| 2.2.1 Individuals who monitor poultry are knowledgeable and experienced in monitoring flock health, the recognition of disease conditions, and timely response protocols. | |
| 2.2.2 Daily procedures for observation, and culling if necessary, are followed. | |
| 2.2.3 A daily mortality log is maintained for each flock. | |
| 2.2.4 Unusual morbidity or mortality triggers contact with a veterinarian and disease diagnosis action. The suspicion of diseases that are contagious, of economic importance, or reportable triggers a "disease response plan" that provides guidance to individuals on the appropriate procedures to follow. |
| Section 3 - Operational Management | Self Audit or X |
|---|---|
| 3.1 Mortality and Manure Management | |
| Mortalities 3.1.1 Daily procedures are followed with respect to dead birds including collection and removal from the production area. |
|
| 3.1.2 A dead poultry storage system, which protects the carcasses from scavengers and insects until final disposal, is utilized on the premises. | |
| 3.1.3 Carcass disposal, including any on-farm disposal (incineration, composting and burial), is done in accordance with provincial or municipal guidelines. If a rendering service is utilized then the pickup is performed to minimize any biosecurity risk. | |
| Manure Management 3.1.4 Manure is suitably handled and stored to minimize the risk of transferring disease organisms to poultry flocks. |
|
| 3.2 Premises, Building, Equipment and Vehicule Sanitation | |
| 3.2.1 A sanitation program is in place that applies to premises, building, equipment and vehicle sanitation. | |
| 3.3 Facility Maintenance | |
| 3.3.1 A program for facility maintenance is in place. | |
| 3.4 Water, Feed, Bedding Management | |
| Water 3.4.1 A water management program is in place to ensure that water is potable and meets local guidelines for poultry consumption. |
|
| Feed 3.4.2 Feed is obtained and stored in a manner that minimizes the risk of contamination by pathogens. |
|
| Bedding 3.4.3 Bedding is obtained and stored in a manner that minimizes the risk of contamination by pathogens. |
|
| 3.5 Pest Control Program | |
| 3.5.1 An integrated pest control program is present. | |
| Garbage Management 3.5.2 Garbage is effectively and safely disposed. |
|
| 3.6 Biosecurity Program and Training | |
| 3.6.1 All people working on the premises are knowledgeable of, and understand the rationale behind and importance of, biosecurity and biosecurity protocols. | |
| 3.6.2 All people working on the premises have reviewed the applicable biosecurity-related instructions as needed, based on their assigned tasks. |
Annex B - Sample Standard Operating Procedures - Procedures for Barn Entry and Exit
The following is an example of a set of procedures for minimizing disease carriage while moving personnel in and out of a barn. The process may vary among producers.
Irrespective of the method used, the goal is to create a separation between the internal environment (flock housing area) and the external environment (non-flock housing area).
Procedures for barn entry using an anteroom
- Ensure that outerwear and footwear entering an anteroom are visibly clean.
(Ensure that premises-designated footwear and outwear worn in the CAZ is free of manure, soil, and organic debris. If not, prior to entering the anteroom, brush off outerwear, and remove soil and other organic material from footwear - use a boot pail with a brush and clean solution of disinfectant - paying particular attention to the tread.)
- Step into the anteroom.
- Remove outerwear (coats, sweaters, coveralls), and store in an area designated for outside clothing.
- Wash or sanitize hands.
- Remove outside footwear. Step over a demarcation line or barrier (bench, painted line), and put on designated inside-barn footwear.
- In some instances, footwear will be removed, and staff will walk through a corridor or around a partition prior to donning the clean footwear.
- Benches work well and allow staff to remove outerwear first, sitting on the bench to remove outside footwear, turning 180 degrees to face the barn door access and donning footwear and barn-designated gear.
- Put on barn-designated outerwear - coveralls, headcover, and gloves. (Wash hands again if clean gloves are not used.)
- Step into the bird housing area.
Note: Cleaning and disinfecting barn-designated boots prior to entering the bird housing area will provide an added layer of security, removing any contaminants that may have been carried into the anteroom.
Click on image for larger view
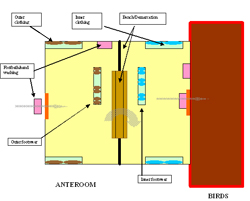
Description for - Concept 4
An anteroom (yellow) with areas designated for outside clothing and footwear (to the left), a bench (centre), and areas designated for inside clothing and footwear (to the right), protects the flock housing area (red).
Procedures for barn exit using an anteroom
- Brush or scrape off all organic material from barn-designated footwear before leaving the bird housing area.
- Step into a footbath containing disinfectant, ensuring the outside of the footwear is thoroughly covered by disinfectant, paying particular attention to the tread.
- Wash or sanitize hands, if possible.
- Remove outerwear (while still wearing gloves, if worn), being careful to avoid touching the inside of clothing or coveralls.
- Remove gloves.
- Remove footwear and step over line demarcation on the floor, and put on outside footwear.
- If a bench is being used, sit down and remove barn-designated footwear, turn 180 degrees, and put on outside-designated footwear.
- If a corridor system is used, walk the length of the corridor and into the clean area before putting on outside-designated footwear.
- Wash or sanitize hands.
- Put on outside clothing, step through a footbath, and depart.
Further information:
BC Agricultural Research and Development Corporation
Annex C - Producer Self-Quarantine Protocol
Dr. Victoria Bowes, B.C. Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Fisheries
This protocol presents to the producer a course of action during the suspicion of an infectious disease. This plan is an excellent example of procedure, but other protocols regarding quarantine and infectious disease do exist. It is recommended that all producers are familiar with local or industry-accepted procedures.
Background
Upon the suspicion of an infectious disease in a poultry flock, the following set of guidelines should be followed by the producer. The intention of this protocol is to limit the spread of disease between barns and, most importantly, the spread of disease off-farm.
Situation - There has been an unexplained:
- increase in mortality;
- change in production parameters, such as feed or water consumption, egg production, or shell quality, etc.; or
- onset of clinical signs of disease.
Action plan
1) Obtain an answer
- Start your own on-farm investigation. Gather together all relevant documents, including health records of all flocks currently on the farm.
- Call your veterinarian with a complete description of the problem, including time of onset, duration, and whether things are getting worse or resolving over time. Offer your suspicions as to your thoughts on what the problem might be.
- Review and provide copies of production and mortality records.
- Provide representative birds and/or samples for diagnostic investigation:
- Call in your veterinarian to do on-farm necropsy and sampling techniques.
- Take birds and/or samples to a local poultry veterinarian and/or to the Vet Lab. (Note: there may be special precautions required when moving birds and/or samples off-farm. Consult your veterinarian for proper procedures.)
2) While you wait
- Follow the advice of your veterinarian, which may involve interim treatment of the flock, based upon the disease suspected.
- Review and list the on-farm traffic, visitors, and bird movements in the previous 10 days. Refer to visitor log.
- Immediately adopt enhanced biosecurity protocols. Service unaffected barns first and/or dedicate a specific employee to the affected barn(s). (Note: Enhanced biosecurity protocols should be prepared beforehand, in consultation with your veterinarian.)
- Immediately restrict on- and off-farm access by locking gates and requiring phone-ahead pre-arrangements for deliveries and pickups. Suspend all unnecessary traffic.
- Inform all family members and employees of the situation. Request confidentiality until diagnosis is confirmed.
- Follow strict personal biosecurity procedures for leaving the farm (e.g. non-farm clothing, footwear, and vehicle), especially if meeting with other poultry industry members, even socially.
- Postpone scheduled vaccinations until a diagnosis is confirmed.
- Postpone movements of any birds on or off-farm.
- Dispose of dead or culled birds, using an approved method: on-farm is preferable; composting or incineration is recommended. Treat as infectious material.
- If there is a strong suspicion of a highly infectious disease, such as infectious laryngotracheitis (ILT), pox, avian infectious bronchitis (IBV), or avian influenza (AI), based on the visible lesions found at necropsy but before laboratory confirmation, request that the feed or egg truck make your farm the last stop of the day.
3) When a diagnosis is confirmed
- If the diagnosis confirms a "reportable" disease, either the CFIA (federal disease) or your producer association (provincial disease), will have been informed at the same time. Follow up. Prepare records and notes for review.
- In the case of a "reportable" disease, follow the directions and recommendations of the regulatory agency, but do not hesitate to ask questions.
- Modify or initiate treatment of flock as directed by your poultry veterinarian.
- Follow enhanced on-farm biosecurity procedures for at least 10 to 14 days following the end of treatment or the resolution of clinical signs.
- If they have not already been informed, update your service industry representatives and producer groups of the diagnosis and the measures undertaken for containment.
- If practical, inform neighbouring poultry operations.
- If appropriate, make provisions for birds moving directly to slaughter, in which case the processor should be informed.
- Recommended: Post enhanced biosecurity signs at gates, indicating that an infectious disease has been diagnosed and that access is restricted.
4) Getting back to normal
- Enhance the regular on-farm cleaning and disinfection procedures for the affected barns. Extend clean "downtime" as long as possible.
- Continue to monitor for disease reoccurrence in the same or subsequent flocks, watch for clinical signs, and submit follow-up samples.
- Record the event in the production records with as much detail as possible.
- Return to regular biosecurity measures.
Important note:
Pathogenic Newcastle disease (NDV), avian influenza (AI) and Salmonella pullorum and gallinarum are federally reportable diseases. The CFIA has developed disease response plans and strategies for these diseases upon their identification in domestic flocks.
The national immediately notifiable diseases are infectious laryngotracheitis (ILT), avian cholera (pasteurellosis), chlamydiosis (psittacosis, ornithosis), duck hepatitis, avian encephalomyelitis, egg drop syndrome (avian adenovirus), goose parvovirus infection (Derzsy's disease), and turkey rhinotracheitis (avian pneumovirus, swollen head syndrome). The CFIA must be notified if these diseases occur; however, limited action is taken, and only with respect to certification of meat product for export to certain countries.
Specific provinces have a list of provincially notifiable diseases that are of significant economic concern, and there may be specific action response plans to the occurrence at the industry level or mandated by the provincial government. The most common ones are infectious laryngotracheitis (ILT) and mycoplasma in breeder birds and turkeys.
All other diseases are "unregulated" and are a private issue between you and your veterinarian. Your confidentiality will be respected, but your cooperation in informing your industry service representatives of a potential infectious disease problem is encouraged and appreciated.
It's the right thing to do!
Further information:
BC Agricultural Research and Development Corporation
Annex D - Barn Cleaning and Disinfection in Inclement Weather
Freezing temperatures
- Place additional emphasis on dry cleaning to reduce the time required for wet cleaning.
- Provide supplementary heat to raise barn temperatures to allow wet cleaning and disinfection to occur.
- Focus on critical areas where birds are housed to reduce the volume of water applied: bird contact areas (floors, nest boxes, cages, walls to a height of three feet, feeders, and waterers). Dry clean the ventilation system.
- Add propylene glycol, and use machines capable of heating water, to increase the effectiveness of detergents and disinfectants and to prevent wash and disinfectant solutions from freezing.
- Increase the surface contact time for disinfectants.
- If wet cleaning cannot be performed, thoroughly dry clean the barn, and raise and maintain barn temperatures; this can be effective at inactivating pathogens. The temperature and time required for pathogen inactivation vary for different organisms and should be discussed with your veterinarian.
- Thoroughly drying the barn after any cleaning stage is important for pathogen inactivation.
Cold and wet weather
- Raise barn temperatures.
- Use warm to hot water when using detergents and disinfectants.
- Increase the concentration and surface contact time of the disinfectant. Rain and wet surfaces can significantly reduce the concentration of cleaning and disinfectant solutions.
Additional measures
- Disinfectant fogging, disinfectant foam, fumigation, and steam cleaning are measures that may be employed in adverse weather conditions.
- Steam cleaning can reduce the amount of water required and increases temperature to reduce pathogen load.
- Consult with commercial cleaning companies, disinfectant manufacturers, industry experts, and veterinary professionals on sanitation measures when environmental conditions impair routine cleaning and disinfection.
Annex E - Footwear Sanitation
Footwear sanitation is vital for a strong biosecurity program. As visitors or employees, people can enter a premises and have no physical contact with structures or animals, except for footwear. The process of footwear sanitation, and the best method for your premises, are worth investigating.
Generally, there are three approaches to footwear sanitation: premises-dedicated footwear, disposable foot coverings, and footbaths.
Premises-dedicated footwear
Having several pairs of footwear for employees and visitors is an option. Regardless of the type of footwear, it is important to follow two important guidelines:
- The footwear does not leave the biosecurity zone to which it is dedicated; and
- The footwear is sanitized on a routine basis.
Generally, the use of dedicated footwear will require an anteroom process (described in Annex B).
Disposable foot coverings
Disposable foot coverings can be a relatively cheap method of footwear sanitation. Before entering a premises or biosecurity zone, foot covers are placed over footwear. Upon exit from the biosecurity zone, the foot covers are removed and disposed of.
Some advantages to foot covers:
- They are inexpensive.
- The covers never leave the site.
- They are small, lightweight, and compact, making it easy to store them at each biosecurity access point.
- They are quick and easy to use.
Some disadvantages:
- They are easily torn.
- Outside footwear is worn in biosecurity zones.
- They require biosecure disposal.
Some of these disadvantages can be counteracted by cleaning, disinfecting, and drying outside footwear before the coverings are put on.
Footbaths
Note: The use of footbaths is not promoted by On-Farm Food Safety (OFFS) programs, due to the high degree of maintenance required for efficacy and the potential for creating disease reservoirs. It is widely accepted that footbaths are most effective in clean areas and that they should always be used in combination with other preventative actions.
Some advantages to foot baths:
- They are easy to use and inexpensive.
- The optics of having a footbath in front of an entrance encourages its use.
- If used correctly, all surfaces, including deep treads, are exposed to disinfectant.
Some disadvantages:
- They are high maintenance, in that footbaths need to be monitored closely. Disinfectant solutions should be changed routinely and the container cleaned on a regular basis.
- Contact time is required for effective sanitation.
- Depending on the disinfectant used and its concentration, footbaths may be ineffective against all pathogens of concern.
- Some disinfectants are expensive.
If footbaths are the chosen option for your premises, it is important to understand the process required for their effective use. The four steps for footwear sanitation using a footbath are as follows:
- Remove visible debris from the footwear. This requires the physical removal of dirt, mud, manure, etc., using equipment such as a boot brush. Pay extra attention to treads.
- Wash footwear with a detergent. This step removes any oils, grease, or biofilms that may be invisible.
- Apply disinfectant. (This is the process of stepping into the footbath.)
- Ensure appropriate contact time. To be effective, the disinfectant should be in contact with the surfaces of the footwear for a period of time. Most manufacturers provided this information on the disinfectant's container. Depending on the concentration and pathogen, the time is generally about 10 minutes.
Further information:
BC Agricultural Research and Development Corporation
Annex F - Sample Standard Operating Procedures - Using Footbaths
The following procedure is for use by all persons entering and exiting a biosecurity zone requiring footwear sanitation.
- Remove visible debris from footwear, using the provided equipment (boot brush).
- Wash footwear with the water and detergent provided. Pay extra attention to treads.
- Step into the footbath, completely submersing the footwear for 5 to 10 seconds.
- Exit the footbath.
- Wait for (required time as recommended by manufacturer) before proceeding.
Annex G - Sample Standard Operating Procedures - Footbath Maintenance
Footbaths are to be controlled using the following monitoring schedule:
- Clean and maintain footbaths every Thursday before end of day.
- Check footbaths daily before start of day.
- If a footbath requires cleaning or recharging, do so immediately.
The following seven steps are to be carried out as required by the footbath monitoring schedule:
- Empty the used disinfectant into a bucket.
- Wash the footbath container with hot soap and water.
- Empty the used soap and water into the bucket containing the used disinfectant.
- Rinse.
- Empty the rinse water into the bucket.
- Recharge the footbath with fresh disinfectant at the desired concentration.
- Dispose of the water and used disinfectant in the bucket. (This is site specific, but should occur without crossing biosecurity zones.)
Further information:
BC Agricultural Research and Development Corporation
Annex H - Sample Mortality Log
Several examples can be found at BC Agricultural Research and Development Corporation
Annex I - Disinfectants
Terminology
"Disinfectants" are chemical compounds applied to inanimate (non-living) objects to destroy or irreversibly inactivate disease-causing organisms.
"Disinfection" refers to the inactivation of disease causing organisms and includes but is not limited to chemicals, heat, and ultraviolet light.
Product regulation
Health Canada regulates the registration of disinfectants in Canada and provides a Drug Identification Number (DIN) prior to their marketing; this number will be listed on the disinfectant container.
Selecting a disinfectant
Disinfectants are evaluated by Health Canada using strict criteria; however, efficacy is determined under controlled laboratory conditions, and the use of disinfectants on a farm site requires that they be used according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Disinfectant selection is based on a variety of factors, including the following:
- the chemical properties of the disinfectant;
- the type(s) of organism targeted for inactivation;
- the cleanliness of materials to be disinfected;
- the composition (e.g. wood, metal, rubber) of the surface to be disinfected;
- the temperature of surfaces and disinfectant;
- contact time;
- concentration;
- application method;
- the presence or use of other chemicals;
- pH;
- characteristics of the water (presence of dissolved solids, degree of contamination);
- environmental considerations (the presence of streams and wildlife); and
- cost.
These factors will affect the likelihood of a disinfectant performing as indicated by the manufacturer.
Choose broad-spectrum disinfectants with minimal toxicity that are easy to apply and that are effective under a variety of environmental conditions.
Disinfectant storage
Disinfectants have different shelf lives, depending on the chemical composition of the product, and often have a "best before" date. Chemicals degrade over time, reducing the effectiveness of the product: this often accelerates after a product has been opened. Use unexpired disinfectants and ensure lids, tops, bags are securely fastened for storage. Store in cool, dry, dark areas or according to manufacturer's recommendations.
Disinfectant application
Disinfectants are most effective when applied to clean, dry surfaces. Organic material (litter, soil, manure, etc.) on equipment, boots, and structures significantly reduces the activity of disinfectants, so these surfaces must be cleaned prior to disinfectant application.
Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for application, paying strict attention to the concentration required and contact time. Some disinfectants require rinsing as their final step. Follow local government regulations regarding the application of disinfectants to ensure compliance with environmental legislation.
Once disinfectants are mixed with water or other chemicals, their shelf life decreases dramatically, so they must be replenished regularly. This may be daily for some products and weekly for others.
Disinfectants used for cleaning boots and other heavily contaminated equipment must be replenished frequently and are only effective if properly applied; boot baths or dips with disinfectants are often heavily contaminated with disease-causing agents, are ineffective, and must be used with caution.
Further information:
Annex J - Impact of Federal Disease Control and Response Measures - Producer Considerations for Premises Design and Procedures
As mentioned in Annex C, the CFIA has developed disease control and response plans to address detections of federally reportable diseases. The measures applied differ, depending on the disease detected; however, the strategies are generally aimed at eradicating the disease, and restoring Canada's "disease-free" status as quickly as possible.
Premises actions
In most instances, where contagious diseases are detected on a site, the CFIA will declare the entire premises "infected", as per the Health of Animals Act. This allows control measures to be applied to all structures, equipment, animals, animal products and by-products etc. to prevent disease transmission off-site. The design of the site and procedures used can affect where and how control measures are applied.
Control measures often include the following:
- movement controls;
- surveillance (testing for disease);
- humane destruction of infected flocks;
- disposal of infected and contaminated carcasses, animal products and by-products, materials and other objects;
- cleaning and disinfection of the infected premises;
- compensation payments; and
- recovery procedures to allow restocking.
The CFIA will conduct epidemiological investigations, which include, but are not limited to, determining the source of infection, determining methods of transmission, and identifying locations where disease may have been transmitted (significant risk contacts).
Premises design
Upon suspicion or detection of a federally reportable disease on a poultry premises, all areas of the premises, equipment, and materials used in raising, caring for or handling poultry, their products and by-products would be deemed "infected" by the CFIA. This includes barns, composting areas, manure storage, vehicles, equipment, etc. Producers should be aware that the locations of structures on their sites will affect control actions taken, as follows.
Location of flock housing
Housing areas (barns, open ranges) located in close proximity to each other on the same legal land description will often be treated under one CFIA declaration of an "infected premises"; disease identified in one housing area will result in disease control measures being applied to all housing areas on the site. Barns or housing areas located on a different premises that have shared equipment, staff, animals, or other potential carriers of disease would also be declared infected, and control measures would be applied.
If a producer can establish that a different but co-owned premises is epidemiologically distinct (with no cross utilization of staff or equipment, no link due to movement of animals, etc.), these sites would be monitored for disease. Reduced control actions may be applied to separate barns on an infected site if there is sufficient physical separation and they are epidemiologically distinct. Flocks which have significant value (breeder flocks, flocks with rare/unique genetics) should be located on a different premises from that of the main flock, and measures employed to ensure there are no epidemiological linkages between them.
Location of compost and manure
Compost and manure are considered as potentially contaminated with disease organisms. Access to areas where they are stored should be controlled. These areas should be located far enough from flock housing areas to eliminate the risk of disease introduction to the flock, and managed to prevent disease release. If central manure and compost sites are used - with the movement of all manure and litter from different barns and/or other sites to one location - the detection of disease in any barn or any site will result in control actions being applied to the central areas.
Note: This information is provided for information purposes only; disease response and control actions vary depending on the nature of the pathogenic agent, the course of an outbreak, and the geographic and demographic location of the outbreak.